Social Objective
advertisement

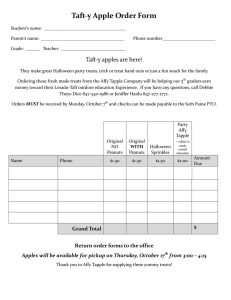
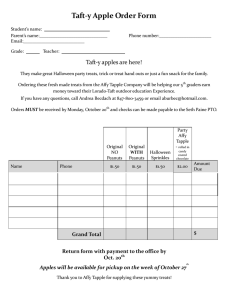
Secondary Curriculum, Instruction & EL SERVICES Explicit Direct instruction Orientation Phase October 2011 Orientation Phase 5-7 minutes The teacher carries the cognitive load. Objectives Learning Language Social Activate Prior Knowledge Sub skill Review Universal Experience Communicate Expected Results Three types of Objectives LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Focus is content LANGUAGE OBJECTIVE: Focus is Academic Language (tied to Learning Objective) SOCIAL OBJECTIVE: Focus is on student interaction and behavior during cooperative structures (i.e. pair-share) Learning Objective A learning Objective is a standards-based statement that describes what students will be able to do independently at the end of a lesson. Language Objective Language Objectives 1. Target a specific language skill that can be taught during the lesson. 2. Must have student interaction. Social Objective Social Objectives are the : Rules and standards for behavior Communicate expectations with regards to behavior and outcomes of group interaction Processes and procedures as they apply to collaborative work TAPPLE Write the three types of objectives on your white board. Share your answers with your partner. A more in-depth look at…. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Components of a Learning Objective • Concepts: main ideas • Skills: measurable behavior • Context: 1. 2. Resources to be used Specific methods to be used CONCEPT The CONCEPT is the main idea of the Learning Objective. FOR EXAMPLE: “Write a five-paragraph summary of a newspaper article” Summary is the concept. SKILL The SKILL is the verb in the Learning Objective. FOR EXAMPLE: “Write a five-paragraph summary of a newspaper article” Write is the skill. The skill taught during a lesson should match the skill required in the Independent Practice. CONTEXT • A CONTEXT is any specific condition under which the Objective will be executed. • “Write a five-paragraph summary of a newspaper article” The context describes the resources to be used— newspaper article. TAPPLE On your whiteboards write the three components of a Learning Objective and share with your partner. Where do standards-based Learning Objectives come from? Standards-based Learning Objectives come right from the state content standards. Content standards actually contain multiple Learning Objectives. WRITING STANDARDS-BASED LEARNING OBJECTIVES There are four steps to writing a standards-based Learning Objective: 1. 2. 3. 4. Select a grade-level content standard. Identify all the concepts and skills included in the standard. Deconstruct, or break down, the standard into specific Learning Objectives. Select or create matching Independent Practice. Step #1: Select a content standard: History-Social Science Know about the life of Confucius and the fundamental teachings of Confucianism and Taoism Step #2: From the content standard, identify Skills Describe Concepts (main idea, noun) Life of Confucius Fundamental teachings of Confucianism Fundamental teachings of Taoism Context(s) (condition if present) None in this particular standard Step #3: Deconstruct the content standard into specific Learning Objectives Describe the life of Confucius. Describe the fundamental teachings of Confucianism. Describe the fundamental teachings of Taoism. Step #4: Select or create matching independent practive Independent Practice Oral presentation Class discussion Completing a graphic organizer Final Objective: SWBAT describe the life of Confucius through the use of a a graphic organizer Tapple Discuss the four steps to writing a learning objective and list those steps on your white board. Teaching the Learning Objective to the Students During the EDI lesson, you always teach the Learning Objective to your students. Teach Learning Objectives in three steps Step #1: PRESENT the Learning Objective to the students Step #2: Have the students INTERACT with the Objective. Step #3: Use TAPPLE to check that students can describe the Learning Objective Tapple Discuss the three steps to presenting the learning objective to your students with your partners. Discuss at least one method that can be used to encourage student interaction with the standard. A more in-depth look at . . . LANGUAGE OBJECTIVES WHAT IS A LANGUAGE OBJECTIVE: • Language Objectives are used to advance English Learners’ use of the academic English— already contained in a lesson—that is necessary for them to be successful in the lesson. • The teacher does this by purposefully engaging students in structured Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing. LANGUAGE OBJECTIVE SERVE TWO PURPOSES 1. Identify and support new language. 2. Advance a student’s use of English in general so they are more successful with the lesson. A More In-Depth Look . . . Social Objectives What is a Social Objective? • To enable students to successfully function in a collaborative environment, teachers must explicitly teach these interactive structures in their classrooms through the use of social objectives and direct instruction Why is it important to create opportunities for students to Collaborate? • Promote 21st century skills such as; critical thinking and problem solving, communication, agility and adaptability. REFLECTIVE QUESTONS 1. Do I explicitly teach the behaviors I expect from my students or do I merely engage in telling them about the desired behavior? 2. When I deliver lessons on behavioral expectations, do I gradually release the responsibility of the learning in that lesson or do I show students and then expect them to do it themselves? 3. Do my students have consistent opportunities to engage in peer-based discussions and productive group work in the classroom? 4. Do I use these types of interactive structures with intentionality and purpose? Are the structures preplanned or mostly used spontaneously? 5. Could I be more systematic and explicit in addressing student engagement, behavior and learning for my students. EXAMPLE OF A SOCIAL OBJECTIVE Think-Pair-Share - Involves a three step cooperative structure 1. Students think silently about a question posed. 2. Individuals pair up and exchange thoughts. 3. The pairs share their responses with other pairs, other teams, or the entire group. Social Objective: Students will be able to actively listen and restate their own and their partners ideas. A more in-depth look at . . . ACTIVATING PRIOR KNOWLEDGE APK is used to provide: A connection between something students already know and the new content they are going to learn. How to Activate Prior Knowledge APK is done in three steps: 1. Activate UNIVERSAL EXPERIENCE OR SUB-SKILL REVIEW 2. Interact 3. Connect TAPPLE Write the three steps to Activating Prior Knowledge on your white board. As you are watching the EDI lesson component of APK, be ready to identify the three steps of APK by using your index cards: 1. 2. 3. Activate Interact Connect Activating Prior Knowledge TAPPLE Discuss when the three steps of APK were demonstrated in the video. Communicate Expected Results The final step to Orientation is when the teacher communicates the results of the lesson. Example: Students will complete a Graphic Organizer Students will complete notes on the causes of WWII Students will complete 10 practice problems Students will create an outline for their essay This should be addressed while reviewing the agenda for the period. Exit Ticket 1. List the three types of objectives. 2. State the four domains from which a language objective is written. 3. List the three components of a Learning Objective. 4. List the two methods to Active Prior Knowledge. 5. What is the purpose of a social objective? 6. Why is it important to incorporate collaboration time into a lesson?