Perpendicular & Angle Bisectors
advertisement

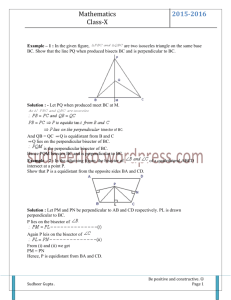
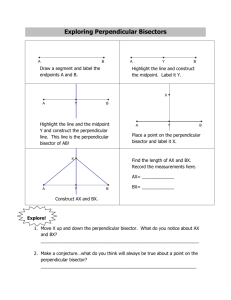
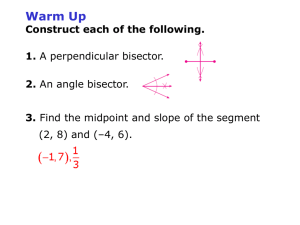
Perpendicular & Angle Bisectors Lesson 5-2 Learning Goal: Use properties of perpendicular and angle bisectors Reviewing vocabulary What does perpendicular mean? To intersect at a 90o angle What does a bisector do to a segment or angle? Cuts it into two equal pieces Think about it… Where can I place a t-shirt stand so it is equidistant from the Roller Coaster and Spaceship? The distance from a point to a segment Compare triangle ADC and Triangle BDC. If the above is true, how does AC compare with BC? Why? Equidistant – a point that is the same distance from two objects Example 1: Using the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem A) What is AB? B) What is QR? Think about it…Answer time! Example 2: Structure Placement Where can I place a t-shirt stand so it is equidistant from the Roller Coaster and Spaceship? Paddle boats and Spaceship? Classwork part A Workbook pg 123-124 #4-7, 14-19 Back to Notes The distance from a point to a line is the length of the perpendicular segment from the point to the line. Example 3: Using Angle Bisectors Theorem A) What is RM? B) What is FB? Would Perpendicular Bisector or Angle Bisector be useful? Which school is equidistant from the subway stations at Union Square and 14th street? Is St. Vincent’s Hospital equidistant from Village Kids Nursery School and Legacy School? Would Perpendicular Bisector or Angle Bisector be useful? Where should you position yourself so you have the best chance of stopping the ball, along the perpendicular bisector to XY or angle bisector of angle P? Note the difference… An angle bisector contains all the points equidistant from 2 LINES. A perpendicular bisector contains all of the points equidistant from 2 POINTS. Classwork part b Workbook pg 125 #1-6 Homework: chapter 4 review Part 1: Triangle congruency worksheet Part 2 (do on the back of worksheet): textbook pg 291 #9 – 12 AND pg 293 #1, 9, 10, 13, 14 We will go over these before the test on Tuesday.