Chapter 1 -- Lesson 1.2
advertisement

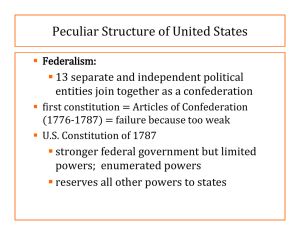
UNIT 1 – Law, Justice and You Chapter 1 – OUR LAWS Lesson 1.2 – Types of Laws What are the sources of our laws? Created at all 3 levels of government: federal, state, and local Consist of constitutions, statutes, administrative regulations and case law LAW Constitutional Documents the rights of individuals and states the power and limits of government Statute Created by Legislatures elected by voters (Congress, State and Local Legislatures Case Consists of decisions and opinions of judges Administrative Created by Government Agencies (FCC and Social Security Office) Constitutional Law constitution – a document that sets forth the framework of a government When constitutions are adopted or amended, or when courts interprets constitutions, constitutional law is made. We are governed by the U.S. Constitution and the constitution of Ohio Supreme Court has final interpretation of U.S. Constitution Main instrument for allocating powers between people and their government is the federal Constitution Constitutional Law Bill of Rights – protects people from actions of their government Federal Constitution allocates powers between the federal and state governments Gives Federal Government the power to regulate both foreign and interstate commerce. State and federal constitutions allocate governmental powers among the three branches of government: executive, legislative and judicial. System of checks and balances Statutes Statutes -- laws enacted by state legislatures or federal legislatures Composed of elected representatives of the people Ordinance – legislation at the local level Administrative Regulations Administrative agencies – governmental bodies formed to carry out particular laws BMV of Ohio, Social Security Administration Usually controlled by executive branch of government Case Law The judicial branch of governments creates case law Made after a trial has ended and one party has appealed the result to a higher court Appellate court publishes its opinion, that may state new rules to be used Federal courts establish federal case law State courts establish state case law Stare decisis – Latin for to adhere to decided cases What happens when laws conflict? Constitutions – highest source of law Federal Constitution – supreme law of the land Unconstitutional -- Status of a law that conflicts with a constitution and which is therefore invalid. Main Types of Laws Civil Law – refers to wrongs against individual persons. One person sues another Police do not take action Liable – defendant loses a civil case and must pay money to plaintiff (victim) Criminal Law – refers to crimes against society. The government, acting in the name of all people, investigate the alleged wrongdoer. Main Types of Laws Procedural – deals with methods of enforcing legal rights and duties Specifies how and when police can make arrest and what methods can be used in a trial 2 types Civil procedure – used when civil law has been violated. Criminal procedure – defines the process for enforcing the law when someone is charged with a crime. Main Types of Laws Substantive Law – defines rights and duties Concerned with all the rules of conduct except those involved in enforcement. Defines offenses, such as murder, theft, vehicular homicide, breach of contract, etc. Main Types of Law Business Law – also known as commercial law, covers rules that apply to business situations and transactions. Largely concerned with civil law, especially contracts. TORTS – private wrongs (i.e. civil offenses) against people and organizations. Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) – large set of business statutes which simplified, clarified, and modernized many laws relating to commercial transactions. Uniform laws governing business and commercial transactions. Business activities also governed by criminal law.