WL Unit 5 (Werewolf)Braxton
advertisement

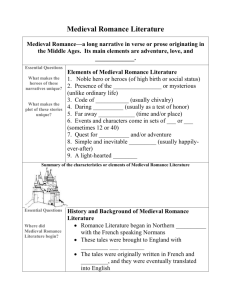
Unit 5: From Decay to Rebirth The Middle Ages: A.D. 450-1300 The Lay of the Werewolf Medieval Romance Saga • A romance is a narrative that tells of strange, sometimes supernatural, events in exotic settings. • In the Middle Ages, the term referred to the tales that depicted the heroic deeds and courtly love of noble knights and ladies. • Today, the genre has expanded to include any work that features idealized characters in an exotic setting, particularly one that focuses on a struggle between good and evil. Medieval Romance Saga(cont’d) • Chivalry is the real core of the medieval romance. • Courtly love is an important element of chivalry; for this reason, romance sagas are sometimes known as chivalric romances or courtly romances. • The main characters of the romance saga were usually kings, knights or a brave warrior who follows the chivalric code of behavior: values of courage, virtue, piety, loyalty to a ruler, and the idealized love of a noble lady. Medieval Romance Saga • The Medieval Romance Saga is characterized by the key features: – – – – Romance Hero A Heroic Quest Supernatural Elements Symbols and Archetypes • Examples of Medieval Romance Sagas: The Legend of King Arthur, and Sir Gawain and the Green Knight. Focus Questions • How are the characteristics of a legend similar to the characteristics of an epic? • What makes the two genres different? Author background Marie de France • Works were crucial to the development of short stories. • Was well-educated, and a member of nobility. • Works combined elements of the classical, Christian, and Celtic traditions (a hero, who travels to a magical land, and learns the secrets of Christianity). • Works were often a radical departure from the time period. Her works often promoted that a man and woman should marry because of genuine love versus an arrangement based on politics and economics. Literary elements (revisited) • Archetypes: details, plot patterns, character types, or themes that appear in the literature of many different cultures. • Examples of archetypes might be: • 1. A quest: the pursuit of someone or something of great importance. • 2. Disguised identity: Characters use disguises, transformations, and tricks to hide their true identities. Literary Elements (revisited) • Symbols: a person, a place, an animal, or an object that has its own meaning but also suggests a larger meaning. • Example: a rose may represent love. • In medieval literature, the entire story centers on a symbol. The Lay of the Werewolf Essential Questions • Why have people chosen the wolf as the form that evil humans often take when they turn into beasts? • Based on the two types of Archetypes mentioned, what type is this short story?