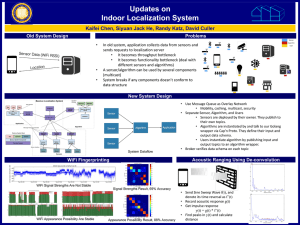
Document
advertisement

An Integrated WiMAX/WiFi Architecture with QoS Consistency over Broadband Wireless Networks Hui-Tang Lin, Ying-You Lin, Wang-Rong Chang, and Rung-Shiang Cheng IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference 2009 報告者 : 李宗穎 Outline Introduction Description of Network Model Bandwidth Allocation and Management Performance Evaluation Conclusions Introduction WiMAX and WiFi have emerged as promising broadband access solutions for the latest generation of wireless MANs and LANs an integrated architecture utilizing a novel WiMAX/WiFi Access Point (W2-AP) device to effectively combine the WiMAX and WiFi technologies Integrated WiMAX/Wifi System a single WiMAX BS, operating in a licensed band, serves both multiple WiMAX Subscriber Stations (SSs) and multiple W2-APs Proposed MAC Layer Module MultiMAC dynamic switching between different MAC protocols ex: adding a byte to the header of the frame for identification purposes SoftMAC encapsulate a WiMAX PDU into a single WiFi PDU over 802.11a OFDM PHY or to decapsulate a single WiFi PDU into its WiMAX PDU. MAC Module in W2-AP Device UL Aggregator/Classfier Packet Classification temporarily buffer the UL data packets based on their corresponding priority BW-REQ Aggregation aggregate all bandwidth demands at the same QoS level from WiFi nodes into a single bandwidth request MAC Module in W2-AP Device The UL and DL bandwidth information is passed down to the DL/UL-MAP Generator MAC Module in WiFi Node/WiMAX BS WiFi Node modified by adding MultiMAC, SoftMAC and 802.16 SS-MAC functions WiMAX BS the MAC layer is the same as that defined in the IEEE 802.16 standard Two-Level Hierarchical Bandwidth Allocation (THBA) W2-AP attempts to aggregate bandwidth demands having the same level of QoS Frame Operation in Level A/B Second-Hop Frame Gap WiFi and WiMAX networks use different frequency bands, and thus the problem of interference is neglected Simulation Model Total Bandwidth DL/UL Ratio 64Mbps 1:1 TDD Traffic Type CBR (kbps) Interval (ms) VoIP (UGS) 64 20 Video (rtPS) 128 10 Web (BE) 64 12.5 three specific bandwidth allocation protocols THBA scheme Independent bandwidth allocation control Each W2-AP aggregates all the bandwidth demands with the same QoS level received from its WiFi nodes The W2-AP directly allocates its own bandwidth to its WiFi nodes based on their bandwidth requirements and buffers the packets sent from the WiFi nodes WiMAX with EDCA control IEEE 802.11e NIC card to employ a priority-based EDCA bandwidth contention protocol for accessing the channel Mean end-to-end delay of various traffic classes for various network offered loads Mean end-to-end delay of various traffic classes for the number of VoIP connections within the network Mean end-to-end delay versus number of WiFi nodes per WiFi hotspot Conclusion By using the W2-AP and modify 802.11 NIC card, the integrated architecture enables the use of a common protocol operation between the WiMAX and WiFi components of the network THBA mechanism can reduces the end-toend delays of high priority traffic Comment 英文寫的很難懂 沒有較詳細的頻寬分配方法 雖然只要軟體升級,但要修改到WiFi節 點會比較造成支援度便利性不足