Generation and reading of the 12 lead ECG

Generation and reading of the
12 lead ECG
AWC Chow
The 12 lead ECG
Advantages
• Common clinical tool
• Independent marker of cardiac disease
• Non-invasive
• Rapid information acquisition
• Cheap
• Gold standard for arrhythmia management
The 12 lead ECG
Disadvantages
• Average of potentials
• Limited resolution
• Snapshot of activity
• Electrical and not haemodynamic data
Right bundle
Posterior inferior fascicle
Nonspecialised atrial tissue
Left bundle
Anterior superior fascicle
+
+/-
-
History of the ECG
• 1842 -Carlo Matteucci shows that an electric current accompanies each heart beat.
• 1874 - Sanderson and Page record the heart's electrical current with a capillary electrometer
• 1887 - British physiologist Augustus D.
Waller publishes the first human electrocardiogram.
• 1901 - Einthoven develops the string galvometer
• 1910 – Eithoven’s triangle
Theoretical consideration
• Myocytes have a resting potential
• Transmembrane flux create voltage difference
- activation
• Cellular coupling cause rapid deploarisation
• Ionic flux seen ECG deflections
Theoretical considerations
• Resting state - no potential/field change
• Depolarisation - boundary potential change
• Represented as a dipole/vector
• Restitution of polarity: repolarisation
Theoretical considerations
• Greater muscle mass
– Larger potential change
– Larger voltage changes of ECG
• Direction of activation dependent on
– Site of initiation
– Specialised conduction system distribution
– Anatomical considerations
» Barriers (scar, valves)
» Muscle mass
RA
I
II III
LA
RL LL
aVR +210
III +120 aVF +90
II +60 aVL -30
I 0
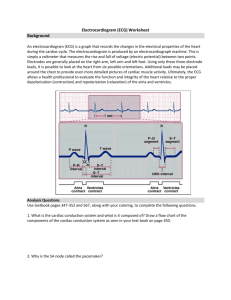
PR
P
QRS
T
QT
Diagnostic criteria for LVH
There are many different criteria for LVH.
• Sokolow + Lyon (Am Heart J, 1949;37:161)
S V1+ R V5 or V6 > 35 mm
• Cornell criteria (Circulation, 1987;3: 565-72)
SV3 + R avl > 28 mm in men
SV3 + R avl > 20 mm in women
• Framingham criteria (Circulation,1990; 81:815-820)
R avl > 11mm, R V4-6 > 25mm
S V1-3 > 25 mm, S V1 or V2 +
R V5 or V6 > 35 mm, R I + S III > 25 mm
• Romhilt + Estes (Am Heart J, 1986:75:752-58)
Point score system
Causes of RBBB
• normal finding in children and tall thin adults
• right ventricular hypertrophy
• chronic lung disease even without pulmonary hypertension
• anterolateral myocardial infarction
• left posterior hemiblock
• pulmonary embolus
• Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome - left sided accessory pathway
• atrial septal defect
• ventricular septal defect
Causes of LBBB
• left anterior hemiblock
• Q waves of inferior myocardial infarction
• artificial cardiac pacing
• emphysema
• hyperkalaemia
• Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome - right sided accessory pathway
• tricuspid atresia
• ostium primum ASD
ECG Analysis
• Rate
• Rhythm
• PR
• QRS
• Axis
• QT interval
• ST segment
60-100b/min
SR
<200ms
<120ms
-30 to +120
<500ms
ECG