Overview of Disabilities for Paraprofessionals
advertisement

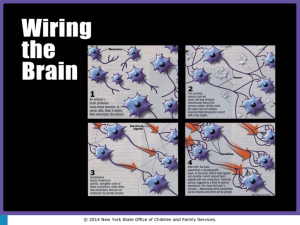
Planning for Students with Learning Needs …Universal Design Special Education Department Ellen J. Stoltz, Ph.D. Coordinator Three P’s Purpose: To provide Grade 2 teachers with background knowledge to promote effective instruction by presenting observable traits of students with learning needs…AND WHAT WE CAN DO ABOUT IT! Presentation: Power Point, large- and smallgroupwork, lesson-building with Universal Design; Pay-off: Increase skill in turning challenge into possibility by planning with Universal Design; Ice-Breaker Activity Identify one instructional accommodation and one classroom management strategy you already use in your classroom. Select someone from your table/group to share with large group. Ice-Breaker Activity Instructional Accommodations: Classroom Management Strategies: Disability Categories ID= HI= LSH= VI= Intellectual Disability Hearing Impairment Speech and Visual Language Impairment Emotional Disturbance OHI= SLD= OI= MD= Other Health Impaired Specific Learning Disability Orthopedic Impairment AUT= TBI= DD= Autism Traumatic Brain Injury Developmental Delay DeafBlind ED= Multiple Disabilities Incidence in Hartford Total Students with Disabilities=3658 60 50 40 30 Percent 20 10 0 LD ID ED SLI AUT •Setting the Scene and Activating Prior Knowledge 1. Conceptual Framework of Universal Design 2. Disrupt the Deficit Paradigm… 3. Person First…. 4. Instructional Connectivity 5. Minimize Impact/Maximize Opportunity Neurodevelopmental Constructs Across the Grades Temporal-Sequential Ordering: time, seriation, problem-solving Spatial Ordering: patterns,geometric imaging, whole-to-part, spatial concepts, nonverbal thinking Memory: Abstract, symbolic information, procedural recall, rapid recall of facts, Neurodevelopmental Constructs Across the Grades 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Executive Functions Activation…prioritizing, organizing Focus…sustain and shift attention Effort…regulate alertness Emotion…manage and modulate Memory…working, recall, LTM, STM Action…monitor and self-regulate Characteristics of Students with Learning Disabilities Achievement below ability; 60-80% of students with LD are males; Comprise 4-10% of population, Familial pattern; Inconsistent performance; Short- and long-term memory deficits; Disorganized in thought, action, and materials; Poor spatial awareness and sequencing in time and space; Socially immature; misinterpret social cues; What will students with LD struggle with? Numerical Proportional Reasoning Geometry and Measurement Algebraic reasoning: Patterns and Functions Probability What will students with LD struggle with? (or how does the student’s disability interfere with benefiting from the general education curriculum?) Relational and positional concepts Fractions, decimals One more Skip counting Place value Patterns Equations Multi-step word problems Money Subtraction and division Calendar and time Estimation Operational signs Strategies for Students with LD Increase Memory: Make it Multisensory…seeing (V),hearing (A), saying (A), doing (K), writing (V,K,T), acting (VAKT); Increase Organization: Provide routines, graphic organizers for math concepts, visual symbols for math-problem-solving, Utilize Downward Extensions and Task Analysis: i.e. number sentences and equations…@@@=@@_; recognize vs. identification Team Work Use the VAKT tool on the next page to design instructional accommodations to a Fact Family lesson. Teaching FACT FAMILIES in Multisensory Ways… Visual: Auditory: Kinesthetic: Tactile: Characteristics of Students with Other Health Impairments limited strength, vitality or alertness, including a heightened alertness with respect to the educational environment, attention deficit with/without hyperactivity disorder; tuberculosis, rheumatic fever, nephritis, asthma, sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, epilepsy, lead poisoning, leukemia, or diabetes, adversely affects a learner’s performance Characteristics of Students with OHI-ADHD ADD/ADHD: Distracted by sound and movement, impulsive, inconsistent across settings, taskdependent; hyperalert; Moves from one activity to the next; incomplete work; Winded, easily fatigued, little interest in activities, low motivation; Lethargic, low energy, disorganized thinking; Did you know that… ADHD can occur in different lobes of the brain? Characteristics of Students with OHI-ADHD attention deficit with/without hyperactivity disorder; difficulty with ALL six executive functions; impairs the neural circuits that function as conductor of the symphony of the brain Strategy: teacher needs to serve as conductor by organizing, initiating, reduce sound and movement, sustain motivation; Chadd.org Classroom Management for Students with ADHD Scheduled breaks Hi-protein or complex carb snacks Visual schedule 3:1 praise ratio Elapsed timer Fidget toy Differential Reinforcement of Other Behavior (DRO) Characteristics of Students with Intellectual Disabilities Below average intellect AND adaptive skills, IQ=70ish or below; Adaptive functioning= communication, social, self-help skills; No specific personality and behavioral features: may be placid, dependent, aggressive, impulsive; Strategy: 80-100 repetitions with drill, concrete examples, personalized experience,realia, manipulatives, VAKT Team Work: Application Math Objective Universal Design Procedures Classroom Management Student Products Characteristics of Students with Speech and Language Impairment Impaired articulation, expressive language, receptive language; May occur with spoken or sign language; Limited vocabulary, simple grammar and sentences, unusual word order; slow speech; circumlocutions; Poor language comprehension; misarticulations; Overlap with students with ED; Utilize Power Words from Word Wall; Ask students to retell directions to team; Utilize peers as language models; Characteristics of Students with Emotional Disturbance Inability to learn due to poor peer and adult relationships; Abnormal feelings and behaviors under normal circumstances; Physical symptoms or fears associated with school; Emotional/Social behaviors that are of a marked degree and have lasted for longer than six months AND affect learning; 2-16% of population; Bright, easily bored, distracted; Characteristics of Students with Emotional Disturbance Argumentative, defiant, blames others, loses temper easily; mood swings; Verbal and/or physical aggression; agitated; Passive, socially reclusive; Receptive and expressive language concerns; Low self-esteem; poor memory and decisionmaking; Acting out; poor social relationships; Strategy: anticipate behaviors, be proactive, use preferred activity for leverage, stay calm; puzzle reinforcer, VAKT Characteristics of Students with Autism Impaired development in social interaction and communication; Restricted repertoire of activity and interests; Lack of social/emotional reciprocity; Lacks awareness of others, prefers solitary interests; Delayed language comprehension; Triggers: gym floor, florescent lights, noise, movement, inconsistency Strategies for Students with Autism Visual Supports, such as icons, pictures, photo album of school locations, staff Elapsed timer Numbered turn takers Transition warnings, such as bells, claps, lights Routines Preferred activity alternated with work Concept Map Content Process Product Readiness Profile Interests Bloom’s Taxonomy Grouping Presentation and Response Style Document Project Demonstration Drawing What Can You Do To Improve Teaching and Learning? Understand your own Knowing-Doing gap when you teach. Build your presentations with the product in mind. Know there are better ways of doing things…tap your internal experts! PLAN grouping, traffic flow, multi-sensory tasks, environmental triggers, choices Don’t Assume! Apply Bloom’s Taxonomy to guide lessonplanning, i.e. knowledge vs. application Embed accommodations and modifications into the lesson for all students to access; Think VAKT and Task Analysis Repetition: similar (drill) and diverse (multiple ways) to learn the same material Putting It All Together to Plan for All Students… Universal Design Lesson Plan Objective Universal Design Procedures Classroom Management Student Products Share Plans… Additional Ideas… Measure and Display Successes for Learning and Behavior; Link to BIP; Increase Student’s Awareness of How Disability Affects Learning and Behavior; Link to IEP; Utilize an Array of Consistently Applied Strategies to Ensure Success, i.e. highlighting verbs, restating directions in student language; Focus on Student Strengths and Interests for Preferred Activities (leverage); Utilize Visual Supports for Learning and Behavior, such as authentic pictures of student working, daily schedule; point system (individual and group) with puzzle reinforcer and preferred activity; elapsed timer Questions? stole001@hartfordschools.org; Kindergartensigns.com Environments.com www.4teachers.org www.help4teachers.com www.tandl.leon.k12.fl.us/lang/Ellessonspage.html www.borenson.com http://.timetimer.com