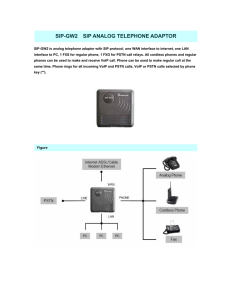
VoIP
advertisement

VoIP PRESENTATION BY HÜSEYİN SAVRAN 220702044 OUTLINE PSTN an brief history of telephone PSTN ( Public Switched Telephone Network) Known structure of conventional telephone network. İstanbul, yeditepe PSTN Call Direction Ankara, METU PSTN history Since the telephone was invented in the late 1800s, telephone communication has not changed substantially . A Change of Perspective Traditional View Cable Data Broadcast Telephony Wireless A Change of Perspective Current View Data Cable Broadcast Telephony Wireless A Change of Perspective Reality Web Voice Email Data Video File Transfer These Count as Phones? MOTIVATION What is VoIP IP TELPHONY (VOICE over IP) Transmission of voice telephone calls using internet infrastructure. Why need to IP Telephony? Economic (uses internet, IP routers...) Further savings. Because underlying network infrastructure can be shared. a single set of equipment, wiring, network connection enough. Example: a company with reduced telephone costs. Why need to IP Telephony? Cont. Not only voice but also video is transmitted using similar concepts. Spreads at a fast pace. For instance there isn’t any internet cafe which doesn’t have tiny video cameras over their monitors. Why need to IP Telephony? Cont. Independent. Much larger selection of service providers to provide voice and video communication services . No geographical restriction! Located virtually anywhere in the world! Keep in mind! IP Telephony must be backward compatible with existing PSTN. There are several communication schemes: VoIP to VoIP Broadband Network VoIP VoIP Call Direction IP Protocol VoIP to POTS with Internet İstanbul, yeditepe Internet/Broadband New Delhi PSTN VoIP Server/Gateway India Call Direction IP Protocol VoIP to POTS without Internet Server/Gateway İstanbul, kayışdağı Miami, FL PSTN VoIP CO LATA Call Direction IP Protocol Miami Basic Idea Behind VoIP Continuously sample audio. Convert each sample to digital form. Send the resulting digitized stream accross an IP network in packets. Convert the stream back to analog for playback. Before the procedure above, the system must handle call setup. Phnumber to IP. Encoding, Transmission, and Playback Two groups have introduced standards for IP telephony International Telecommunications Union(ITU), controls telephone standards. Internet Engineering Task Force(IETF), controls TCP/IP standards. Encoding Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) TransmissionReal-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) Note: RTP is not a tranport-layer protocol. It is a tranfer protocol that operates at Layer 5. Each RTP message is encapsulated in UDP datagram, which is then encapsulated in an IP datagram for transmission. Why UDP instead of TCP? Higher overhead of TCP does not make sense for telephone call. Because audio must stream! No wait for missing packets. Play missing part as silence. Why UDP instead of TCP? UDP Offerrs best-effort delivery. to handle duplication, delay, out-of-order delivery, each RTP message contains: A sequence number A real-time clock value What does real-time clock value do? • Allows a receiver to construct the axact temporal sequence of the data. – İf a packet is missing , the receiver knows exactly how long to wait before starting to play the next packet Signaling Systems and Protocols Signaling: The process of establishing and terminating a call. Includes: – – – Mapping a phone number to location Finding a route to the called party Handling other details such as call forwarding Signaling System 7 (SS7) for traditional telephone system. Signaling Protocols IETFSession Initiation Protocol (SIP) ITUH.323 Aboves must be able to interact with SS7 Internet/Broadband New Delhi İstanbul, yeditepe PSTN VoIP Call Direction Server/Gateway India IP Protocol A Basic IP Telephone System Two basic components interconnected by an IP internet. *IP telephone *Media Gateway Controller Media Gateway Controller IP telephone INTERNET IP telephone Media Gateway Controller Media gateway handles voice IP telephone INTERNET PSTN Signaling gateway handles setup Analog telephone