File
advertisement

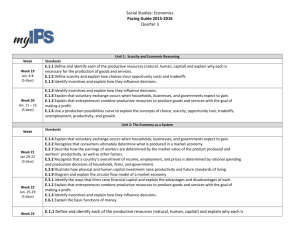
MICROECONOMICS • SSEMI1 The student will describe how households, businesses, and governments are interdependent and interact through flows of goods, services, and money. • a. Illustrate by means of a circular flow diagram, the Product market; the Resource market; the real flow of goods and services between and among businesses, households, and government; and the flow of money. • b. Explain the role of money and how it facilitates exchange. • a. Illustrate by means of a circular flow diagram, the Product market; the Resource market; the real flow of goods and services between and among businesses, households, and government; and the flow of money Click ME!!! Circular Flow Market Economy Mixed Economy • b. Explain the role of money and how it facilitates exchange. – MONEY IS: • A medium of exchange • A unit of account • A store of value – In our economy, money is the most effective medium of exchange when purchasing goods. Click ME!!! • SSEMI2 The student will explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. • a. Define the Law of Supply and the Law of Demand. • b. Describe the role of buyers and sellers in determining market clearing price. • c. Illustrate on a graph how supply and demand determine equilibrium price and quantity. • d. Explain how prices serve as incentives in a market economy. • a. Define the Law of Supply and the Law of Demand. – LAW OF SUPPLY: Higher Price = Higher Quantity Supplied (direct relationship) – LAW OF DEMAND: Lower Price = Higher Quantity Demanded (inverse relationship) • b. Describe the role of buyers and sellers in determining market clearing price. • c. Illustrate on a graph how supply and demand determine equilibrium price and quantity. • d. Explain how prices serve as incentives in a market economy. – The price is the amount of money needed to buy a particular good or service. – In a market, the price and quantity exchanged are determined by the interaction of demand and supply. – Changes in demand or supply alter the price as well as the quantity bought and sold at that price. • SSEMI3 The student will explain how markets, prices, and competition influence economic behavior. • a. Identify and illustrate on a graph factors that cause changes in market supply and demand. • b. Explain and illustrate on a graph how price floors create surpluses and price ceilings create shortages. • c. Define price elasticity of demand and supply. • a. Identify and illustrate on a graph factors that cause changes in market supply and demand. • Changes in SUPPLY or DEMAND (not quantity supplied or quantity demanded) cause the supply or demand curve to shift. – Increase in Supply or Demand: Curve shifts right – Decrease in Supply or Demand: Curve shifts left Factors that change demand • Population • Income • Consumer tastes • Price of complements • Price of substitutes • Expectations of a change in price Factors that change supply • Cost of inputs • Technology • Government Regulation – Taxes – Subsidies • Expectations of a change in price • b. Explain and illustrate on a graph how price floors create surpluses and price ceilings create shortages. • SURPLUS – Price above equilibrium – Qd < Qs • SHORTAGE – Price below equilibrium – Qd > Qs • Price Ceiling – legally established maximum price. – Governments enact price ceilings when they fear that the price might be higher than they desire it to be. – Creates a shortage – Example: rent-control • Price Floor – is a legally established minimum price. – Governments enact price floors when they fear that the price might be lower than they desire it to be. – Creates a surplus – Examples: farm products and the minimum wage. • c. Define price elasticity of demand and supply. – elasticity of demand is the way of measuring how much quantity demanded will change in response to a change in price. • SSEMI4 The student will explain the organization and role of business and analyze the four types of market structures in the U.S. economy. • a. Compare and contrast three forms of business organization—sole proprietorship, partnership, and corporation. • b. Explain the role of profit as an incentive for entrepreneurs. • c. Identify the basic characteristics of monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, and pure competition. • a. Compare and contrast three forms of business organization—sole proprietorship, partnership, and corporation. Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation -Most Common -Easiest to start -Unlimited liability -Two or more owners -Business is a legal entity, -Easy to secure funding & risk separate from its owners is shared -Most complex to start -Can sell stock to raise money • b. Explain the role of profit as an incentive for entrepreneurs. – Profit (making money) is the incentive for entrepreneurs to start new businesses and invent newer and more cost-effective ways of producing goods. Click ME!!! • c. Identify the basic characteristics of monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, and pure competition. Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Monopoly # of Sellers Many Many Few (2-4) One Variety of Goods None Some Some None Control over price None Some Some Total Barriers to Entry None Few High Complete Examples Jeans Airlines NFL Apples