File
advertisement
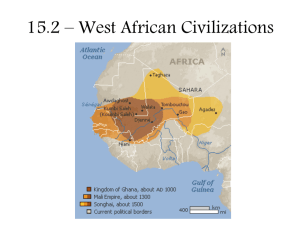
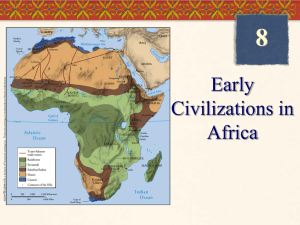
AFRICA IN THE MIDDLE AGES HOMEWORK CHECK What was the main disagreement that the Almohads had with the Almoravids? They thought they were a better race. 2. The Almoravids stole their land. 3. They had moved away from traditional Islam. 4. They thought the Almoravids were too much like Christians. 1. 59% 36% 5% 0% 1 2 3 4 The part of North Africa that is today in the countries of Libya, Tunisia, Morocco, and Algeria, is called… 1. The Madrid 2. The Mediterranean 3. The Masjid 4. The Maghrib 96% 0% 1 4% 2 0% 3 4 According to the book, daily life for the Efe is not governed by… 1. Formal written laws 68% 2. The laws of nature 32% 3. Morality 0% 4. Traditions 0% of the tribe The Cherokee are to the United States, as the __________ are to the Congo. 1. The Igbo 2. The Egyptians 3. The Almohads 4. The Efe 87% 4% 1 9% 0% 2 3 4 AFRICA IN THE MIDDLE AGES North and Central Africa LEARNING GOAL AND RUBRIC 4. Discuss the main ideas about West African societies and support them with details. 3. Point out and discuss the main ideas about West African societies. 2. With help, you are able to point out and discuss the main ideas about West African societies. 1. Even with help, no success. MUSLIM STATES OF NORTH AFRICA • The Spread of Islam (632-750): sometimes with armies and sometimes peacefully • By 670, Muslims had spread to the Maghrib (Coastal area on the Mediterranean Sea; today: Tunisia, Libya, Algeria, Morocco). • Newly converted Muslim rulers in north Africa used Islamic Law (called what?). • Some countries in north Africa still use Shari ’a today. • The Berbers were a north African ethnic group that converted to Islam. • They had two empires that sprung up, one right after another in the Middle Ages. MUSLIM STATES OF NORTH AFRICA • The Almoravids • Berbers, 1000s • Religiously based group, who ended up taking over a large part of Northwest Africa and parts of Spain (where they were called the Moors) MUSLIM STATES OF NORTH AFRICA • The Almohads • Another group of Muslim-based reformers, 1100s • They thought the Almoravids had gotten off track. Overthrew the Almoravids • They took over most of the land of the Almoravids and united most of the Maghrib of north Africa for the first time. What is the name of the Islamic Law that some Muslim governments use? 1. Sunni 0% 2. Patrilineal 0% 3. Berber 0% 4. Shari’a 100% FASTEST RESPONDERS (IN SECONDS) 2.82 Austin Leach 4.77 5.2 5.71 6.01 Brean Mathis Orlando Colon Caitlyn Colvin Jordan Ulee The Almoravids took over part of which European country? 1. Italy 9% 2. France 5% 3. Nigeria 9% 4. Spain 77% FASTEST RESPONDERS (IN SECONDS) 3.53 Orlando Colon 3.72 3.85 4.09 4.8 Madison Fitzpatrick Jonathan Weir Bailey Lunt Jeremy Burke The Maghrib is the coastal region in north Africa along which sea? 1. The Black Sea 0% 2. The Aegean Sea 3. The Mediterranean Sea 0% 100% 4. The 0% Red Sea FASTEST RESPONDERS (IN SECONDS) 1.29 Caitlyn Colvin 1.42 2 2.08 2.38 Darrius Davis Carah Gedeon Madison Fitzpatrick Brean Mathis LEARNING GOAL AND RUBRIC 4. Discuss the main ideas about West African societies and support them with details. 3. Point out and discuss the main ideas about West African societies. 2. With help, you are able to point out and discuss the main ideas about West African societies. 1. Even with help, no success. AFRICA IN THE MIDDLE AGES West African Empires GHANA • The Sahara Desert • Trade difficult with horses • Berbers started using Camels • The Berbers traveled through the territory of a chief (called a Ghana) • Ghana became the name for this whole area • The kings of Ghana began taxing the traders traveling through their land TRADE: LIFELINE FOR GHANA • Salt and Gold were traded • Gold • Salt mined in Ghana needed by Ghana • The Berbers were traders and also brought cloth, weapons, etc. • The kings of Ghana became rich from taxing all of the trade • Ghana 800 AD was an empire by AN EMPIRE OF TRADE • Ghana’s king controlled the trade and was very rich • He took over other chiefs • He was religious, political, and military leader • Islam came into Ghana by trade, not by war • Only the rich and powerful became Muslims and learned to speak and read Arabic • In 1076, the Almoravids conquered Ghana, hurting the gold & salt trade. Turn to the person next to you and answer these: 1. Why would the disruption of trade destroy Ghana’s power? 2. Why do you think only the rich and powerful converted to Islam in Ghana? Which North African ethnic group was responsible for conquering Spain and bringing Islam to West Africa? 1. The 0% 2. The 0% 3. The Berbers Magyars Muslims 0% 4. The 0% Igbo MALI • By 1235, Mali had become a kingdom. • It grew wealthy on new sources of gold as Ghana slowly died to the west. • Trade started to come through Mali, not Ghana. • Sundiata leader. • Mansa was Mali’s first great = emperor • Sundiata had great military and political power MANSA MUSA OF MALI • In 1255, Sundiata died • The next rulers were Muslims. • Mansa Musa reigned from 1312 to 1332. • He expanded the empire and appointed governors • Mansa Musa’s Hajj (1324-5) • He built up Timbuktu (mosques and universities) • Many scholars moved to Mali • Ibn Battuta In Mali for 1 yr. • Wrote about Musa and the fair and peaceful society • What valuable trade good made Mali so wealthy? 1. Cotton 0% 2. Ivory 0% 3. Silver 0% 4. Gold 0% Turn to the person next to you and answer these: 1. What are some stereotypes about Africa? How might the story of Mansa Musa break stereotypes about Africa? 2. How did the environment affect the empires of Ghana and Mali?