Themes of Biology
advertisement
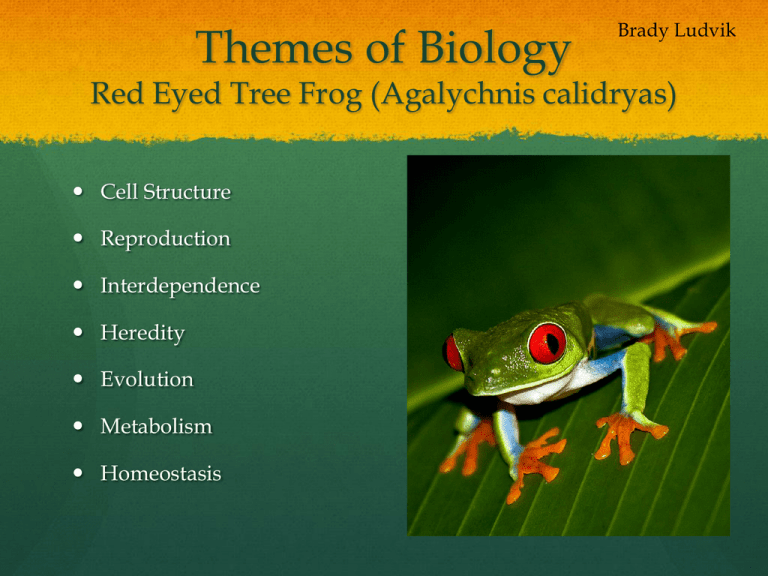
Themes of Biology Brady Ludvik Red Eyed Tree Frog (Agalychnis calidryas) Cell Structure Reproduction Interdependence Heredity Evolution Metabolism Homeostasis Cell Structure This frog is a multicellular organism as are all animals. It has skin cells and blood cells like many other animals. Why do different cells have different shapes?—they have different shapes because different types of cells have different jobs and they need certain parts to do their job. What organelles do cells have?—Some organelles include the mitochondrion, the ribosomes, and lysosomes Reproduction The red eye tree fog reproduces by sexual reproduction. Then when the female is ready to lay her eggs, she finds a leaf overhanging a pond so when they hatch, they fall into the water. These eggs are all held together in a jelllike casing How many eggs are there per laying?—About 20 to 60 eggs How long does it take for them to hatch?—About 1 week Homeostasis An example of homeostasis for the red eye tree frog is that it is an amphibian, so it needs to be in the water every once in a while to moisturize their skin and to drink water. How often do they need to go in the water?—every couple hours their instincts tells them to go into the water Why do they dry out so easily from being out of the water?— They can breath through their skin, but to do this their skin must be very thin, so they use the water to moisturize themselves Evolution One example of evolution of evolution for this animal is its feet. They have feet that help they stick to vertical surfaces to stay away from predators. They also have skin that blends in with their surroundings and to confuse their predators. Why do they have such thin skin?—they have adapted to breath through their skin Why do they have red eyes?—their eyes are red so that their attacker is startled so they can get away Metabolism The red eyed tree frog’s diet consists of fly’s, moths, grasshoppers, crickets, and dragonfly's. They eat mostly insects because in the rain forest, there is a large abundance of them and there isn’t a lot to eat that is smaller than them other than smaller frogs. How much does it eat a day?—About 15 fly’s, crickets What nutrients does the frog get from its diet?—A couple of the nutrients that it needs is Calcium and Vitamin 3D Heredity The basic body shape of the frog is given through heredity. Also the colors on the side of its body is passed down though generations through heredity. Is the shade of red on its eyes passed down through heredity—yes, there are many different hues of red that can be a hereditary trait Is its feet a hereditary trait?— yes, they all have large sticky feet, so that means that their parents must pass the trait down to them Interdependence The frog is interdependent on the fly and other insects like it because if the fly and insect population went down, so would the frog population because their pray is not abundant. What would happen if the frog population went down?—the fly and small insect population would rise because of the decrease in their predator's population. What would happen if the fly’s food population decreased?—the fly population would go down which in turn would lower the frog population











