Force and Motion: Physics Presentation
advertisement

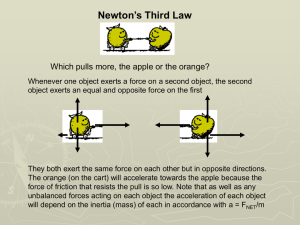
force a push or a pull has magnitude and direction arrows represent the magnitude arrowhead represents the direction shown in Free Body Diagrams common types of forces Force Symbol Definition Direction Friction Ff The contact that acts to oppose sliding motion between surfaces Parallel to the surface and opposite the direction of sliding Normal FN The constant force exerted by a surface on an object Perpendicular to and away from the surface Tension FT The pull exerted by a string, rope, or cable when attached to a body and pulled taut Away from the object and parallel to the string, rope, or cable at the point of attachment finding net force Two horizontal forces, 225 N and 165 N are exerted in the same direction on a crate. Find the net horizontal force on the crate. If the same two forces are exerted in opposite directions, what is the net force on the crate? Be sure to indicate the direction of the net force. defining systems draw a picture that defines each system: a piano hanging from a pulley at rest a book on top of a table being pushed to the left a ball resting in your hand newton’s second law of motion Fnet a m a shopping cart full of groceries has a mass of 150 kg. if you push the cart to the right with 1500 N, what will the acceleration of the cart be? a semi-truck accelerates at 6 m/s2. if the mass of the truck is 5000 kg, what force on the truck must the engine produce? mass and weight mass is the measure of matter in an object; a fundamental property of an object that is not affected by the forces that act upon it weight is a measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object acceleration due to gravity the rate at which an object accelerates towards the center of the Earth on Earth g= 9.8 m/s2 On Earth, a scale shows that you weigh 585 N, what is your mass? What would the scale read on the moon if g=1.6 m/s2? newton’s first law of motion an object at rest will remain at rest an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force inertia a property of mass the tendency an object has to resist a change in motion newton’s third law of motion all forces come in pairs for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction force pairs do not cancel because they act upon different surfaces a physics textbook is motionless on the top of a table. If you give it a hard push with your hand, it slides across the table and slowly comes to a stop. Use Newton’s 3 Laws to answer the following questions. 1. why does the book remain motionless before the force of the hand is applied? 2. why does the book begin to move when your hand pushes hard enough on it? 3. why does the book eventually come to a stop?