Ghana: A Trading empire
advertisement

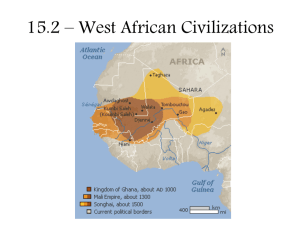
Bell Ringer • How did Ghana control the trans-Saharan trade? • Why were camels important? • What is an oasis? CH 8: Ghana- A Trading empire Kingdom of Ghana • Started before 500 CE, and lasted until about 1200 • Located in a semi-arid land (receives rain, but not much) • Modern Day: Mali & Mauritania • The first mention of the Empire of Ghana was from Arab Scholars, but it was a flourishing empire by that time. • Ghana means “war chief” • Ghana was an important empire as it was very important in terms of trade, and they controlled a large supply of gold. Land of Gold • Arab scholars described Ghana as a land of Gold. • The King was the head of the military, which made him very powerful. • The King taxed all gold that passed through the kingdom, and all gold found in the Empire had to be given to the king. • The King used governors to help rule the Empire (he paid them, they obeyed) Matrilineal Inheritance • The royal inheritance was Matrilineal • When the King died his Sister’s son would inherit the throne. Trade • Ghana benefited from its geography. North Africa wanted to trade with West Africa. • Traders had to cross through Ghana, which taxed them heavily on their goods. • Control of the trans-Saharan trade made the King of Ghana extremely rich. History of Trade • Trade across the Sahara was difficult in history. • However the introduction of the Camel & Islam made trade easier. • Invading Muslims introduced Camels, which were great for the Desert. • Ghana also defeated the invading Muslims, who controlled West Africa. Their desire to trade benefited Ghana. • Traders would use caravans, or travel in groups. • Traders would wait until after the rainy season, when water and grass could be found along the trade route. • Traders would go from Oasis to Oasis. • The entire trip took about 2 months to complete. The Journey Gold & Salt • Of the many items traded Gold & Salt were the two most important. • Gold has long been considered valuable throughout the world. • Salt is valuable as a part of people’s diet and for food preservation. Wangara: Gold • A part of Africa known as Wangara had a large supply of gold they were willing to trade. • Apparently no one knew where the gold was but the Wangara people. • Stories state that miners captured by traders would rather die then reveal the location of the Gold. • One story says when a miner was killed the Wangarian people stopped trading for 3 years to prove a point Taghaza: Salt • West Africans needed salt • In Taghaza salt was located about 3 feet below the earth • The only thing in Taghaza was salt, and without salt it would have never existed. • Miners relied on Caravans to bring them food, if the caravans didn’t show up the salt miners starved. Taxes • Ghana had a complex system of taxes for traders going through their empires. • Traders were taxed going into and out of Ghana. • Most traders didn’t mind as the Army of Ghana secured the trade routes, and made traveling in their empire extremely safe. • Traders would also sell some of their goods at the market place in Kumbi (Ghana Capital) • One of the biggest markets in Africa, also had a slave market. • Wood, Silk, Cotton, Dates, Figs, Grain, Leather, Gold, Salt • Gold dust was the main currency Ghana Falls • Ghana peaked in about 1000 CE • Muslim Warriors would take control in 1076, and the King would regain control in 1087 • West Africa would fall (making Ghana less important), & Ghana would deplete their resources. • 1203 a rival took over Kumbi, and Ghana ended • Mali would become the next major empire in Africa after the fall of Ghana. Class Work • Take 5-8 Minutes • Make Up 3 Multiple choice questions based on Ghana. • Write out the full question and provide multiple answers A-D (obviously one of them should be a correct answer).