PowerPoint - WordPress.com
advertisement

Sixth edition: what’s new?
Chapter 1:
access nets
ISP ecosystem
packet switching vs.
circuit switching
Chapter 2:
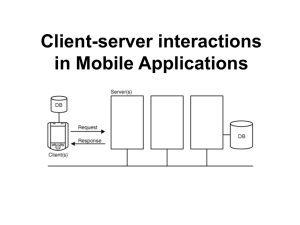
socket programming
with Python
Chapter 3:
TCP splitting
rdt streamlining
Chapter 4:
router architectures
BGP sidebars
Chapter 5:
reorganized, streamlined
DOCSIS cable network
case study
data center networking
Chapter 6:
cellular and 4G
Chapter 7:
adaptive streaming video
CDNs, Google
Netflix, YouTube, Kankan
Supplementary materials
Homework problems:
many new and revised
improved solution manual
Powerpoint slides:
revised and extended
gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose-ross-ppt-6e
Python socket labs:
web server
UDP pinger
SMTP mail client
multi-threaded web proxy
ICMP pinger
video streaming
Wireshark labs:
revised and improved
Java applets:
some improvements
Interactive HW problems:
totally new!
gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose/test
Video notes:
totally new
Socket programming: Java vs Python
Python and Java
explicitly expose sockets
Python:
no streams
less house keeping
code much shorter
much easier to explain to programming
novices
Python:
access to raw sockets
ICMP pinger
Python UDP client
include socket library
from socket import *
serverName = ‘hostname’
serverPort = 12000
create UDP socket
clientSocket = socket(socket.AF_INET,
socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
get user input
message = raw_input(’Input lowercase sentence:’)
send user input to server
thru UDP socket
clientSocket.sendto(message,(serverName, serverPort))
read reply from socket
modifiedMessage, serverAddress =
clientSocket.recvfrom(2048)
print out received string
and close socket
print modifiedMessage
clientSocket.close()
Java stream jargon
input
stream
Client
Process
process
output
stream
inFromServer
A stream is a sequence of
characters that flow into or out
of a process.
An input stream is attached to
some input source for the
process, e.g., keyboard or
socket.
An output stream is attached
to an output source, e.g.,
monitor or socket.
outToServer
monitor
inFromUser
keyboard
input
stream
client
TCP
clientSocket
socket
to network
TCP
socket
from network
Java UDP client: first half
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
Need to talk
About OOP
Need to talk
about streams
class UDPClient {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
BufferedReader inFromUser =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
DatagramSocket clientSocket = new DatagramSocket();
InetAddress IPAddress = InetAddress.getByName("hostname");
Need to create
place holders
Need to do
type conversion
byte[] sendData = new byte[1024];
byte[] receiveData = new byte[1024];
String sentence = inFromUser.readLine();
sendData = sentence.getBytes();
Java UDP client: second half
DatagramPacket sendPacket =
new DatagramPacket(sendData, sendData.length, IPAddress, 9876);
clientSocket.send(sendPacket);
Place holder
DatagramPacket receivePacket =
new DatagramPacket(receiveData, receiveData.length);
clientSocket.receive(receivePacket);
String modifiedSentence =
new String(receivePacket.getData());
Additional lines
System.out.println("FROM SERVER:" + modifiedSentence);
clientSocket.close();
}
}
Chapter 4: changes
4.1 introduction
4.2 virtual circuit and
datagram networks
4.3 what’s inside a router
4.4 IP: Internet Protocol
4.5 routing algorithms
link state, DV,
hierarchical
4.6 routing in the Internet
RIP, OSPF, BGP
4.7 broadcast and multicast
routing
forwarding tables computed,
pushed to input ports
routing
processor
high-seed
switching
fabric
router input ports
router output ports
“match plus action”
Network Layer 4-9
Chapter 5: changes
5.1 introduction, services
5.2 error detection,
correction
5.3 multiple access
protocols
DOCSIS case study
5.4 LANs: addressing, ARP,
Ethernet, switches,
VLANS
5.5 link virtualization: MPLS
5.6 data center networking
5.7 a day in the life of a web
request
Internet
Border router
Load
balancer
Access router
B
A
1
C
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Link Layer 5-10
Chapter 7: Multimedia Networking
7.1 Multimedia Apps
7.1.1 Properties of video
7.1.2 Properties of audio
7.1.3 Types of apps
Streaming stored video
Conversational VoIP
Streaming live video
7.2 Streaming video
7.2.1 UDP streaming
7.2.2 HTTP streaming
Simple fluid analysis
7.2.3 Adaptive streaming
& DASH
7.2.4 CDNs
Enter deep; Bring home
DNS: intercept requests
Server selection strategies
Geographically closest,
real-time measurements, IP
anycast
7.2.5 Case Studies
Google, Netflix, YouTube,
Kankan
7.3& 7.4 VoIP
Skype expanded
7.5 Network support
Streamlined
Netflix case study
Netflix registration
and payment servers
Amazon Cloud: movie
ingestion, version creation,
CDN upload, manifest file
distribution, and Web pages
Upload versions
to CDNs
CDNs
Manifest
file
Registration
and payment
Video chunks
(DASH)
Client
Interactive end-of-chapter exercises
need: large set of problems/exercises that
students can solve (and obtain answers)
professors can generate (with solutions) for quizzes, tests
many important exercises lend have structure that
allow many variations of exercise to be generated:
Quantitative comparison of packet switching and circuit wwitching
End-to-end delay
Internet checksum
TCP RTT and timeout
TCP congestion window evolution
Dijkstra's Link State algorithm
Link Layer (and network layer) addressing, forwarding
check out: http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose/test
Interactive end-of-chapter exercises
Interactive end-of-chapter exercises
Video Notes
VideoNotes: selected pre-recorded on-line
video/audio/ppt (e.g., Camtasia) segments:
walkthrough, discussion of selected topics (e.g., BGP
basics, a day day in the life of an HTTP request)
walking through, solving sample problems
demonstrations (e.g., traceroute, Wireshark)