File
advertisement

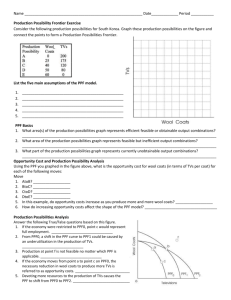
Economics 111.3 Winter 14 January 13th, 2014 Lecture 3 Appendix to Ch. 1, Ch. 2 Ceteris Paribus Assumption • In order to isolate the relationships that exist between two variables, other things must remain the same. • Endogenous variables: the variables that the the model in question is studying. They are “inside” a theory or model. The values of endogenous variables are determined in the model • Exogenous variables: all the other real-world variables that the model in question is not studying. The values of exogenous variables are determined outside the model: the model takes their values & behavior as given. Graphing a Relationship Among 3 Variables Presenting Information Visually Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) Ch. 2 (up to p. 38) PPF: Production Possibilites Frontier PPF is a graph that shows the various combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available factors of production and the available production technology Quantity Technology (Capital , Land , Labour , ...) PPF model assumes: o full employment o productive efficiency (producing goods & services in the least costly way) o fixed resources 𝑸 = 𝑨𝒇(𝑲, 𝑳, 𝑵, 𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒓𝒆𝒑𝒓𝒆𝒏𝒆𝒖𝒓𝒔𝒉𝒊𝒑) o fixed technology o two goods pizzas symbolize consumer goods Cans of cola (better - industrial machines) symbolize capital goods The Production Possibilities Frontier The Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF): a graph that shows the combinations of two goods the economy can possibly produce given the available resources and the available technology Example: Two goods: computers and wheat One resource: labour (measured in hours) Economy has 50,000 labour hours per month available for production. Production Possibilities Curve 𝑸 (𝒄𝒐𝒍𝒂) = 𝑨𝒇(𝑲, 𝑳, 𝑵, 𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒓𝒆𝒑𝒓𝒆𝒏𝒆𝒖𝒓𝒔𝒉𝒊𝒑) 𝑸 (𝒑𝒊𝒛𝒛𝒂𝒔) = 𝑨𝒇(𝑲, 𝑳, 𝑵, 𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒓𝒆𝒑𝒓𝒆𝒏𝒆𝒖𝒓𝒔𝒉𝒊𝒑) Shape of the Curve • concave to the origin Economic Rationale • Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost (resources are not completely adaptable to alternative uses, thus as we make more pizzas, the number of cans of cola we have to give up (per pizza) increases) How to measure the Opportunity Cost • Opportunity cost is measured in terms of rate at which a person (or an economy as a whole) will give up the good, measured on the vertical axis to get one additional unit of the good, measured on the horizontal axis, and at the same time remain on the same PPF The PPF and Opportunity Cost Recall: The opportunity cost of an item is what must be given up to obtain that item. Moving along a PPF involves shifting resources (e.g., labor) from the production of one good to the other. Society faces a tradeoff: Getting more of one good requires sacrificing some of the other. The slope of the PPF tells you the opportunity cost of one good in terms of the other. Production Possibilities and Opportunity Cost – In moving from E to F, the quantity of pizzas increases by 1 million. – The quantity of cola decreases by 5 million cans. – The opportunity cost of the fifth 1 million pizzas is 5 million cans of cola. – One of these pizzas costs 5 cans of cola. Production Possibilities and Opportunity Cost – Note that the opportunity cost of a can of cola is the inverse of the opportunity cost of a pizza. – One pizza costs 5 cans of cola. – One can of cola costs 1/5 of a pizza. Opportunity Cost and Marginal Cost Allocative Efficiency Allocative efficiency implies producing goods & services most wanted by society • Marginal Benefit is the extra benefit associated with consuming one more unit • Marginal Cost is the extra opportunity cost of that extra unit • Decide on allocative efficiency by comparing Marginal (extra) Cost (MC) to Marginal Benefit (MB) As the economy shifts resources from beer to mountain bikes: Beer Why the PPF Might Be Bow-Shaped PPF becomes steeper opp. cost of mountain bikes increases Mountain Bikes At point A, most workers are producing beer, even those that are better suited to building bikes. So, do not have to give up much beer to get more bikes. Beer Why the PPF Might Be Bow-Shaped A At A, opp. cost of mtn bikes is low. Mountain Bikes At B, most workers are producing bikes. The few left in beer are the best brewers. Producing more bikes would require shifting some of the best brewers away from beer production, would cause a big drop in beer output. Beer Why the PPF Might Be Bow-Shaped At B, opp. cost of mtn bikes is high. B Mountain Bikes Why the PPF Might Be Bow-Shaped So, PPF is bow-shaped when different workers have different skills, different opportunity costs of producing one good in terms of the other. The PPF would also be bow-shaped when there is some other resource, or mix of resources with varying opportunity costs (E.g., different types of land suited for different uses). Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in markets. Macroeconomics is the study of economy-wide phenomena, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. These two branches of economics are closely intertwined, yet distinct – they address different questions.