Western Democracies Stumble: Post-War Issues & Depression
advertisement

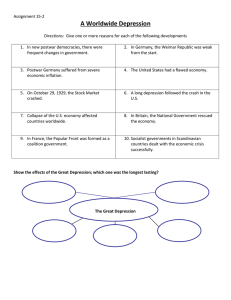
The Western Democracies Stumble 11.2 NOTES Standard and Objective 10.8.2 Understand the role of appeasement, nonintervention (isolationism), and the domestic distractions in Europe and the United States prior to the outbreak of World War II Objective- Students will understand the economic and social problems of Europe and the U.S. prior to WWII I. Politics in the Postwar World Western Democracies faced problems economically and socially Irish Republican Army(IRA) wins independence from Britain for most of the country The “Red Scare”- fear of communists, led to restricted immigration U.S., isolationism II. Postwar Foreign Policy France feared it border with Germany built the Magiont Line- fortifications Britain looked to relax the punishment of Germany France refused Kellogg-Briand Pactagreement for nations to not use war to get stuff Disarmament- reduction of armed forces, most reduced navies League of Nations weak, does not enforce policy III. Postwar Economies Britain-high unemployment, low wages led to a general strike in 1926 France recovered slowly Germany was hurt by repartitions U.S. booms IV. The Great Depression Why did it happen? Falling demand and overproduction Less demand-> factories cut back->more unemployed->less demand Financial crisis- risky borrowing, inflated stock prices, nervous panic U.S. puts up tariff other raised tariffs-> trade stood still Great Depression- painful time of global economic collapse V. The U.S. Reacts to Depression Pres. Herbert Hoover-no government interference in private business Pres. Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR)- introduces the “New Deal”- social and economic programs FDIC- protect bank investments Social Security- help for elderly Aid Farmers Work Programs New Deal failed to end depression but did ease the pain and pave road to recovery later Questions What does this cartoon think about the ideas of the new deal? Questions