hunting-malware-v4 - Tenable Discussions Forum
advertisement
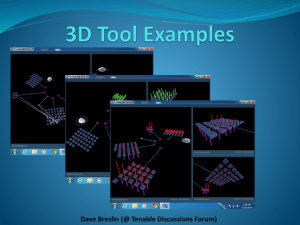
Leveraging Continuous View to Hunt Malware Why hunt for malware? Malware is another form of vulnerable software that has been introduced into your network. Hunting modern malware is much more about enterprise vulnerability and configuration auditing that traditional anti-virus agent based discovery. At one end of the spectrum, finding an open port can make you fail a compliance audit. On the other end of the spectrum, you can have a fully patched systems with a RAT, Trojan, botnet, .etc on it. Scanned services Traditional Vulnerability Management Config Unique Underlying Architecture Connectors for Complete Context Advanced Analytics Massive App Library Updated Daily. Unique Sensors 100% Asset Discovery Dashboard and Report Designer YOUR NETWORK • • • • Port Scans Botnet Malware System Tests • • • • Real-time Ports User Agents Network Logs DNS & Web Queries • • • • Netflow Process Logs Botnet Anomalies • 2D Dashboards • Data mining • 3D Visualization • Spreadsheets • Command Line Tools Topics • Sweet Orange • RedKit • ComFoo RAT • Zeus P2P • Neutrino • Tenable Botnet/Malware Detection Technology Sweet Orange Exploit Kit Hunting for IP Addresses http://www.malwaresigs.com/2013/07/30/malvertising-on-youtube-com-redirects-to-sweet-orange-ek/ URI associated with systems redirected to Sweet orange web pages List of IP addresses associated with Sweet Orange Create watchlist LCE has events (mostly from PVS) to these IPs Example URI from blog: Detected query with PVS: The sniffed URIs match URI !!! RedKit Indicators from May 2013 DHS Weekly Synopsis Product Are we hosting RedKit content? • Keyword search for PVS plugin 7039 • Generic SC searches for Nessus scan results Manual search of hosted URL/URI content in any Did someone query RedKit content? Search PVS logs: • • • Search LCE proxy logs Search PVS Web logs Search PVS & DNS logs Example Domain_Summary query Refine search to avoid generic match Comfoo RAT Secrets of the Comfoo Masters http://www.secureworks.com/cyber-threat-intelligence/threats/secrets-of-the-comfoo-masters/ • Look for failed credential Nessus scans • “ipnat” running in system logs PVS will log the queries and they can be discoverable as shown below. • Nessus web scan results – which ports? • PVS web scan sniffing results – all ports! • • PVS plugin 2 – client side usage PVS plugin 16 – outbound client side usage The detected port traffic on 1688 was bittorrent <custom_item> type: AUDIT_POWERSHELL description: "Comfoo Masters - ServiceDLL Check" value_type: POLICY_TEXT value_data: "(cmmos.dll|jacpet.dll|javadb.dll|mszlobm.dll|netfram .dll|netman.dll|ntdapie.dll|ntdelu.dll|ntobm.dll|odbm.d ll|senss.dll|suddec.dll|tabcteng.dll|vmmreg32.dll|wini nete.dll)” powershell_args : "Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\system\CurrentControlSet\Services\*\Param eters | select PSPath,ServiceDll | format-list" check_type : CHECK_NOT_REGEX powershell_option : CAN_BE_NULL </item> Search registry for evidence of Comfoo. <custom_item> type : AUDIT_POWERSHELL description: "Comfoo Masters - Find DLLs" value_type : POLICY_TEXT value_data : "" powershell_option: CAN_BE_NULL powershell_args: "get-childitem -recurse c:\ -include cmmos.dll,jacpet.dll,javadb.dll,mszlobm.dll,netfram. dll,netman.dll,ntdapie.dll,ntdelu.dll,ntobm.dll,odbm.dl l,senss.dll,suddec.dll,tabcteng.dll,vmmreg32.dll,wini nete.dll -erroraction silentlycontinue|select directory,name|format-list" </custom_item> Search file system for evidence of Comfoo. • • • • • 257 domain names Powerful command-line search associative-search.sh Searches DNS, MD5 & SSL https://discussions.nessus.org/ message/19698#19698 • Ran 1 hour to search all domain names across 6 months of data ZeuS-P2P http://www.cert.pl/PDF/2013-06-p2p-rap_en.pdf Infected computer has BOTH UDP and TCP ports open between 10,000 and 30,000 Manually finding systems with TCP and UDP ports between 10,000 and 30,000 is tricky. Filter on an asset list of IPs with UDP ports 10k to 30k for those IPs with TCP ports in the same range. Need to save a list of IPs with UDP 10,000 to 30,000 and then filter that list with a TCP filter of 10,000 to 30,000 These hashes were already part of the malware cloud database; i.e., Nessus or LCE Client would have found these. Neutrino A New Exploit Kit in Neutrino http://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/a-new-exploit-kit-in-neutrino/ Neutrino Take IPs from blog post and create a SecurityCenter watchlist named Neutrino Also Covered at MalwareSigs http://www.malwaresigs.com/2013/08/29/30-days-of-neutrino-domainsips/ Search for any hits in past 30 days and then do a port summary to see port 8000 activity. Extend search to 50 days and see some more activity. VirusTotal claimed the following DNS names were in use by Neutrino on various dates On Aug 5, we saw lots of queries for ifjtjdhcywssbhdxk.dyndns-mail.com recorded by the PVS. This DNS name was NOT on the list from the blog for Aug 5th nor any other day, but was very close. Differences in DNS names at VirusTotal and in “live” use can result from many things including variants and different behaviors based on where it is run. Tenable Botnet/Malware Detection Technology Tenable Botnet/Malware Detection Technology • Passive Web Traffic Analysis • Malicious Process Detection • Botnet Detection based on IP reputation PVS passively logs all DNS lookups, web queries and network traffic in real-time. This event indicates there have been nine web queries in the past 30 days which were related to known botnet activity. These are the nine queries, each one to a known malicious botnet or malware related site. Nessus scans identify malicious processes with cross-industry index of known bad hashes LCE Windows agents perform malware detection on all running processes. The LCE checks all IDS, login, netflow & PVS logs against a botnet reputation database Nessus checks systems for active botnet connections, settings and content Nessus also identifies systems running unique and unknown processes Each of these checks, and many others, is leveraged by realtime dashboards to identify malware