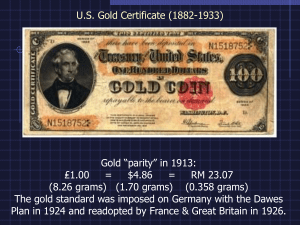
How did the Great Depression weaken Germany?
advertisement

How did the Great Depression weaken Germany? Learning objective – to understand the impact of the Great Depression on Germany. I can describe the main elements of the impact of the Great Depression on Germany. Grade D I can explain and make links between the different ways the Great Depression hit Germany. Grade B/C I can explain and analyse the impact of the Great Depression on Germany and can reach a substantiated judgement about its significance. Grade A/A* Starter This word cloud is in the shape of Heinrich Brüning, Chancellor of Germany between 193032. Choose three words, look out for them in the presentation and write why each word is significant in this lesson. How did the Great Depression affect Germany? Breakdown of democracy Fall in international trade Rise of extremism Failure of economic policies Social breakdown Why did events in America hit Germany so badly? How did Parliamentary democracy breakdown in 1930? By 1930, the government found itself with growing number of unemployed wanting benefit payments, but had much less tax to pay them with. In March, 1930 the coalition government could not agree on how to handle the crisis and resigned. No coalition could be formed. As a solution, Hindenburg appointed the new Chancellor, Heinrich Brüning, to govern with emergency powers under Article 48 of the constitution. The Reichstag was now bypassed and Germany was ruled by Presidential dictatorship. What was the impact of the Reichstag elections in 1930? To break the deadlock and to establish a united Reichstag, Brüning called an election in September. However, this backfired as the Nazis capitalised upon the fears and discontent of Germans and made significant headway winning 107 seats – making the Nazis the second largest party in Germany. The election only served to divide the Reichstag further and give the impression that democracy involved squabbling politicians over which job they would get in cabinet while doing nothing about the real problems. The Reichstag met fewer and fewer times. How did the rise of extremism impact upon German politics? People began to lose faith in the Weimar Republic and democracy itself. People wanted a ‘strong man’ in charge and saw the Weimar Republic as too weak. Both the Nazis and the Communists gained significant headway in the 1930 election. Both presented themselves as decisive groups outlining what they wanted to do – but not sharing HOW they were going to do it. With the growing extremism, there was growing political violence on the streets of Germany, contributing to a febrile and tinderbox atmosphere. Why were Brüning’s economic policies unpopular? Brüning decided to follow a tough economic policy, which meant – • Cuts in government spending. • Raising taxes. • Cutting wages. welfare Brüning urged Germans to make sacrifices and relied on Hindenburg to pass these measures. He felt a tough economic policy was needed in order to avoid hyperinflation. However, the policies did not stimulate the economy quickly enough and confidence continued to fall. How did the Great Depression impact upon German people? Unemployment spiralled to 5.6 million Rising starvation Farmers continued to do badly Businesses closed Banking crisis Revisiting the Starter Which words did you pick? Why were they significant in the lesson? Main activity Fill in the table with as much evidence as you can. This task will help you sort out evidence into clear sections and can help you structure an essay. Remember to make an overall judgement which is substantiated. Which impact do you think was the most important? Extension task Construct a timeline of key events in Germany between 1929 and 1932. Plenary – My Brain Subheading – My Brain Draw an outline of your brain. Fill your drawn brain with all the things you have learnt in this lesson. This can be in the form of key words, drawings, bullet points, lists – anything you like so long as it summarises your learning and that others can understand it.