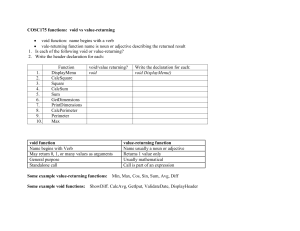
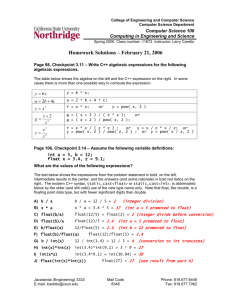
Unit 16 P1, M1, D1
advertisement
Procedural Programming
P1, M1, D1
UNIT 16 - Criteria
Procedural programming
• A list of instructions telling a computer, stepby-step, what to do, usually having a linear
order of execution from the first statement to
the second and so forth with occasional loops
and branches. Procedural programming
languages include C, C++, Fortran, Pascal, and
Basic.
Functions
• So far our programs have been fairly short, but as programs
become more sophisticated the number of lines of code
will increase to hundreds and thousands of lines of codes.
We need to have a way to break our program up into
manageable chunks (books are broken up into chapters,
organisations are broken up into departments, etc)
• Sometimes we wish to do the same thing in several
different places in our programs and we don’t want to have
to go and write the same code all over again (or even have
to use the editor copy and paste tools). Sometimes we
want to reuse a chunk of code we wrote for a previous job.
Sometimes we want to be able to break a program up into
chunks and get different people to write different bits and
then tie them together at a later date.
Example 1
Imagine a program where we want to show the same message to the user in several
different places in a program.
Enter your age : 11
**************
***thank you***
**************
Enter your height in metres: 1.64
**************
***thank you***
**************
Enter your weight in kilograms: 52
**************
***thank you***
**************
Code
#include <iostream.h>
void thankYou(void); // function prototype
void main ()
{
int
float
age; // variables to store age, height and weight
height, weight;
cout << “Enter your age: “;
cin >> age;
thankYou();
// call function
cout<<“enter your height in metres: “;
cin >> height;
thankYou();
// call function
cout <<“ Enter your weight in Kilograms: “;
cin >> weight;
thankYou();
// call function
} // end main
Void thankYou (void)
// function definition
{
cout <<“**************”<<endl;
cout<<“***thank you***”<<endl;
cout<<“**************”<<endl;
} // end thankYou
a) We have a function prototype, three
function calls in the body of main and a
function definition
b) The function name is “thankYou” ( you
can name it anything you want just like
variables but its best to name it
meaningful.
c) A function has a return type – in this case
it returns nothing so the type is void.
d) A function can have parameters, these
are specified in the brackets to right of
the function name – this function has no
parameters so we put void
Task 1
• Write a code calling or displaying Hello world
3 times from a function
Example - 2
Imagine program where we want to do the same calculation in several places, such as for
the paint program.
Enter Length 1: 12
Enter width 1: 5
Area of Side 1 = 60
#include <iostream>
Float SideArea (float a, float b); // function prototype
Void main ()
{
float Length1, Width1, Area1; variables to store the length width and area
cout<<“Enter Length 1 :”;
cin>> Length1
cout<<“Enter Width 1:”;
cin>> Width1;
Area1 = SideArea( Length1, Width1); // function definition
cout<<“the area of side one is:”<<Area1;
} // end main
Float SideArea (float a, float b)
{
float temp; // local variables to help with calculations
temp = a*b;
return temp;
} // end SideArea
a) This function has a float return
type
b) It has two parameters named
“a” and “b” = both are of type
float( you can give parameters
any name you want, like
variables.
c) It has a local variable (named
“temp”) within its definition.
Task 2
• Start creating the paint program and use
functions to calculate the area of each side of
the room.
Why modular programming?
• A programming style that breaks down program
functions into modules, each of which
accomplishes one function and contains all the
source code and variables needed to accomplish
that function.
• Modular programming is a solution to the
problem of very large programs that are difficult
to debug and maintain. By segmenting the
program into modules that perform clearly
defined functions, you can determine the source
of program errors more easily
D1
• Graphical Application:
– Think about the help access while playing games?