A Comparison Study on Copy-Cover Image Forgery Detection
advertisement

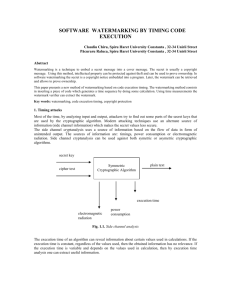
Sheng-Wen Peng 31004109 Introduction WATERMARKING FOR IMAGE AUTHENTICATION COPY-COVER IMAGE FORGERY DETECTION PCA Domain Method EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS Nowadays, due to rapid advances and availabilities of powerful image processing software, modifying the content of digital images becomes much easier with the help of sophisticated software such as Adobe Photoshop. a photograph of Lincoln's head was superimposed onto a portrait of the southern leader John Calhoun There are many ways to categorize the image tampering, and generally, we can tell that some usually performed operations in image tampering are: 1. Deleting or hiding a region in the image. 2. Adding a new object into the image 3. Misrepresenting the image information; to insert and splicing image part of the original image is the one of the most typical method. Watermarking is the popular way to counterfeit the forgery image. Digital watermarking is the process of embedding information into a digital signal which may be used to verify its authenticity or the identity of its owners. There are several characteristic of watermarked image: 1. Robustness 2. Perceptibility 3. Capacity 4. Embedding method The digital watermark, unlike the printed visible stamp watermark, is designed to be invisible to viewers. The bits embedded into an image are scattered all around to avoid identification or modification. Therefore, a digital watermark must be robust enough to survive the detection, compression, and operations that are applied on. However, watermarking techniques have some drawbacks. Fragile watermark is not suitable for such applications involving compression of images, which is a common practice before sharing images on the Internet. The copy-cover technique is the most popular technique for making image forgery. Copycover means that one portion of a given image is copied and then used to cover some object in the given image. Several researchers have explored the copycover image forgery detection. Popescu and Farid used the PCA domain representation to detect the forged part, even when the copied area is corrupted by noise. Principal components analysis (PCA) is known as the best data representation in the leastsquare sense for classical recognition [16]. It is commonly used to reduce the dimensionality of images and retain most information. The idea is to find the orthogonal basis vectors or the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix of a set of images, with each image being treated as a single point in a high dimensional space. Xq = PX For forgery detection, we create an image database composed of 500 images for use in our experiment. 1. Given image loading 2. Convert the image given into gray scale image. Let N be the total number of pixels Let b denote the number of pixels in a square block Using PCA 3. Find the eigenvectors and eigenvalues. 4. Sort the eigenvalues in decreasing order and also the eigenvectors. 5. Compute the projections of the centered testing gram matrix on the ordered eigenvectors (decreasing order of eigenvalues). 6. Lexicographically sort the projected version of the centered testing gram matrix. Let it be denoted by S. 7. For every ith rows i in S, select a number of subsequent rows, sj such that |i-j|<=Rth and place all the pairs of coordinates (xi,yi) and (xj,yj) on to a list P_in. 8. Compute offset for each row of P_in. 9. Compute the frequency offset. 10. Those rows in P_in which have high frequency offsets are the duplicated regions Frank Y. Shih* and Yuan Yuan ‘’A Comparison Study on Copy-Cover Image Forgery Detection’’ 2010 Digital Watermarking from Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_waterm arking Principal component analysis from Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Principal_comp onent_analysis Prem Kumar ‘’Digital Image Forensics (Copypaste forgery detection)’’ 2010