Measurement
advertisement

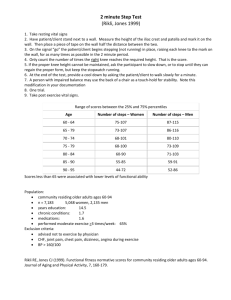
Chapter 2 …Measurement Why measure? • Without measurement, how can you reliably assess progress in… – Learning? – Recovery? – …or even assess current performance strengths and weaknesses? • Idea behind this bit is to introduce some assessment methods used in motor learning and performance Two measures of performance • Performance outcome measures – FG%; QB rating; Time for 40m dash – Result only – do not indicate movement used to achieve the result • Performance production measures – Joint angle changes, position-time graphs, EMG traces – Focus on descriptors of the movement used to achieve the result • See table 3.1, p. 24 Performance outcome measures • Reaction time – Time from presentation (“onset”) of stimulus to the start (“initiation”) of the movement • Initiation refers to observed or measured physical movement, and is usually particular to the measurement device • Example: – 100m sprint Performance outcome measures • Reaction time Warning signal “Go” signal Initiation of response Termination of response Fore period Time Reaction time Movement time Response time Performance outcome measures • Reaction time (RT) – 1 signal, 1 action: simple RT – More than 1 signal, more than one action: choice RT – More than 1 signal, only one requiring a response: discrimination RT Performance outcome measures • Reaction time (RT) – Fractionated (with EMG): • Pre-motor Time: Perceptual & cognitive processes • Motor Time: Muscle vs. inertia Performance outcome measures • Error Scores – Who is best? A. B. C. Performance outcome measures • Error Scores – Who is best? • Depends on whether you’re talking about Accuracy Bias Consistency Performance outcome measures • Error Scores – 1-dimensional versions – Accuracy – absolute error (AE) • Average of positive deviations from the target Thrower Throw attempts So AE = the average length of these lines Target line Performance outcome measures • Error Scores – 1-dimensional versions – Bias – constant error (CE) • Average deviation (+/- both count) Thrower So CE = average position – either a “bit” short or a “bit” long Throw attempts Target line Performance outcome measures • Error Scores – 1-dimensional versions – Consistency – variable error (VE) • Grouping - how close are throws to each other? Thrower So VE = clustering Throw attempts Target line Performance outcome measures • Error Scores – 2-dimensional versions – Radial error & others • Same general thing, but computationally more tricky – similar concepts of bias, consistency, and accuracy Accuracy Bias Consistency Performance outcome measures • Error Scores – continuous skills – Root-mean-square-error (RMSE) • Like a longer version of AE Target line Path taken The RMSE is roughly the average length of all the vertical lines Performance production measures • Kinematics 3-d reconstruction of joint angles Performance production measures • Kinematics Position-time plot Performance production measures • http://www.usc.edu/dept/LAS/kinesiology/exsc408l/powerpoint/sldaniela/complete/sld001.htm Performance production measures • http://www.usc.edu/dept/LAS/kinesiology/exsc408l/powerpoint/sldaniela/complete/sld001.htm Velocitytime chart Performance production measures • http://www.usc.edu/dept/LAS/kinesiology/exsc408l/powerpoint/sldaniela/complete/sld001.htm Angle-angle diagram Performance production measures • Our diagrams – both for a free throw at basketball Performance production measures Elbow Extension Knee 1 8 6 3 4 Knee 5 7 2 Flexion Flexion Elbow Extension Joint angle (radians) 3.5 3 2.5 2 Elbow - FT Knee - FT 1.5 1 0.5 0 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 Ball release Time 2.9 Knee (radians) Position-time plot Finish 2.4 Start Angle-angle diagram 1.9 0.5 1 1.5 2 Elbow (radians) 2.5 3 Summing up… • Go over those last few slides enough times to allow yourself to “get it”…if you still don’t, then try mapping out a few movements yourself, or move on to the online discussion. • OK?