The PowerShell + AD management notes can
advertisement

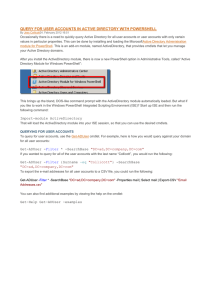
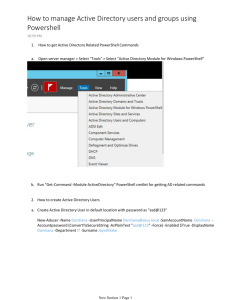
Managing Active Directory with PowerShell JOSEPH MOODY Starting Tips for PowerShell Use PowerShell ISE. Script pane on top + Console on bottom How to Use Help ◦ Get-Help Get-ADComputer -full ◦ Get-Help Get-ADUser –examples ◦ Select cmdlet – press F1 Some examples will span multiple lines – when typing them, type them as a single line. Staying Up to Date Update PowerShell: Current version is 4, 5 to be released in August. ◦ $PSVersiontable will show you your current version. ◦ Install latest Windows Management Framework to update PowerShell. If you are on at least version 3, you are good for today. Update your Help on 1st use by running update-help. ◦ Create a monthly update task. ◦ Must be ran as an administrator Methods of Management Two Modules for Active Directory Management ◦ Default Active Directory Module ◦ Quest AD Module AD Module: ◦ 2008 R2 + domain, cmdlets are verb-ADnoun ◦ import-module ActiveDirectory Quest Module: ◦ requires 3rd party software, cmdlets are verb-QADnoun ◦ Add-PSSnapin Quest.ActiveRoles.ADManagement Exploring with PowerShell Get-Command –Module ActiveDirectory (Get-Command –Module ActiveDirectory).Count Or use the Command Add-On ◦ View – Show Command Add-On ◦ Filter module to Active Directory – filter name for search Exploring Active Directory Verbs Nouns Add Reset Computer Disable Set Group Enable Unlock GroupMember Get Move New Remove Rename OrganizationalUnit User Getting Information from AD Get-ADComputer GAMCN01 ◦ PowerShell assumes GAMCN01 is the value for –identity Get-ADComputer GAMCN01 -Properties * ◦ We can now filter off of these properties Get-ADComputer -filter 'Name -like "GAMCN*"' Get-ADComputer -filter 'Enabled -eq "false"' ◦ -eq, -ne, -like, -notlike Selecting, Sorting, and Exporting Three cmdlets to know: ◦ Select-Object: alias is select ◦ Sort-object: alias is sort ◦ Export-CSV All use Piping (|) or input from variables. Pipe symbol is shift + backslash. Ex: get-process notepad | stop-process Selecting Properties Get-ADComputer -filter 'Name -like "GAMCN*"' | select-object Name Get-ADComputer -filter 'Name -like "GAMCN*"' | select name,OperatingSystem ◦ Why is the OperatingSystem row blank? Get-ADComputer -filter 'Name -like "GAMCN*"' -Properties OperatingSystem | select name,OperatingSystem Sorting Properties Get-ADComputer -filter 'Name -like "GAMCN*"' -Properties PasswordLastSet | select name,PasswordLastSet ◦ What column are we sorted by? Get-ADComputer -filter 'Name -like "GAMCN*"' -Properties PasswordLastSet | select name,PasswordLastSet | Sort-object PasswordLastSet Exporting Data Get-ADComputer -filter 'Name -like "GAMCN*"' -Properties PasswordLastSet | select name,PasswordLastSet | Sort-object PasswordLastSet | export-csv .\Computers.csv ◦ -append ◦ -notypeinformation Troubleshooting Tip: If a script like the one above doesn’t work, test each part independently. Creating New Objects Find out what your computer name is – write down your station number (ex: N01) New-ADComputer requires four parameters: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Name SAMAccountName Path (OU Location) Enabled Status New-ADComputer -Name “Test-N01" -SamAccountName “Test-N01" -Path "OU=PowerShell,OU=UnAssigned,OU=Domain Sites,DC=GCBE,DC=local" -Enabled $True Variables to Know: $True, $False, $Null Modifying with Set Objects can be modified by piping results from a get command to a set command ◦ Syntax example: Get-ADComputer | Set-ADComputer ◦ Use the command add-on to view the Set parameters Get-ADComputer -Identity Test-N01 | Set-ADComputer -Location "Brunswick,GA" Now use Get-ADComputer and verify the location is set. Whatif parameter is your friend! Use it when making mass changes to test. Get-ADComputer -Filter 'Name -like "Test-N*"' | Set-ADComputer -Location "Brunswick,GA“ – whatif Disable and Tag - Lab Use the Get command to Find Your Test Computer. Disable Your Test Computer’s AD Account Set the Computer’s Description to the Current Date ◦ Hint: (Get-Date) In a live environment, you would move these disabled computers into a dedicated OU. Examples Most of these examples use the Quest AD cmdlets. This module can be downloaded or you can substitute the normal AD cmdlets. 1. Cleaning Up Stale AD Accounts 2. Creating New Users 3. Renaming Computers 4. Updating Groups