File
advertisement
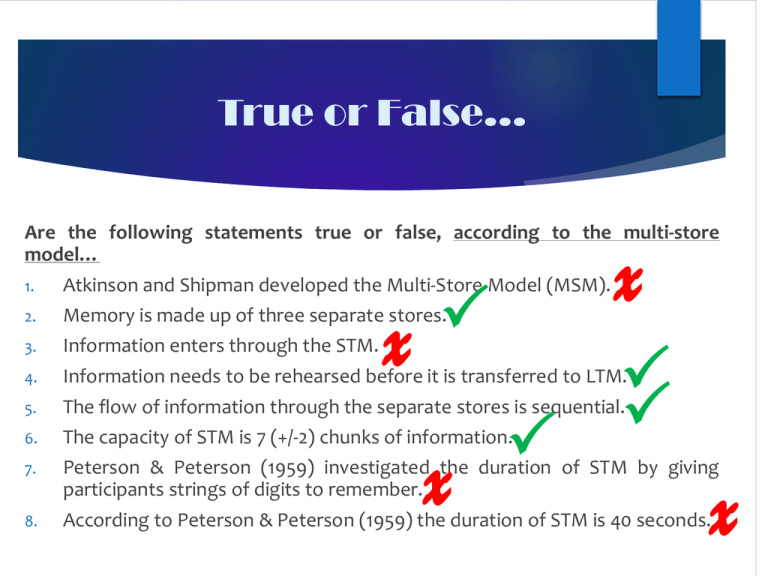
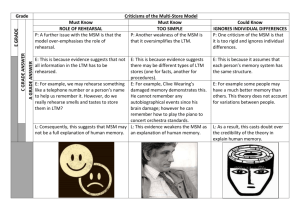
True or False… x Are the following statements true or false, according to the multi-store model… 1. Atkinson and Shipman developed the Multi-Store Model (MSM). 2. Memory is made up of three separate stores. 3. Information enters through the STM. 4. Information needs to be rehearsed before it is transferred to LTM. 5. The flow of information through the separate stores is sequential. The capacity of STM is 7 (+/-2) chunks of information. 6. x P x P P P x 7. Peterson & Peterson (1959) investigated the duration of STM by giving participants strings of digits to remember. 8. According to Peterson & Peterson (1959) the duration of STM is 40 seconds. Duration of LTM Task – Identify the aim, method, results and conclusion of Bahrick et al. (1975). Tested 400 US grads on their memory for former classmates photos, years later, by getting them to match names to photos. 90% accuracy for remembering faces & names 34 years after graduation. Investigate the duration of LTM. Memories stored in LTM can last a life time! Evaluating the Multi-Store Model You MUST be able to state BOTH the strengths & weaknesses of the model. Strengths of the MSM Case Studies – Clive Wearing, Milner Laboratory Evidence Brain Scans? Case Studies Clive Wearing Clive Wearing Some of the strongest evidence for a separate STM and LTM comes from patients who have suffered brain damage. Loss of memory is usually selective – it affects one type of memory but not another. What type of memory is impaired for Clive Wearing? Does this provide support for Atkinson & Shiffrin's (1968) Multi-Store Model? Why? Clive Wearing The Case of Clive Wearing, Part 1a The Case of Clive Wearing, Part 1b Laboratory evidence Duration of STM Peterson & Peterson (1959) Duration of LTM Bahrick (1975) Capacity of STM Miller (1956) 7 (+/- 2) Brain scans Bran scans have shown different areas of the brain are activated when people perform STM and LTM tasks. Weaknesses of the MSM Flashbulb Memories Case Studies - KF Flashbulb Memories What’s the difference between the following memories? The two memories below are written response to the question: “How did you first hear the news of the Challenger disaster?” Memory 1: Written in the fall of 1988, long after the event by an Emory Senior, called RT. It was a vivid recollection for which RT rated it 5 out of 5 for her confidence in it’s accuracy. Memory 2: Was written by RT two and a half years earlier, just 24 hours after the Challenger disaster…. Flashbulb Memories REHEARSAL is central to MSM but there is lots of evidence to suggest that you do not always need to rehearse information for it to be passed into LTM. Can you think of examples? “Flashbulb Memory” Where highly emotional, shocking events (e.g.9/11) go into LTM with NO rehearsal. Case Studies Patient KF (Shallice & Warrington, 1966) Brain injuries after a motorcycle accident. He could recall stored information SO his LTM was intact; But his STM was affected, he had problems remembering sounds but he was able to remember images and faces. So what does this suggest about our STM? Essay Questions… Outline and evaluate the multi-store model of memory. (12 marks). Outline (A01) Evaluation (A02) Discuss: Sensory Memory (Capacity, Duration, Encoding) Short-Term Memory (Capacity, Duration, Encoding) Long-Term Memory (Capacity, Duration, Encoding) 2x Strengths and 2x Weaknesses: Strengths include: Clive Wearing Laboratory Evidence The processes involved, i.e. attention, rehearsal etc. and how information flows through the model. Weaknesses include: Flashbulb Memories Patient KF Oversimplified Be clear on why the above are either strengths of the MSM or limitations. Conclusion: In terms of the strengths and weaknesses do you think the MSM is a good or bad model of memory. Essay Questions… Outline and evaluate the multi-store model of memory. (12 marks). 6 marks for outlining the model (A01). A drawing is acceptable but should be accompanied by a description of how information flows through the model and what happens to it. Remember to describe the essential processes of attention and rehearsal. Descriptions of the stores should focus on their capacity, duration and encoding. To get full marks, outline must be detailed and accurate. Evaluation 6 marks for evaluating the model (A02). Good advice would be to choose 4 evaluation points (2 strengths and 2 weaknesses) and describe them well making sure you explain exactly how they either support the model or are a problem for it. Marking… Mark the students answer to Outline and evaluate the multi-store model of memory (12 marks). Highlight the A01 and A02. Give each section a mark and justify your mark. State what went well (WWW) and even better if (EBI)