11_decisionmaking_fall09
advertisement

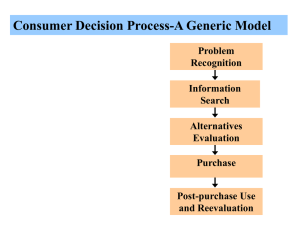
Decision Making Decision Making How do you make purchase decisions? What factors affect your decision? What strategies do you use? Outline your decision making process for a significant product/service you recently purchased How does Decision Making relate to other aspects of CB? What was it? How much did it cost? Where did you buy it? When did you buy it? Why did you buy it? Was anyone with you when you made the purchase? Do you know anyone who used/owned the product before you made your purchase? How important is this product to your lifestyle? At the time of this purchase, was there another product which you seriously considered buying instead of the item selected? What circumstances led to your realization that you should buy the item purchased? Did you purchase the item at the first store visited? Why did you buy at the particular where you made the purchase? 3 Perspectives on Consumer Decision Making 1. 2. 3. Experiential perspective Behavioral perspective Decision making perspective Next day Focus of today Decision Making Perspective SITUATIONS Problem Recognition Rational, informationprocessing approach Move through stages in a linear fashion Information Search Alternative Evaluation Product Choice Postpurchase Processes SITUATIONS Purchase vs. Product Involvement In groups, tell me… The difference? Situations where product involvement is high and purchase involvement is low. Situations where purchase involvement is high and product involvement is low. Why this matters in studying decision making? Involvement and Decision Making Purchase Involvement is: the level of concern for, or interest in, the purchase process triggered by the need to consider a particular purchase is a temporary state not the same as Product Involvement Continuum of Buying Decision Behavior Step 1: Problem Recognition 1st stage of consumer decision process Definition: Is the result of a discrepancy between a desired state and an actual state that is sufficient to arouse and activate the decision process Actual state – how you perceive your situation right now Ideal state – the way you want to feel or be at the present time Activating Problem Solving In groups of 3 or 4 figure out the following… How would you activate problem solving in the following… United Way blood drive (increasing donations) Dixon Recreation Center (increasing activity) A healthier diet Step 2: Information Search Information sources Internal information Actively acquired Past searches Personal experience External information Passively acquired Lowinvolvement learning Actively acquired Independent groups Personal contacts Marketer information Experiential Discussion Choosing a brand/product among available alternatives requires much of the effort that goes into a purchase decision. Which is the greater problem for a consumer: Not having enough choices or having too many choices? Why? Step 3: Identifying Alternatives Evoked, inert, inept: Beer? Toothpaste? fast food? Describe your next car! Characteristics of this car, not just brand What about… 35-year-old couple, both working professional jobs with 5 preteenage children 55-year-old bank president Or Or 30-year-old married, no children, female, school teacher How would you make the decision to buy? Step 4: Product Choice Evaluative criteria: dimensions used to judge merits of competing options Evaluative Criteria Beer Identify brands of beer. What are your evaluative criteria for beer? Type? Importance? Evaluative Criteria Perceptual Mapping of Beer Brand Perception How do you decide? Several alternatives, how do you decided which is the right one for you? Attribute Based Decision Rules 5 decision rules: 1. Conjunctive Non-Compensatory 2. Disjunctive & 3. Elimination Low-involvement 4. Lexicographic 5. Compensatory Compensatory & High-involvement Attribute Based Decision Rules: Noncompensatory Conjunctive: • Set minimum criteria level for each attribute • Eliminate alternatives that do not meet that criteria Disjunctive: • Set minimum criteria for each important attribute • Only accept alternatives that exceed this minimum level Elimination- by aspects: • Determine the importance of attributes • Compare alternatives on the most important attribute • Those not meeting the minimum criteria are eliminated • The next most important attribute is considered Lexicographic: • Consumers determine the most important attribute and select the brand that performs best on that attribute Attribute Based Decision Rules Compensatory: • a high level on one attribute can offset or compensate for low values on other attributes -- high values compensate for poor performance Example: basketball game ticket packages -Seat selection – extremely important -Price – less important Step 5: Postpurchase Processes Postpurchase Dissonance: The doubt or anxiety associated with a purchase Based on cognitive dissonance theory Describe a recent purchase that produced postpurchase dissonance and one that did not. What factors led to these postpurchase processes? Characteristics of the Situation Likely to Contribute to Postpurchase Dissonance Degree of irrevocability Importance to the consumer Difficulty of choosing among alternatives Individual’s tendency to experience anxiety How do consumers attempt to avoid anxiety before a purchase? Avoid the decision Delay the decision Use a purchase decision rule to minimize regret How can Consumers Reduce Postpurchase Dissonance? Increase desirability of brand or product purchased Decrease desirability of rejected alternatives Decrease perceived importance of the purchase Reverse the purchase (return the item) Think about How can marketers improve consumer decisions?