Knowledge Construction Chapter 7
advertisement

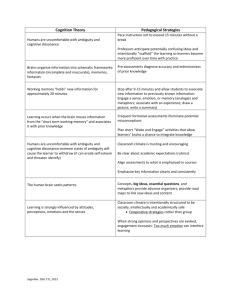
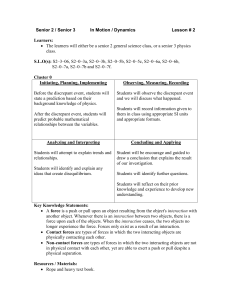
Knowledge Construction Chapter 7 Constructive processes in learning and memory Individual Constructivism: Storage • Influenced by Individual Constructivism: Retrieval • Combining partial information with general knowledge, assumptions about the world – leads to reconstruction errors Social Constructivism • Meaning is jointly constructed – two or more people at the same time • distributed cognition – by groups or cultures over time • science, literature, art Organizing knowledge Concepts • Mental grouping of similar events, objects, ideas, or people • “Smallest units of thought” • Can be concrete (dog) or abstract (noun) • Learned through experience (dog) or direct instruction (noun) Schemas & Scripts • Schema • Script • Influenced by culture Theories • Integrated sets of concepts & principles to explain particular phenomena • “Naïve theories” constructed by individuals Worldviews Promoting effective knowledge construction General Strategies • Provide opportunities for observation, experimentation • Present experts’ perspectives • Emphasize conceptual understanding • Encourage classroom dialogue • Assign authentic activities • Scaffold theory construction • Create a community of learners When knowledge construction goes awry: Addressing learners’ misconceptions Misconceptions • Beliefs inconsistent with accepted and well-validated explanation – world is flat (k-2) – plants “eat” soil, fertilizer (Grades 3-5) – division always leads to smaller number (Grades 9-12) • Individually, culturally constructed • Can inhibit new learning Promoting Conceptual Change • Identify misconceptions before instruction begins • Look for, build on elements of truth in students’ existing understandings • Convince students that existing beliefs need revision • Motivate students to learn correct explanations • Preserve students’ self-esteem; do not ridicule them for misunderstandings • Monitor students for persistent misconceptions Diversity in constructive processes Factors Influencing Constructive Processes • Individual student knowledge • Student core beliefs – culture, religion • To encourage learning: – expose students to diverse perspectives – develop community of learners – accommodate students with special needs The big picture The Big Picture • Learners construct knowledge on their own & in collaboration with others. • Learners integrate what they learn to make generalizations. • Learners’ constructions are sometimes productive and sometimes counterproductive.