Race Ethnicity and Language Workgroup
advertisement

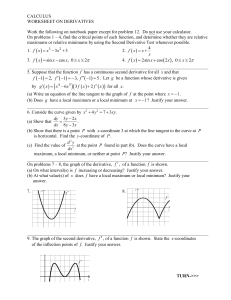
April 4, 2012 Indiana Joint National Public Health Week Conference What is standardized REL data? Specific method of collecting, recording and reporting REL data that is the same across all areas (uniform questions and categories) REL data is reported by the individuals served (“self-reported”) or their families and/or caregivers Standardized method collects, records, stores and reports REL data that is accurate, comparable, and consistent (electronic vs. manual) Develop strategy to prepare, implement, monitor and sustain adherence to standardization guidelines What is the rationale? To make certain all individuals served receive high-quality care To identify and reduce disparities To provide culturally and linguistically appropriate services and materials To ensure equitable access to health care To develop quality improvement programs To comply with regulations National Movement for REL Data Collection American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) 2009 requires hospitals and providers to collect REL data as part of the eligibility for meaningful use payments Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 requires health care programs that receive federal funds to collect REL data Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 requires agencies that receive federal funds must provide interpretation to individuals with Limited English Proficiency Joint Commission requires hospitals to collect race, ethnicity, and preferences for spoken language and written information U.S Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Minority Health, National Partnership for Action to End Health Disparities Goal #5 Research and Evaluation – improve coordination and utilization of research and evaluation outcomes REL Workgroup • Purpose • Explore current methods of race ethnicity data collection and make recommendations to state and local agencies about the collection of race ethnicity data • Goal • Standardize collection and reporting of race ethnicity data across the state Literature Review Race and ethnicity are not genetic but rather social constructs that evolve over time Broad racial groups do not adequately describe diversity of population Collection of socio-economic information is important Evidence supports inclusion of Hispanic Latino category within the race question Race ethnicity data collection is dynamic Community Input Obtain feedback from the community through focus groups REL workgroup developed focus group script to understand what people think about race, ethnicity and language questions asked in a hospital or clinic Focus Groups Twelve focus groups conducted with 124 participants Selected counties in Central, Northern and Southern regions of Indiana Languages English and Spanish Participant demographics Age Gender Race/Ethnicity Educational attainment Focus Group Demographics Focus Group Participants by Age Group 16.7 6.9 18-24 15.7 25-34 35-44 11.8 45-54 55-64 65+ 17.6 31.4 Focus Group Demographics Focus Group Participants by Gender 35.3 Female Male 64.7 Focus Groups Demographics Focus Group Participants by Race/Ethnicity Black, NonHispanic 29.1 American Indian, Non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander, NonHispanic 46.6 4.9 12.6 6.8 White, NonHispanic Hispanic Focus Groups Demographics Focus Group Participants by Educational Attainment Elementary school 12.6 Some high school 35.0 19.4 15.5 17.5 High School Graduate/GED Some college or technical school (13years) College graduate (4 or more years) Highlights When asked about the benefits of collecting REL information: Many participants indicated REL data in health care will help to provide culturally competent care Majority of participants reported it is important to ask REL questions in hospital or clinic to make certain that appropriate care and services are provided Many participants would like to report this information on paper rather than verbally When asked getting reassurance that the REL information will not affect health care Majority racial/ethnic minority participants indicated that it is very to extremely important that they receive reassurance that REL data will not affect health care When asked about collecting race and ethnicity information: Some participants expressed concern, suspicion and lack of trust about the collection of race/ethnicity data reporting that this information would negatively impact on care When asked about collecting language information: Majority of participants were not concerned about the collection of data on language REL data collection projects National: Aligning Forces for Quality and Hospital Quality Network projects funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Health and Human Services, Office of Minority Health REL project State Indiana Hospital Association planning to roll-out REL project statewide Regional Central Indiana Alliance for Health project funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Next Steps Disseminate Engage Recommend Adapt Restructure Implement Questions Thank you Thank You Adrienne Durham, MPH Health Disparities Epidemiologist Indiana State Department of Health Epidemiology Resource Center 2 North Meridian Street Indianapolis, IN 46204 317.233.7895 Fax 317.233.7805 adurham@isdh.IN.gov Chandana Saha, PhD, MPH Research Associate Indiana Minority Health Coalition 3737 North Meridian Street, Suite 300 Indianapolis, IN 46208 317.920.4011 Fax 317. 926.4012 c.saha@imhc.org