Developing an Individual Education Plan
advertisement

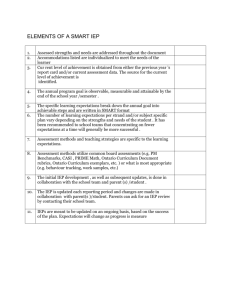
Developing the Individual Education Program (IEP) Be an advocate Be involved Be knowledgeable The Law and the IEP • Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA (1990) and the Reauthorization of IDEA, (1997 & 2004) requires that all children with disabilities, eligible for special education services, must have an IEP. • Physical Education is a direct service required by law. Definition • The Individualized Education Program (IEP) is an educational plan of action or guide for teachers to assist students with disabilities in their education. . • Physical Education participation is determined by need based on an assessment. The Referral • Physical Education Teacher • Subject area teacher • Child Study team or special services team • Administrator • Parent • School nurse The Individual Education Program Part One: The meeting with with parents, and school personnel who jointly make decisions about a child’s educational program. Part Two: A written document that describes the decisions reached at the meeting. Actions to Get involved in the IEP Process • Contact the classroom teacher • Contact the school administrator • Contact the IEP committee chair or special education director • Collaborate with other professionals • Attend the IEP meeting • Speak to parents IEP Document Components • Present Level of Performance assessment of skills, fitness or behavior • Measurable Goals – annual and short term • Services provided to meet the goals • Progress report Present Level of Performance • Present levels of skill and fitness achievement and functional performance are objective data acquired from a variety of assessments. • Describes the student’s level of performance on motor skills and/or fitness or behavioral needs if applicable. • Provides a baseline for future assessment. Assessment information • School Records – Performance in previous Physical Education classes. • Standardized skill tests -TGMD -2 , APEAS II • Fitness tests – Brockport, APEAS II or Fitnessgram • Teacher Constructed Tests – Skill or fitness Can be Qualitative and/or Quantitative. • Observations –Skills or behavior report Developing Goals • Goals are based on the results of the assessment data. • Annual goal for improvement. – What the student will achieve in one year. • Formative goal. – Short term goals or benchmarks that are determined for achievement to meet the annual goal. Use SMART Goals Specific – action defined Measurable – criteria and rubric Achievable – lead to success Realistic - meaningful Time – length of time is determined Measurable Goals Include: • The action (what?) • The conditions under which the action should occur (how?) • A criterion for mastery of a specific task (at what level?) How fast, how far, how many, maturity of form. Goal Example • The student will be able to run 1 mile in 10 minutes and 30 seconds. • Action = Run • Condition = 1 mile • Criteria = 10 minutes 30 second Develop goal related activities • What activities will you develop that will help the student achieve the set goals? • Activities should be curriculum related. • Activities can focus on life long learning. • Activities should address the NJ Core Content Standards for Health and Physical Education. • Developmentally appropriate. Goals for Elementary Level are based on: • • • • • • • Locomotor skills Manipulative skills Body awareness Spatial awareness Balance Strength Aquatics, Games and dance Goals for Secondary Level are based on: • • • • • • Sport skills and Game Play Physical Fitness Aquatics Lifetime activities Community-based activities Dance Ongoing data collection • How will you record progress toward the goal?. • Use report forms, anecdotal notes, test forms, student journal writing, conferences. • What is the frequency of recording? . Determine Services • Placement (where) GPE, or Segregated PE or a combination • Schedule of services (beginning and end dates, how often) • Program modifications, (equipment, assistance) Annual Progress Report • Written documentation of tests and observations that address the goals. • Test results Pre and Post • Formative assessments that address the goals. Progress Report • Teacher maintains a written anecdotal record of his or her observations. What is the student able to do, what is difficult for the student and what observable evidence supports your claim? • Report includes standardized or teacher constructed tests and results. • Description of report frequency. • Recommendations.