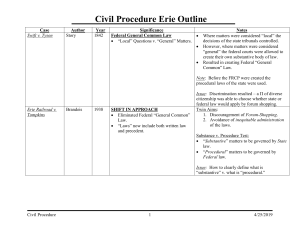
law_pp_6
advertisement
+ Categories of Law + International Law Laws that govern the conduct between independent nations. Generally created by customs. Some organizations also have international legal status United Nations – Universal Declaration of Human Rights. UN peacekeepers, the ‘blue helmets’, go to warring nations to help restore peace. International Court of Justice (ICJ) – based at The Hague in the Netherlands. Hears disputes amongst member nations and their government. + Domestic Law Law’s made within a nation’s borders (case and statute law) Two Sections – Substantive Law and Procedural Law The Law International Law Domestic Law Substantive Procedural + Substantive Law Defines the rights, duties, and obligations of citizens and levels of governments. Includes the right to own and protect property, to enter into a contract and seek remedies if the contract is broken. Procedural Law The law that prescribes methods of enforcing the rights, duties, and responsibilities found in substantive law. Includes the gathering of evidence, following the legal requirements to a lawful arrest, and adhering to correct trial procedures. + Public Law A category of substantive law regulating the relationship between the government and its citizens. Constitutional Law – basic laws, principles, and standards all other laws must adhere to. Administrative Law – Most influential in the everyday lives of Canadians. Law related to the relationship between people, government departments, boards and agencies. Criminal Law – Law that identifies crimes and prescribes punishment. These crimes are described in the Criminal Code of Canada and other statutes. + The Law International Law Domestic Law Substantive Public Law Constitutional Law Administrative Law Procedural Private Law Criminal Law + Private Law Law that deals with the legal relationships between individuals and individuals/organizations (not including the government). The main purpose is to compensate people who have been harmed by the wrongful acts of others. Tort: law that holds people responsible for damage they cause another person as a result of accidental or deliberate action Contract: provides rules regarding agreements between people and businesses. Family: deals with various aspects of the family (marriage, property division, custody, child support, divorce). Wills and Estates: concerned with the division and distribution of property after death. Property Law: governs ownership rights in property (ownership and transfer). Employment Law: governs employer-employee relationships. + The Law International Law Domestic Law Substantive Procedural Public Law Constitutional Law Administrative Law Criminal Law Private Law Tort Law Family Law Contract Law Property Law Wills and Estates Employment Law