Using the Framework for Teaching to Support Effective Teacher
advertisement

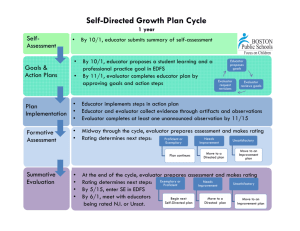
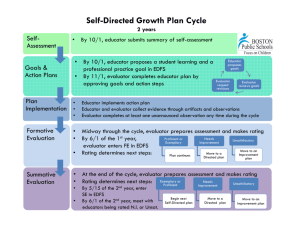
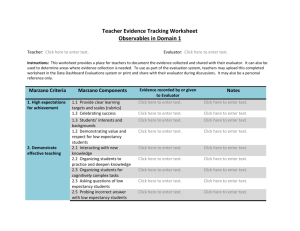
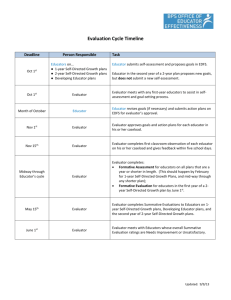
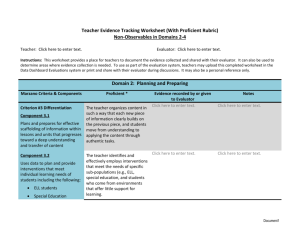
USING THE FRAMEWORK FOR TEACHING TO SUPPORT EFFECTIVE TEACHER EVALUATION Mary Weck, Ed. D Danielson Group Member Domain Focus Domain 1 – Planning and Preparation Domain 2 – The Classroom Environment What a teacher knows All aspects of and does in teaching that lead to a preparation for culture for learning in the classroom. teaching. Domain 4 – Professional Responsibilities Professional responsibilities and behavior in and out of the classroom. Domain 3 – Instruction What a teacher does to engage students in learning. Framework Vocabulary - p. 3 4 Domains 22 Components 76 Elements Priorities of the FfT Cognitive Engagement “Proficient” = students must be engaged cognitively. “Distinguished” = cognition, meta-cognition, and student ownership of their learning. Constructivist Learning Proficient practice must have evidence of learning experiences designed to facilitate students construction of knowledge. A Framework for a career… • Novice Initial Teaching Certification • Master Teacher National Board Certification Levels of Performance 6 Levels of Performance Unsatisfactory – Teaching shows evidence of not understanding the concepts underlying the component - may represent practice that is harmful - requires intervention Levels of Performance Unsatisfactory – Teaching shows evidence of not understanding the concepts underlying the component - may represent practice that is harmful - requires intervention Basic – Teaching shows evidence of knowledge and skills related to teaching - but inconsistent performance due to lack of experience Levels of Performance Proficient - Teaching shows evidence of thorough knowledge of all aspects of the profession. Students are engaged in learning. This is successful, accomplished, professional, and effective teaching. Levels of Performance Proficient - Teaching shows evidence of thorough knowledge of all aspects of the profession. Students are engaged in learning. This is successful, accomplished, professional, and effective teaching. Distinguished – Classroom functions as a community of learners with student assumption of responsibility for learning. (Based on research for NBPTS) Evaluation as an intervention to improve student achievement ESEA views teacher evaluation as an intervention to improve student achievement “Addressing gaps in access to teacher quality is the most critical element of a successful education reform agenda….students whose initial achievement levels are comparable have vastly different academic outcomes as a result of the sequence of teachers to which they are assigned… ” (Peske, Haycock, 2006) RESEARCH FINDINGS: Cincinnati’s Use of the Framework for Teaching Teachers have substantial effect on student achievement Correlation between evaluation using the FFT and student achievement Evaluation using the FFT found: Unsatisfactory and basic: students had lower gains than expected (based on test scores from previous years) Proficient: students made expected gains Distinguished: students made positive gains IDENTIFYING EFFECTIVE CLASSROOM PRACTICES USING STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT DATA , National Bureau of Economic Research, 2010 Therefore… …. Quality teaching = improved student learning ESEA / RTTT emphasizes teacher evaluation models that emphasize feedback to improve learning and growth, and the use of research based criteria to assess teacher effectiveness Evaluation Process Basis for evaluation • Quality of work – Standards of Practice • Student progress • Professionalism Plan for gathering data • Processes and procedures for gathering information about quality of work • Procedures for gathering information about student progress • Information about professionalism End result • Rating • Direction for professional growth • Determination of Employment • Money • Other Evaluators Role Basis for evaluation – Knowledge of the Standards • Evaluators must understand the Framework • Evaluators must have a focus on constructing meaning through cognitive engagement • Evaluators must be able to identify appropriate data (evidence) to paint an accurate picture of educators work Plan for gathering data – Fidelity to Process • Evaluator must understand the process including it’s intent or purpose. • Evaluator must follow process with fidelity, engaging the educator in discussion along the way • Evaluator must maintain consistency and fairness from educator to educator End result – Quality of the Product • Evaluator must align evidence to appropriate component • Evaluator must level evidence accurately • Evaluator must have sufficient evidence to support rating • Evaluator must have skill in engaging educator in conversation around level and direction for future Considerations Differentiation for career stages Novice Experienced Needing assistance Role of collaboration in teacher growth Examination of the culture for learning in the district and the schools Importance of a focus on cognitive engagement from “top” down Being clear about expectations