AP/ADMS 4940 Technology Management
advertisement

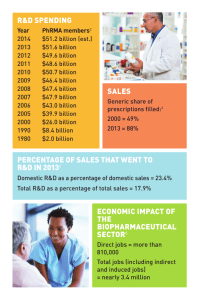
AP/ADMS 4940 Technology Management Session 1 Today’s Agenda Administrative issues Course outline review Course expectation Overview of technological innovation Administrative Issues Contact Info: You-Ta Chuang, ychuang@yorku.ca Office: RM233, Atkinson Building Course materials: All materials are available on e-Resources Cases can be purchased through Ivey School of Business Course Outline Review Learning Objectives To develop an awareness of the range, scope, and complexity of the phenomena, issues, and problems related to managing technological change. To develop understanding of "state of the art" concepts for managing technological change and the relationship between technological change and strategy. To develop a conceptual framework for assessing and auditing the technological capabilities Evaluation Midterm exam 30% Oct 22, in class, close book Coverage – readings from Sessions 1-6, excluding cases Final exam 20% Date: TBA Coverage – readings from Session 8 – 11, including group projects; excluding cases Participation 15% Your performance relative to class average; York’s 9-point scale Group work 35% Group work Session summary (5%) Lead discussion (5%) Group project (25%) Three progress reports (5%) Group presentation (20%) Overview Technology: This refers to the theoretical and practical knowledge, skills and artifacts that can be used to develop products and services as well as their production and delivery systems. Technology can be embodied in people, materials, cognitive and physical processes, plant, equipment and tools Technological Innovation: This can be technology-based or facilitated by technology. We define successful technological innovation as that which returns the original investment plus some additional returns Technological innovation is now the single most important driver of competitive success in many industries Many firms earn over one-third of sales on products developed within last five years Product innovations help firms protect margins by offering new, differentiated features. Process innovations help make manufacturing more efficient. BUT….. Technological innovation can lead to Shorter product lifecycles (more rapid product obsolescence) More rapid new product introductions Greater market segmentation And…return on investment??? Biopharmaceutical Companies’ Investment in R&D Total Biopharmaceutical Company R&D and PhRMA Member R&D: 1995–20091 $60 $51.80 $47.60 $47.9 $47.4 $50 $40 $29.8 $31.0 $30 $20 “ $65.3 $63.2 $63.7 $56.1 $15.2 $16.9 $19.0 $21.0 $22.7 $34.5 $37.0 $39.9 $43.4 $45.8 $26.0 “ Expenditures (Billions of Dollars) $70 The pharmaceutical industry is one of the most research-intensive industries in the United States. Pharmaceutical firms invest as much as five times more in research and development, relative to their sales, than the average U.S. manufacturing firm.2 $10 $0 1995 1996 1997 1998 Entire Pharma Sector 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 (est) PhRMA Member Companies' R&D Expenditures Sources: 1Burrill & Company, analysis for PhRMA, 2005–2010 (Includes PhRMA research associates and nonmembers) in PhRMA, “Profile 2010, Pharmaceutical Industry;” PhRMA, “PhRMA Annual Membership Survey,” 1996-2010; 2CBO, Research and Development in the Pharmaceutical Industry, 2006. — Congressional Budget Office The Cost of Developing a New Drug Has Greatly Increased Cost to Develop One New Drug1 $1.4 Billions (Constant Dollars, Year 2000) $1.3B $1.2 $1.0 $0.8 $800M $0.6 $0.4 $300M $0.2 $100M $0.0 1979 1991 2000 Sources: 1J. DiMasi and H. Grabowski, "The Cost of Biopharmaceutical R&D: Is Biotech Different?," Managerial and Decision Economics, 2007; J. DiMasi et al., “The Price of Innovation: New Estimates of Drug Development Costs,” Journal of Health Economics, 2003. 2005 Probability of Success for Investigational Drugs Is Small Approximately 20% of self-originated new drugs that enter clinical testing will receive U.S. marketing approval.1 Clinical Approval Success Rates by Therapeutic Class1 Source: 1Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development, “New drugs entering clinical testing in top 10 firms jumped 52% in 2003-05,” Impact Report, 2006. Roadmap of topics What is innovation Source of innovation/Types of innovation How to measure innovation performance Strategy and competition Choosing innovation projects Collaboration strategies How to protect innovation Organizing for innovation What’s on next week Topics: Nature and Importance of Innovation; Sources of Innovation Readings: The Council of Canadian Academies, 2009. Innovation and Business Strategy: Why Canada Falls Short: Chapter 2 Birkinshaw, J., Bouquet, C., & Barsoux, J. (2011). The 5 myths of innovation. MIT Sloan Management Review, 52(2), 43-50. Davenport, T. H., Prusak, L., & Wilson, H. J. (2003), Who's bringing you hot ideas and how are you responding? Harvard Business Review, 81(2), 58-64