presentation
advertisement

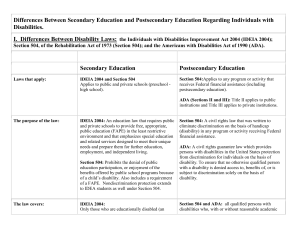
Entitlement vs. Eligibility The Differences Between Public and Postsecondary Education for Individuals With Disabilities March 30, 2011 Gus Ekhardt, M.Ed. Federal Laws Applicable for Students with Disabilities in Public School (K-12) • The Individuals with Disabilities Improvement Act (IDEIA 2004) • The Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (Section 504) • Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA) Individuals with Disabilities Improvement Act (IDEIA 2004) IDEIA (2004) describes what students are entitled to receive during their public school career. Key Differences at the Postsecondary (College) Level • Legal rights and responsibilities for college students • Legal differences between secondary and postsecondary education • Increase in complexity and unpredictability • Change in student responsibilities Federal Laws that Apply to Postsecondary Education • Americans with Disabilities Act • Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (Section 504) • A civil rights law enacted to eliminate discrimination on the basis of disability in any program receiving federal assistance • Section 504 of this law prohibits the denial of public education participation because of a child’s disability Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA) • A civil rights law enacted to provide person’s with a disability protection from discrimination based on disability • ADA states that no otherwise qualified individual with a disability is denied access to the benefits of or is subject to discrimination based solely on their disability Legislative Purpose To provide equal opportunity for individuals with disabilities to access education. Determining a Disability • The college has no obligation to identify students with disabilities • Students must document the existence of a disability as defined by Section 504 and ADA Fundamentals • Students must self-identify • Documentation of disability must be comprehensive, qualified, and current • Documentation must establish a disability that significantly limits learning and supports specific requested accommodations The student, not the school is responsible for obtaining disability documentation. Documentation Requirements Necessary to Receive Support Universal • Clearly stated identification of disability • The student’s functional limitations in an academic environment – impact of the disability • The signature, printed name, title, and professional credentials of the evaluator • Date of the evaluation Must be Completed by a Qualified Individual Licensed Psychologist Neuropsychologist Psychiatrist Medical Doctor Information must be current within 3 years Diagnosis & DSM Code Reasonable Accommodations Considered on a course by course basis, once disability status is determined. Self-Advocacy • Student must be able to describe their disability and identify their strengths and areas of need • Student is responsible to identify any accommodations needed • Student must become a competent selfadvocate Communication Templates Reduce anxiety Increase effectiveness Instruction Professors are not required to modify or alter assignments and deadlines. Grades & Tests • Any changes to how tests are given (extended time, test proctors) are available only when supported by disability documentation • Professors expect students to read, save and consult the course syllabus which details course expectations, assignments, and grading Student Responsibilities • Students must be able to structure their own time • Students will need to study at least 2 to 3 hours for each hour of class time • Tutoring services do not fall under disability services accommodation requirements Support Systems • These systems exist and are available • The student must seek out, ask for the help, and follow through Resources • National Clearinghouse on Postsecondary Education for Individuals with Disabilities: http://www.heath.gwu.edu • Association on Higher Education and Disability: http://www.ahead.org/ • National Secondary Transition Technical Assistance Center: www.//nsttac.org • Pennsylvania Training and Technical Assistance Network: www.pattan.net • Financial Aid for Students through the US Department of Education’s Office: http://www.ed.gov/index.jsp • The Financial Aid Information Page: www.finaid.org • Pennsylvania Career Zone: http://www.pacareerzone.org