2 MB 11th Sep 2013 Parent Workshop
advertisement

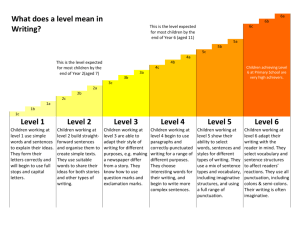
Assessment for Learning (AfL) ‘The important thing is not that every child is taught but that is given the wish to learn.’ John Lubbock 1832 WALT Understand how assessment works in key stage 1. Develop understanding of the language of AfL. Know the expected levels of attainment in Key Stage 1. The Big Picture The two main forms of assessment are formative and summative. SUMMATIVE determines what has been learnt. FORMATIVE furthers the learning on a day to day basis. Both have a place in schools. Summative Assessment Summative assessments are externally moderated in Years 2 and 6. In all other year groups these assessments are moderated internally. Core Subjects Key Stage 1 Key Stage 2 Literacy Literacy Speaking and listening Reading Writing (including spelling and handwriting) Reading Spelling and Grammar Maths Science (Writing) Maths Science Teacher Assessment Carried out as part of normal teaching practice. Evidence is taken across a range of pieces of work. Purpose to identify next learning steps. KS1 SATs The tests will help to inform the teacher assessment. 1 overall level for each subject reported to parents. KS1 Test/ task organisation Normal day – activities are kept ‘low key’ One to one, or in small groups Some whole class Children asked to do their best Teachers explain what the children have to do Children must work without teacher help KS 1 - Reading Task Children are asked to read a Level 1, 2 or 3 book as appropriate. The teacher will keep a running record of fluency, expression and accuracy. KS1 - Reading Test Comprehension booklet Level 2 or 3 as appropriate. • Year 1 – Phonics screening check KS1 – Writing Two writing tasks One longer - about 45 mins – eg a recount or a story One shorter - about 30 mins, eg an invitation or a postcard Done on different days Spelling test Marks for handwriting Externally moderated KS1 - Maths Teacher assessment Level 1 Level 2 or level 3 test KS1 – Science All Teacher assessment 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 attainment targets: Scientific Enquiry Life Processes & Living Things Materials & their Properties Physical Processes Overall Level given What does assessment look like in the classroom? Active involvement of the learner Sharing Learning Objectives and Success Criteria Effective Questioning Effective Feedback Self and Peer Evaluation Strategies School: Clear learning objectives – WALT or LI Clear success criteria Talking partners. Open questioning with appropriate wait time. Opportunities for self and peer evaluation, e.g. thumb tool, green – go, , Success criteria review, marking ladder, reviewing targets. Positive and constructive feedback, relevant to the WALT or LI e.g. what the child has done well , next step comments. Levels In Primary Schools children’s work is levelled using a set of criteria. Children are generally working between levels 1 – 3, depending on age and ability. The numbers of levels do not correspond to the year groups e.g. a child in year 4 could be working at level 3. Year 1 children may still be assessed using EYFS criteria. ‘BEST FIT’ FEEL OF NATIONAL CURRICULUM LEVELS Context Support Language for thinking Communicating and Recording Speaking/listening reading, writing, maths, science English, maths, science Level 1 Immediate interest With help ‘Do you think it will bounce on this floor ?’ Describe Recognise and name Begin to extend ideas Express simple views Like –dislike Talk Pictures Labels Simple charts Level 2 Topics near to child’s experiences topics that interest them With support ‘What do you think will happen when we …..? ‘how could you find out ?’ Level 3 Range of contexts Sequence Words and phrases Interesting vocabulary Compare Sequence of sentences Sort Use symbols/diagrams to record Make own suggestions With support prepares table for results, pictograms, bar chart Record in variety of ways Explain Link cause and effect Standard measures recorded Simple generalisations Limited support/ Prompts ‘ remember to make a prediction’ Begin to understand meaning beyond the literal Systematic approach to problems Sentences extend ideas logically Beginning, middle, end NOFAN Never Occasionally Frequently Always Naturally 6a What does a level mean in Writing? 6b 6c This is the level expected for most children by the end of Year 6 (aged 11) 5a 5b 5c 4a 4b This is the level expected for most children by the end of Year 2(aged 7) 4c Children achieving Level 6 at Primary School are very high achievers. 3a 3b 3c 2a 2b 2c 1a 1b 1c Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Children working at level 1 use simple words and sentences to explain their ideas. They form their letters correctly and will begin to use full stops and capital letters. Children working at level 2 build straightforward sentences and organise them to create simple texts. They use suitable words to share their ideas for both stories and other types of writing. Children working at level 3 are able to adapt their style of writing for different purposes, e.g. making a newspaper differ from a story. They know how to use question marks and exclamation marks. Children working at level 4 begin to use paragraphs and correctly-punctuated writing for a range of different purposes. They choose interesting words for their writing, and begin to write more complex sentences. Children working at level 5 show their ability to select words, sentences and styles for different types of writing. They use a mix of sentence types and vocabulary, including imaginative structures, and using a full range of punctuation. Children working at level 6 adapt their writing with the reader in mind. They select vocabulary and sentence structures to affect readers’ reactions. They use all punctuation, including colons & semi-colons. Their writing is often imaginative. Reading 6a What does a level mean in Reading? 6b 6c This is the level expected for most children by the end of Year 6 (aged 11) 5a 5b 5c 4a 4b This is the level expected for most children by the end of Year 2(aged 7) 4c Children achieving Level 6 at Primary School are very high achievers. 3a 3b 3c 2a 2b 2c 1a 1b 1c Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Children working at level 1 are able to recognise some common words, and use simple sounding out to read others. They can understand simple stories that they have read. Children working at level 2 use a mix of skills to read words and can therefore read simple stories or other types of writing. They can talk about what they have read. Children working at level 3 show understanding of what they have read, including making simple inferences about things such as the feelings of characters in a story. They read fluently when reading aloud. Children working at level 4 are able to draw inferences about characters and actions in stories. They can read a variety of types of writing. They can explain some simple decisions made by authors, such as use of layout features in non-fiction writing. Children working at level 5 are able to read complex texts and find a range of information from them. They are able to explain some choices made by authors, such as particular vocabulary choices and can confidently ‘read between the lines’. Children working at level 6 show insight into the ways authors create texts, and can use quotations to explain their understanding. They can explore the relationship between authors, characters and the reader based on what they read and wider context. Numeracy 6a What does a level mean in Maths? 6b 6c This is the level expected for most children by the end of Year 6 (aged 11) 5a 5b 5c 4a 4b This is the level expected for most children by the end of Year 2(aged 7) 4c Children achieving Level 6 at Primary School are very high achievers. 3a 3b 3c 2a 2b 2c 1a 1b 1c Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Children working at level 1 are able to count and read and write the numbers up to 10. They can carry out simple calculations using numbers up to 10. They can sort things, such as shapes, into different categories based on their properties. Children working at level 2 understand place value in numbers. They recognise patterns such as odd and even numbers. They can use skills like doubling and halving, and know numberpairs off by heart (e.g. knowing that 6+3 = 9) Children working at level 3 can work with numbers up to 1000. They can use simple fractions, begin to learn their times tables and solve problems in £ and p. They can use 2d and 3d shapes, and reflect simple 2d shapes. They can create simple graphs. Children working at level 4 know their tables up to 10x10. They use efficient methods to carry out + - x & ÷ calculations. They can use fraction percentage and decimal values. They can use graph axes and scale measures, and can calculate simple averages. Children working at level 5 understand the relationships between numbers less than 0. They can multiply 2-digit by 3digit numbers. They can find the area and perimeter of shapes. They create and interpret graphs. They begin to use simple algebra. Children working at level 6 work with confidence using a range of numbers, including calculations with fractions. They can solve simple algebraic equations. They can build a range of graphs, and can use fractions to calculate probability of various events. Progress Alongside a child's level of attainment we are also closely monitoring the amount of progress they make each term. Those children who are not making expected progress are quickly identified by the class teacher or the assessment coordinators and are given the support they need to close the gap.