Didactical Elements - aausmed
advertisement

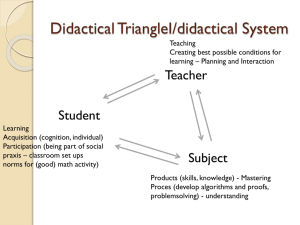
Didactical Elements Didactic TriangleI/didactical System Teacher Student Subject Didactic Triangle/didactical System Teacher Student Examples: Subject Mathematics/Science Didactic Triangle/didactical System Student Teacher Examples: Subject Mathematics/Science Didactic Triangle/didactical System Subject Mathematics/Science Student Examples: Teacher Subject didactics Basic asumption about whether it makes sense to talk about didactics: Despite individuals involved we will find some general phenomena and mechanisms characterazing teaching and learning Subject didactics has as it’s domain to describe teaching and learning processes within a given teaching subject. Didactic positions Teaching and learning is just a simple transfer of knowledge from teacher to student (copy – paste) The mind is not a vessel to be filled but a fire to be ignited. (Plutarch 46-119 AC) Reference Write down the description of a (small) part of a teaching course which in some way because of teacher student interaction seems interesting to you. (age group, topic, ………….) This situation will be your reference for the concepts and theories we are going to present. External didactical transformation Analyze your teaching topic for scientific knowledge and for every day knowledge and evaluate who and what affected what it was about and the choice of teaching methods. Didactic transpositions Subject didactics has as it’s domain to describe teaching and learning processes within a given teaching subject. Scientific Knowledge Practice and every day knowledge External didactical transposition Teaching Knowledge Internal didactical transposition Teaching Institution Subject/topic in a didactical system External didactical transformation Ontology: Clarify the existence and characteristics of the subject domain. Two positions: Platonism: Real reality is the world of ideas and concepts – what we see are reflections or shadows Materialism: Ideas are tools created to understand the reality. Do we invent or discover mathematics?? External didactical transposition Stakeholders: Political, public, scientific and educational institutions Critical perspectives: Ethics (atomic bomb, pollution), model critic gender agenda, western dominated External didactical transposition Why teach mathematics/science? The discourse on stating the reasons for teaching a subject is important becuase the actual reasons - constitute the (teaching) subject - refer to relations between (teaching) subject and the underlying scientific subject - Play a role in planning teaching and communicating about teaching External didactical transposition Categories of reasons Personly utility (utility argument) Collective utility (economy argument) Personly formation (culture argument) Collective formation (democracy argument) External didactical transposition Constituting the school subject Demarcation and identification: Mathematics as a school subject is found in all countries with almost same content Science is found as different school subject constructions External didactical transposition Constituting the school subject To be described in terms of goal and content ideally mutually referring in a balanced way In practice you find either clear goal with weak examples of content or clear list of content with less reference to goal New trend: specifying core topics and values of the subject along with presentation of paradigmatic examples External didactical transposition Constituting the school subject: In practice the following are very strong players in the constitutioning process: The textbook External tests and examinations Teacher communities Physical and material conditions Knowledge – how? Knowledge - how A model for acknowledgment in science and mathematics in a didactical context ”Short cut” Didactical transpositions Subject didactics has as it’s domain to describe teaching and learning processes within a given teaching subject. Scientific Knowledge Practice and every day knowledge External didactical transposition Teaching Knowledge Internal didactical transposition Teaching Institution Subject/topic in a didactical system Didactical TriangleI/didactical System Teacher educator Teacher Student How to teach Mathematics Mathematics Didactical TriangleI/didactical System Teacher Student Subject Didactical relation model Hiim and Hippe. Prerequsites for learning assesment frame conditions (set up) Learning process goal content Didactical relation model Hiim and Hippe. Prerequisites for learning: The students’ skills, knowledge, understanding, feelings, values, general background Frame conditions: Rules and regulations, economy, material, time, equipment, tradition and climate for collaboration Goal: What is the purpose, what are the students expected to achieve Content: What is the topic, succession – intellectual as well as emotional aspects Learning process: How will learning take place, organizing of work, involving students in decisions, theory – practice connection Assessment: What should be assessed (products, learning process, outcome, participation) and how. External didactical transformation Analyze your teaching topic in the perspectives of the didactic relation model Did it bring in some new lightning on your teaching situation? http://www.aausmed.wordpress.com/