What DOK Level?

Standards Academy
Grades 3 and 4
Day 1
Objectives
• Understand the Critical Areas of our grade levels.
• Examine the importance of vertical alignment across our grade levels.
• What is conceptual understanding?
• Cognitive Rigor Matrix
Who are we?
• Name
• School
• District
• Years spent teaching 3 rd or 4 th grade
• Your objective(s)
– Keeping those previously mentioned in mind
Norms
Things we all need in order for our time together to be productive……….
1. .
2. ..
3. …
4. ….
Vertical Alignment
Vertical Alignment
1. Form six groups.
a) Operations and Algebraic Thinking Grade 3 b) Operations and Algebraic Thinking Grade 4 c) Operations and Algebraic Thinking Grade 5 d) Number and Operation Fractions Grade 3 e) Number and Operations Fractions Grade 4 f) Number and Operations Fractions Grade 5
2. Spend 10 minutes reading your portion of the core and discuss it with your group to solidify your understanding.
3. Re-group so that you are now composed of 3 members one from each grade level.
a) 3, 4, 5 Numbers and Algebraic thinking b) 3, 4, 5 Numbers and Operations Fractions
4. Discuss the big ideas from your grade level reading and take notes.
5. Combine groups of three, still working within your domain but you should now have 6 members with notes.
6. Create a poster displaying the vertical alignment for grades 3, 4, & 5 within your domain.
Reflection
1. Was this activity helpful for you?
2. If so, why?
3. If not, what would have been more helpful?
4. How will this activity change your teaching next year?
Critical
Areas
Major work of 3
rd
Grade
Major work of 4
th
Grade
Critical Area Graphic
Organizer
• Identify at least one or two important mathematical concepts within this critical area. What do students need to learn prior to these concepts?
• What evidence would convince you that a student understands these concepts?
• What common misconceptions do students have when studying this critical area? What challenges have you had in teaching these concepts?
• How do these concepts support learning in later grades?
Reflection
• How do the critical areas help bring focus to the standards at your grade level?
• How will you use the critical areas to inform your curriculum and guide your instruction?
• What questions do you still have about the critical areas?
• How has this activity increased your understanding of the instructional core?
Conceptual
Understanding
What does understand really mean?
1.
Read the excerpt from Adding it Up.
2.
Form groups of 5-6 and sit together at a table.
3.
The group discusses the question prompt until time is called
4.
The leader’s role is to record the major points of the conversation that take place at the table and to then summarize the conversation using the recorded notes just before rotating to the next table.
5.
The leader stays put; the rest of the group rotates to the next table.
6.
The leader (the one who didn’t move) presents a summary of the conversation recorded from the former group to the new group.
7.
The new group discusses the new question prompt until time is called.
8.
Again the leader takes notes and summarizes.
Round 1
Discuss the following:
The word "understanding" is used frequently throughout the document. What do you think it means and why is it important in a child's ability to learn math concepts?
Round 2
Reflect on the quote:
"A significant indicator of conceptual understanding is being able to represent mathematical situations in different ways, knowing how different representations can be useful for different purposes."
Explain why you think it's important for a child to be familiar with more than one way to solve a problem.
Round 3
Discuss the following:
How can a teacher help students make connections between concepts and representations?
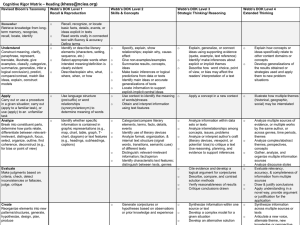
DOK & Cognitive Rigor
1. Develop a shared understanding of the
Cognitive Rigor Matrix.
2. Use the Cognitive Rigor Matrix to:
• Consider rigor expectations in the Common Core
• Examine learning expectations and critical thinking
• Evaluate sample assessments/tasks & rubrics
Before we begin…
Take a couple of minutes to write your personal definition of
“cognitive rigor” as it relates to instruction, learning, and/or assessment.
Let’s apply your rigor definition
Your class is studying addition of fractions with like denominators.
• What is a basic computational question you might ask?
• What is a more rigorous question you might ask?
Hess Article
Annotate:
• ? On parts of the article that need clarification
• ! For any “ ahas” as you read
• Underline or highlight any key terms or vocabulary
• * next to any key/main ideas from the article
The Hess Cognitive
Rigor Matrix: Integrates
Bloom’s & Webb’s
Blooms Taxonomy
What type of thinking
(verbs) is needed to complete a task?
Webb’s Depth of
Knowledge
How deeply do you have to understand the content to successfully interact with it?
How complex is the content?
Blooms Taxonomy
Identify List Draw
Webb’s
Depth of
Analyze
Create
Knowledge
Design
Define
Calculate
Who, What, When, Where, Why
Arrange
Memorize
Repeat
Tabulate
Illustrate
Name
Match
Measure
Recall
Recognize
Use
Categorize
Connect
Level One
(Recall)
Infer
Synthesize
Graph Organize
Apply Concepts
Critique
Level
Four
(Extended
Thinking)
Describe
Explain
Interpret
Level Two
(Skill/
Concept)
Classify
Cause/Effect
Relate
Modify
Predict
Prove
Critique
Revise
Level Three
( Strategic Thinking)
Develop a Logical Argument
Apprise
Formulate
Use Concepts to Solve
Non-Routine Problems
Investigate
Draw Conclusions
Assess
Compare
Estimate
Construct
Compare
Explain
Show
Interpret
Summarize
Hypothesize Differentiate
Webb’s Depth-of-Knowledge
Levels
• DOK 1- Recall & Reproduction-Recall a fact, term, principle, concept, or perform a routine procedure.
• DOK 2- Basic Application of Skills/Concepts-Use of information, conceptual knowledge, select appropriate procedures for a task, two or more steps with decision points along the way, routine problems, organize/display data, interpret/use simple graphs.
• DOK 3- Strategic Thinking-Requires reasoning, developing a plan or sequence of steps to approach problem; requires some decision making and justification; abstract, complex, or non-routine; often more than one possible answer or approach.
• DOK 4- Extended Thinking-An original investigation or application to real word; requires time to research, problem solve, and process multiple conditions of the problem or task; non-routine manipulations, across disciplines/content area/multiple sources.
DOK is about complexity—not difficulty!
The intended student learning outcome determines the DOK level. What mental processing must occur?
While verbs may appear to point to a DOK level, it is what comes after the verb that is the best indicator of the rigor/DOK level.
Let’s see some examples…
It’s what after the verb…
• Describe how two characters are alike and different.
• Describe the information contained in graphics or data tables in the text; or the rule for rounding of a number
• Describe the data or text evidence that supports your solution, reasoning, or conclusions
• Describe varying perspectives on global climate change using supporting scientific evidence, and identify the most significant effects it might have on the planet in 100 years
DOK 1
Recall and Reproduction
Remember
Recall, locate basic facts, definitions, details, events
DOK 2
Skills and
Concepts
DOK 3
Reasoning and
Thinking
DOK 4
Extended Thinking
Understand
Apply
Select appropriate words for use when intended meaning is clearly evident.
Use language structure, word relationships to determine meaning
Explain relationships
Summarize
State central idea
Use context for word meanings
Use information using text features
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Identify the kind of information contained in a graphic, table, visual, etc.
-Brainstorm ideas, concepts, problems, or perspectives related to a topic or concept.
Explain, generalize or connect ideas using supporting evidence
(quote, text, evidence)
Use concepts to solve non-routine problems and justify
Compare literary elements, facts, terms and events
Analyze format, organization and text structures
Analyze or interpret author ’ s craft (e.g., literary devices, viewpoint, or potential bias) to critique a text
Cite evidence and develop a logical argument for conjectures based on one text or problem
Generate conjectures or hypotheses based on observations or prior knowledge
Develop a complex model or approach for a given situation
Develop an alternative solution
-Explain how concepts or ideas specifically relate to other content domains.
Devise an approach among many alternatives to research a novel problem
Analyze multiple sources or multiple text. Analyze complex abstract themes
Evaluate relevancy, accuracy and completeness of information across texts or sources
Synthesize across multiple sources/ texts
Articulate a new voice, theme, or perspective
Selected Response
Constructed
Response
Performance
Tasks
What DOK Level?
What DOK Level?
What DOK Level?
What DOK Level?
What DOK Level?
Find the next three terms in the pattern and determine the rule for the following pattern of numbers:
1, 4, 8, 11, 15, 18, 22, 25, 29, …
Revised Bloom’s
Taxonomy
DOK with Multiplication
Webb’s DOK Level 1 Webb’s DOK Level 2 Webb’s DOK Level 3
Recall & Reproduction Skills & Concepts Strategic Thinking/Reasoning
Remember
Retrieve knowledge from longterm memory, recognize, recall, locate, identify
Understand
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent, translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize, summarize, generalize, infer logical conclusion (such as from examples given), predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain, construct models
Apply
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation; carry out
(apply to a familiar task), or use
(apply) to an unfamiliar task
Analyze
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts relate, differentiate between relevantirrelevant, distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, find, coherence, deconstruct
Evaluate
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect, inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique
Create
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures, generate, hypothesize, design, plan, construct, produce
Draw a model to represent the problem
5 x 3
Find the area of this shape.
Create a table displaying all the factors of 48.
Estimate a reasonable answer for the problem
23 x 8. Explain how you made your estimate and why it is reasonable.
Write a multiplication statement comparing brown eyes to blue.
Webb’s DOK Level 4
Extended Thinking
Compare the 2 strategies used. Explain the process each student used and explain who has the correct answer and why.
Can the distributive property be used with division? Justify your conclusions with data generated from your investigation.
A
Describe the trend displayed in the data table
B
Construct an area model for the polygon from the table with the largest area.
D
E
Make a conclusion based on the data presented, use mathematical relationships to justify your response.
What is the answer to a multiplication problem called?
C
F
DOK
Question
Stems
Create Your Own DOK
Questions
In your tables, create your own DOK grid for:
3.G.1-2 or
4.G.1-3
Wrap Up & Reflect
Questions or Concerns……..
Complete a 4 point evaluation:
• What went well today?
• What could be improved?
• What do you need more support in?
• What did you master?