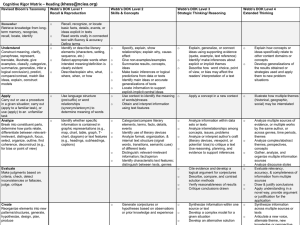
CTE Mentor Collab Nov 19 MCS
San Diego County Office of Education
San Diego County Office of Education
Designated Subjects CTE/Adult Ed Credential LEA
Mentor Collaboration Workshop
Susie Johnson
November 19, 2013
An Overview of
Common Core State Standards and
CTE Model Curriculum Standards
Designated Subjects CTE/Adult Ed Credentials
Susie Johnson
November 19, 2013
CTE Model
Define Literacy across all disciplines
Analyze Instructional Shifts
Explore the “new” CTE Model
Curriculum Standards (MCS)
Deepen your understanding of
Common Core State Standards (CCSS)
Assess the relationship between the
CTE MCS and CCSS
Source: www.corestandards.org
Who’s In?
Who’s Not?
Content Literacy in ALL subjects
Building knowledge through content rich nonfiction
Mathematics Literacy
Focus strongly where standards focus
Reading, writing and speaking grounded in evidence from text, both literary and informational
Coherence: think across grades, and link to major topics within grades
Regular practice with complex text and its academic language
• Rigor: in major topics pursue:
• conceptual understanding,
• procedural skill and fluency, and
• application with equal intensity
Shift 1 Balancing Informational
& Literary Text
Shift 2 Knowledge in the Disciplines
Shift 3
Shift 4
Shift 5
Shift 6
Staircase of Complexity
Text-based Answers
Writing from Sources
Academic Vocabulary
Students read a true balance of informational and literary texts.
Students build knowledge about the world (domains/ content areas) through TEXT rather than the teacher or activities
Students read the central, grade appropriate text around which instruction is centered. Teachers are patient, create more time and space and support in the curriculum for close reading.
Students engage in rich and rigorous evidence based conversations about text.
Writing emphasizes use of evidence from sources to inform or make an argument.
Students constantly build the transferable vocabulary they need to access grade level complex texts. This can be done effectively by spiraling like content in increasingly complex texts.
Shift 1 Focus Teachers significantly narrow and deepen the scope of how time and energy is spent in the math classroom. They do so in order to focus deeply on only the concepts that are prioritized in the standards.
Shift 2 Coherence
Shift 3 Fluency
Principals and teachers carefully connect the learning within and across grades so that students can build new understanding onto foundations built in previous years.
Students are expected to have speed and accuracy with simple calculations; teachers structure class time and/or homework time for students to memorize, through repetition, core functions.
Shift 4 Deep
Understanding
Students deeply understand and can operate easily within a math concept before moving on. They learn more than the trick to get the answer right. They learn the math.
Shift 5 Application Students are expected to use math and choose the appropriate concept for application even when they are not prompted to do so.
Shift 6 Dual Intensity Students are practicing and understanding. There is more than a balance between these two things in the classroom – both are occurring with intensity.
CCSS for K-12
replace
:
◦ English Language Arts
◦ Mathematics
Literacy Standards Grades 6-12
complement:
◦ History/Social Science Standards
◦ Science Standards
◦ CTE Model Curriculum Standards
◦
Emphasizes a focus on disciplinespecific vocabulary
◦
Unique text structures found in informational texts
◦
Reading and writing in all classrooms
◦
Focus on critical analysis and evidence
NAEP Reading Assessment: Distribution of Literary and Informational Passages
Grade
4
8
12
Literary
50%
45%
30%
Informational
50%
55%
70%
Source: National Assessment Governing Board. (2008). Reading framework for the 2009 National Assessment of Educational Progress, http://www.nagb.org/publications/frameworks/reading-2009.doc
Law and Public Safety
1420 – 1740L
Agriculture/Natural Resources
1270 – 1510L
Education and Training
1320 – 1370L
Transportation, Distribution and Logistics
1170 – 1350L
Architecture/Construction
1210 – 1340L
Business and Administration
1210 – 1310L
Health Science
1260 – 1300L
Hospitality and Tourism
1230 – 1260L
Scientific Research/Engineering
1190 – 1250L
Arts/AV Technology/Communications
1100 – 1190L
Source: Aligning the Journey with the Destination, by Gary Williamson, Ph.D.; 2006
Number and Quantity
Algebra
Functions
Modeling
Geometry
Statistics and Probability
Calculus
1. Make sense of problems & persevere in solving them
2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively
3. Construct viable arguments and critique the understanding of others
4. Model with mathematics
5. Use appropriate tools strategically
6. Attend to precision
7. Look for and make use of structure
8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
New system will begin in 2014-15.
CA students will be assessed by the
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium
(SBAC).
Assessments will include:
◦ Performance Assessments (interim & summative)
Selected Response
Constructed Response
Extended Performance Assessments
◦ Re-take option (summative)
The new model curriculum standards are available online at: http://www.cde.ca.gov/ci/ ct/sf/ctemcstandards.asp
Industry
Pathway
Anchor
CCSS
9
Research
Bloom’s Taxonomy (Revised)
Rigor and Relevance Framework –
◦
Bill Daggett
Knowledge Dimension –
◦ Anderson, Lorin and David Krathwohl
Depth of Knowledge –
◦
Norman L. Webb
18
Rigor/Relevance Framework
11
Beyond Knowledge Construct
Knowledge
Metacognitive form a coherent whole
(DOK Level 4)
Procedural how parts relate, find
Coherence
(DOK Level 3)
Conceptual clarify, give examples
(DOK Level 2)
Factual recognize, recall, locate
(DOK Level 1)
Use one-step process to solve routine problems
Performance
Apply multiple step process to solve routine problems
Solve non-routine problems using a sequence of steps
Create solutions to nonroutine real world complex problems using multiple steps and sources
Beyond Knowledge Construct
Knowledge
Metacognitive to form a coherent whole
Procedural how parts relate, find
Coherence
Conceptual clarify, give examples
Factual recognize, recall, locate
Performance
Use Apply Solve Create one-step process multi-step process non-routine solutions to real world to solve a routine to solve routine problems using non- routine , complex problem problems multiple steps problems using multiple steps
13
Factual
Access
Define
Describe
Find
Identify
Label
List
Locate
Match
Name
Recall
Recite
Recognize
Remember
Retrieve
Select
State
Conceptual
Adhere
Apply
Classify
Communicate
Compare
Demonstrate
Develop
Discriminate
Employ
Explain
Implement
Infer
Interpret
Maintain
Organize
Participate
Practice
Promote
Summarize
Transfer
Understand
Use
Procedural
Analyze
Assess
Comply
Compare
Contrast
Deconstruct
Deduce
Defend
Detect
Diagram
Differentiate
Discern
Distinguish
Enhance
Evaluate
Experiment
Explore
Illustrate
Integrate
Research
Solve
Test
Metacognitive
Advocate
Build
Compile
Compose
Construct
Create
Design
Devise
Formulate
Invent
Plan
Predict
Produce
Reconstruct
Reorganize
Synthesize
Beyond Knowledge Construct
14
Knowledge
Metacognitive form a coherent whole
Procedural how parts relate, find
Coherence
Conceptual clarify, give examples
Factual recognize, recall, locate
DOK
3
DOK
2
DOK
1
Use one-step process to solve routine problems
Performance
Apply multiple step process to solve routine problems
Solve non-routine problems using a sequence of steps
DOK
4
Create solutions to non-routine real world complex problems using multiple steps and sources
15
Beyond Knowledge Construct
Knowledge
Metacognitive form a coherent whole
(DOK Level 4)
Procedural how parts relate, find
Coherence
(DOK Level 3)
Conceptual clarify, give examples
(DOK Level 2)
Factual recognize, recall, locate
(DOK Level 1)
List 15 building products and find a “green” alternative to each one
Use one-step process to solve routine problems
Performance
Apply multiple step process to solve routine problems
Solve non-routine problems using a sequence of steps
Create solutions to non-routine real world complex problems using multiple steps and sources
16
Beyond Knowledge Construct
Knowledge
Metacognitive form a coherent whole
(DOK Level 4)
Procedural how parts relate, find
Coherence
(DOK Level 3)
Conceptual clarify, give examples
(DOK Level 2)
Factual recognize, recall, locate
(DOK Level 1)
List 15 building products and find a “green” alternative to each one
Construct a 1/8 th scale model of a garage using only recycled materials
Use one-step process to solve routine problems
Performance
Apply multiple step process to solve routine problems
Solve non-routine problems using a sequence of steps
Create solutions to non-routine real world complex problems using multiple steps and sources
17
Beyond Knowledge Construct
Knowledge
Metacognitive form a coherent whole
(DOK Level 4)
Procedural how parts relate, find
Coherence
(DOK Level 3)
Conceptual clarify, give examples
(DOK Level 2)
Factual recognize, recall, locate
(DOK Level 1)
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using recycled building materials
List 15 building products and a
“green” alternative to each
Use one-step process to solve routine problems
Construct a 1/8 th scale model of a garage using only recycled materials
Performance
Apply multiple step process to solve routine problems
Solve non-routine problems using a sequence of steps
Create solutions to non-routine real world complex problems using multiple steps and sources
18
Beyond Knowledge Construct
Knowledge
Metacognitive form a coherent whole
(DOK Level 4)
Procedural how parts relate, find
Coherence
(DOK Level 3)
Conceptual clarify, give examples
(DOK Level 2)
Factual recognize, recall, locate
(DOK Level 1)
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using building recycled materials
List 15 building products and a
“green” alternative to each
Develop a windresistant solar carport for student parking lots and convince the school board to fund it.
Construct a 1/8 th scale model of a garage using only recycled materials
Use one-step process to solve routine problems
Performance
Apply multiple step process to solve routine problems
Solve non-routine problems using a sequence of steps
Create solutions to non-routine real world complex problems using multiple steps and sources
Bloom’s
3
2
1
6
5
4
C
Levels
D
A B
1 2 3 4 5
Application
© 2012 International
Center for Leadership in
Education
28
Employer
Industry Specific
Pathway Standards
Industry Sector Anchors
(Knowledge and Performance Anchor Standards)
Standards for Career Ready Practice
Standards for Career Ready Practice
1. Apply appropriate technical skills and academic knowledge
2. Communicate clearly, effectively, and with reason
3. Develop an education and career plan aligned to personal goals
4. Apply technology to enhance productivity
5. Utilize critical thinking to make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
6. Practice personal health and understand financial literacy
Standards for Career Ready Practice(cont.)
7. Act as a responsible citizen in the workplace and the community.
8. Model integrity, ethical leadership, and effective management.
9. Work productively in teams while using cultural/global competence.
10. Demonstrate creativity and innovation .
11. Employ valid and reliable research strategies.
12. Understand the environmental, social, and economic impacts of decisions .
4.
5.
6.
7.
1.
2.
3.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Academics
Communications
Career Planning and Management
Technology
Problem Solving and Critical Thinking
Health and Safety
Responsibility and Flexibility
Ethics and Legal Responsibilities
Leadership and Teamwork
Technical Knowledge and Skills
Demonstration and Application
Anchor
Standard
2.0, 3.0, 4.0 . . .
Performance
Indicator
2.1, 2.2, 2.3 . . .
ALL anchor standards should be addressed in every course.
SOME pathway standards should be addressed in every course.
Projects and Assignments should be progressive using the Beyond Knowledge Construct.
Projects and Assignments that don’t address anchor or pathway standards should be dropped or revised to address standards.
35
Arts, Media, Entertainment Construction Trades
36
Changed from
Know
and
Understand
to the use of action verbs that are rigorous, clear, specific and measurable.
CCSS
Pathway
Standards
CTE Model Curriuclum Standards
http://www.cde.ca.gov/ci/ct/sf/ctemcstandards.asp
Common Core State Standards Initiative
http://www.corestandards.org/
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium
http://www.smarterbalanced.org/
San Diego County Office of
Education/Designated Subjects Credentials http://www.sdcoe.net/student-services/rop/Pages/default.aspx
Review this presentation online
http://www.sdcoe.net/human-resources/credentials/Pages/designatedsubject-credentials.aspx
Meet with your new teachers and discuss what you have learned about CCSS and CTE
MCS
Encourage new teachers to ask questions
Explore challenges positively
Remind CTE teachers to reach out to their academic partners
We are here to help!