Ibn Al-Haitham (Alhazen) – The Father of Optics
advertisement

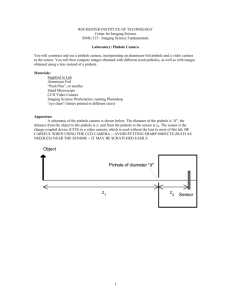
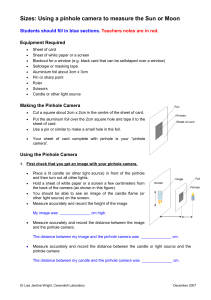
Ibn Al-Haitham (Alhazen) – The Father of Optics An ACE project by Bryan Yan 2I102 Who is he? • Muslim Scientist • Lived during “High point of Islamic Civilization” • Made great contributions to physics, mathematics, astronomy and optics • Born in Barsa • Died at 74 in Cairo • Known for his “Book of Optics” Key Contributions • Concluded that light enters our eyes and not emitted from them • Pinhole Camera • Visual Perception of Optical Illusions How do we see? – Past Theories • Emission theory • Supported by Euclid and Ptolemy • Believed that light was emitted from our eyes How do we see? – Past Theories • Intermission theory • Supported by Aristotle and his followers • Believed that physical particles enter our eyes from an object How do we see? Disputing Past Theories • Light cannot reach astronomical objects once we open our eyes • We are blinded by bright light How do we see? – Accepted Theory (Basis) • Proved that light traveled in straight lines • Reduced reflected and refracted light rays into vertical and horizontal components • Pinhole Camera (more about this later) How do we see? – Accepted Theory • Unified version of geometrical optics and philosophical physics to form modern physical optics • Images are inverted in our eyes • The eye is a medium and lens, neither an emitter or receiver Pinhole Camera – What? • Simple camera without lens • With a single small aperture • Usually a box, but can be done with two white cards of which one has the hole Pinhole Camera – When? Where? • 1021 AD • In “Book of Optics” Pinhole Camera – How? • Light passes through the small hole to form an inverted image on the screen • The image is dim and small, but sharp Pinhole Camera – Why? • Pinhole acts as a lens • Light from surroundings pass through the pinhole, captured on a point on the screen • Light from above is captured below and vice versa Pinhole Camera – Link? • Similar concept to eye • Inverted and sharp image Moon Illusion – Introduction • Moon appears larger near the horizon than it does while higher up in the sky • Illusion still debated • Alhazen’s reasoning most widely available and accepted Moon Illusion – Alhazen’s Principle • Judging the distance of an object depends on • There being an uninterrupted sequence of intervening bodies between the object and the observer Moon Illusion – Alhazen’s Conclusion • When the Moon is high in the sky there are no intervening objects, so the Moon appears close • The perceived size of an object of constant angular size varies with its perceived distance References • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alhazen http://www.ibnalhaytham.net/ http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Al-Haytham.html http://harvardmagazine.com/2003/09/ibn-al-haytham-html http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/738111/Ibn-al-Haytham http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pinhole_camera http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Camera_obscura http://www.muslimheritage.com/topics/default.cfm?articleID=382 http://inventors.about.com/od/pstartinventions/a/stilphotography.htm http://lecerveau.mcgill.ca/flash/capsules/articles_pdf/moon_illusion.pdf http://islamsci.mcgill.ca/RASI/BEA/Ibn_al-Haytham_BEA.htm http://www.ishim.net/ishimj/4/10.pdf http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Ibn_al-Haytham http://www.iis.ac.uk/view_article.asp?ContentID=106742 http://www.nei.nih.gov/health/eyediagram/images/NEA09.gif http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emission_theory_(vision) http://www.popsci.com.au/galleries/craziest-scientific-theories/emissiontheory/6a00d83542d51e69e20120a932bfac970b-500wi_20111012154439_Resized.jpg http://memegenerator.net/instance/13469306 http://images2.wikia.nocookie.net/__cb20081114033730/uncyclopedia/images/1/11/BrightLight.jpg References (Continued) • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • http://images.tutorvista.com/content/feed/tvcs/rectilinear-propagation-of-light.jpeg http://www.healthyeyes.org.uk/index.php?id=2 http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/scienceclips/ages/10_11/see_things_whatnext.shtml http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEC/CC/vision_background.php http://www.pediatriconcall.com/kidscorner/yourbody/our_eyes.aspx http://www.quora.com/Human-Brain/How-can-we-see-images-in-our-mind http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Physical_optics http://www.yorku.ca/eye/invert.gif http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aperture http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Pinhole-camera.svg http://www.nei.nih.gov/healthyeyes/eye_images/Normal.gif http://www.islamic-study.org/iais-images/al-haytham-optics%20book.gif http://www.thegeminigeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/Pinhole-Camera.jpg http://www.curriculumbits.com/physics/how-does-a-pinhole-camera-work/ http://wiki.answers.com/Q/How_does_a_Pinhole_camera_work http://wwwx.cs.unc.edu/~sud/courses/comp235/pinhole-principle.gif http://cw.psypress.com/zaidel/images/figure3_4big.jpg http://www.derekshirlaw.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/moon.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Harvest_moon.jpg http://people.umass.edu/~blaylock/p284/cl0024_hst.gif