Water Properties
advertisement

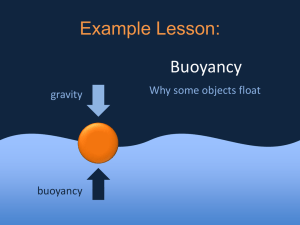
Water Properties Density • The amount of atoms, or stuff, packed into the same space. Which is more dense? • Cold or Hot Water – Cold water-things that are cold become more dense as they shrink • The only exception is ice, cold water becomes more dense until it freezes. It then expands! Quickly watch water temperature and density video Temperature affect on ocean water • Think back to our dissolved oxygen lab • What happened as the temperature rose with relation to the amount of oxygen in the water? • The same thing happens with salt in water • Warmer the water-less salty-less dense • Colder the water-more salt-more dense Quickly watch density of salt water video Density of Salt Water • What happens to the density of water the deeper you go? • It increases in density • Why? • The pressure from the water above is pushing things tighter and tighter! Watch NASA Video on Temperature vs. Salinity Depth of water What variables might change the salinity of the oceans? • What if it rained near a very salty part of the ocean? • Precipitation would add more water and have less salt. • What if lots of water evaporated near a salty part of a ocean? • Evaporation will have less water, more salt. Which is more dense? • Salt water or freshwater? – Salt Water of course • Why? – There is more “stuff” in the water. Practice • I will be calling groups back to practice the density of salt water, cold water, and warm water. • While you are at your seats you WILL work on the following • 39-50 in workbook • Finish your vocabulary assignment for this week. Buoyancy • Buoyancy-the upward force caused by the difference in densities, or more simply-the ability of things to float • How is Buoyancy related to density? • Things float because of density-if you are less dense than something you will float Watch Buoyant force video! Practice Buoyancy Title: How does density create buoyancy • Date: Today’s Date • Directions: Answer all questions and perform all activities • 1. Fill your 2 liter bottle that has been cut in half about ¾ full of water. • 2. Place your boat that is on your desk on top of the water. • 3. What happens? • 4. Why does it float? • 5. How does the boat floating represent buoyancy? • 6. Remove your boat • 7. What will happen when you throw a penny into the water? Why? • 8. How could we get our penny to float using buoyancy of another object? • 9. Place your boat into the water. Place pennies into your boat until the density becomes too great for buoyancy to keep them afloat. • 10. How many pennies did it take counteract the upward force of buoyancy? • Review Questions: – 1. What is buoyancy? – 2. Why is buoyancy important for boats? Show to Stick or Not To Stick Video Cohesion • Ability of like substances to stick together • Water binds to other water molecules to create the cohesion of water. Cohesion • THIS IS WHY WATER DROPS LOOK A LITTLE FUNNY • What happens when you do a belly flop on the water? • You are breaking the cohesive bond between water! Practice Title: Cohesion of water molecules • 1. Place 1 drop of water onto a penny. • 2. Draw a picture from the side of what you see. • 3. Why does the water drop have a dome shape to it? • 4.Keep placing drops on water onto your penny until the drops overflow, be sure to count • 5. How many drops did it take? • 6. Draw a picture of what your penny looked like before you dropped it. • 7. What might have caused your dome of to break? • 8. Repeat the process of making a large dome of water. Then take 1 drop of soapy water and observe what happens. • Review: – 1. What is cohesion? – 2. Why do you think the soap broke the cohesion of the water? – 3. Why is cohesion important? Adhesion • Water molecules have the ability to stick to different substances, sometimes they are absorbed, sometimes they are not. Show to stick or not to stick part of video on adhesion Adhesion Observations Title: Adhesion of water to wood • 1. Using your water bottle on your desk, place your ruler at an angle above the empty cut 2 liter bottle of water. • 2. Do your best to squirt the top of the ruler and make the water end up in the empty two liter bottle. • Review: – 1. What is adhesion? – 2. How did you demonstrate adhesion? – 3. Why do you think adhesion is important to the environment? Capillary Action • The ability of water to “climb”, or defy gravity. • This is how plants get their water and how paper towels absorb water. • The adhesion, ability of water to stick to other substances, allows water to “climb” • The attraction between the paper towel and water is adhesive or its the stickiness of water. Practice Capillary Action • 1. Holding one end of your paper towel, dip the other end into the colored water and watch it “climb”. • Review – 1.What is capillary action? – 2. What causes capillary action? – 3. Why is capillary action so important in nature? Surface Tension • The cohesive and adhesive properties of water create surface tension. • Surface Tension-the strength between water molecules on the surface of water. Watch surface tension video Practice Surface Tension Title: Surface Tension of Water • • • • 1. Fill your plastic cup up almost to the top 2. Toss one paper clip into the water. 3. What happened and why? 4. Attempt to place 1 paper clip so that it stays on top of the surface of the water and does not sink. • 5. Record your observations about what you notice about the water once you get one to float. Specific Heat • Water has a very high specific heat • Specific Heat-the amount of heat needed to heat up a substance • Water takes a long time to boil and will stay warm for a long time. Specific Heat • The beach in summer time • Sand- cold in morning-Hot in afternoon • Water-stays about the same temperature all day and all night Specific Heat • The ocean water will not warm up until late June. It will stay warm until late Sept. • Why does it take so long to warm and yet stay warm for a long time? Watch Specific Heat video Why did the ice cube melt faster on the mystery object? • The mystery element has a lower specific heat therefore it will absorb heat faster. Specific Heat Lab Universal Solvent • What does it mean when we say that water is the universal solvent? • water can dissolve more things than any other substance • Why do things dissolve in substance? • They are soluble or they have the same polarity. • Like dissolves like. The closer the polarity, the charge, the more likely they will dissolve. Watch solute and solvent video Polarity • Attraction between water, the universal solvent, and other substances will cause things to dissolve in them. • Polar=Dissolve • Non-Polar=will not dissolve Watch Soluble vs. Insoluble Video Practice Polarity Substance Oil Sugar Cornstarch Salt Soluble or insoluble Polar or NonPolar Review of Polarity • 1. What is the relationship between polarity and solubility? Tides • What are tides? • Tides are changes in the ocean depths at the beach. • What causes tides? • The gravitational pull of the moon as it rotates around the Earth. • The oceans, as a result of cohesion move as one.