Heat Transfer
advertisement

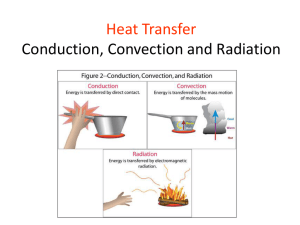
Heat Transfer • Everything is made of molecules. • When molecules gain energy they move faster and create more heat. • (The faster the molecules move the hotter they are) • Heat transfer Evaporation Melting Freezing Condensation Solid liquid Gas Molecules move very slowly! They are close together. Molecules move faster and are more spread apart. Molecules move very fast! They are very spread apart. Pair/Share 1. What happens to molecules as you add heat? 2. Are the molecules of water moving faster or slower in cold water? Why 3. Evaporation is when a Liquid turns into a ____________. Heat is __________. 4. Freezing is when a _________ turns into a ____________. Heat is _____________. 5. If the molecules are moving faster and our more spread out. Was heat added or removed? • Heat • Is the transfer of thermal energy from a hotter object to a cooler one until both objects are the same temperature. (You can not transfer cold or give someone cold) heat transfer video clip Pair/Share 1. Which direction does heat transfer? A. From warmer to cooler B. From cooler to warmer C. both directions 2. When you touch something cold which direction is heat being transferred? Why? 3. Explain why you feel cold when you touch something that is cold. 3 ways that heat is transferred within the atmosphere •Radiation •Conduction •Convection The first method of heat transfer How does heat energy get from the Sun to the Earth? ? RADIATION • Radiation • The direct transfer of energy by infrared electromagnetic Waves. What creates electromagnetic waves? • Sun, fire, light bulbs Video clip 1 video clip 2 Eureka start at 2:30 Pair Share • Partner A: What is radiation and where does it come from. • Partner B: What are three different things that create electromagnetic radiation? • Conduction • The direct transfer of heat from one substance to another • conduction substance that is video clip 1 touching. Ironing Clothes • Eureka That’s Hot Stepping on hot sand. • demo of conduction • flame heating molecules Conduction When you heat a metal strip at one end, the heat travels to the other end. As you heat the metal, the particles vibrate, these vibrations make the adjacent particles vibrate, and so on and so on, the vibrations are passed along the metal and so is the heat. We call this? Example of Conduction Pair Share: Partner A: Using the picture on the right explain the conduction process Pair Share: Partner B: Explain how the picture on the left is conducting heat. • Convection • The transfer of heat by movement of a fluid (liquids and gases). • convection video clip • Heat video clips\Convection 2.asf • ConvectionEureka Cooking peas in water OVEN Dryer Blow Drying your Hair. Water movement Cools at the surface Cooler water sinks Convection current Hot water rises • Heating the troposphere • Radiation, conduction and convection work together to heat the troposphere. • Radiation- heats the Earth • Conduction- Air near earth’s surface is warmed • Convection- the warm air molecules rise and transfer heat to the cooler air molecules. Eventually these molecules cool and sink back down to earth. This creates Convection Currents. Radiation, Convection and Conduction work together to heat the troposphere. review of all 3 types Radiation Convection Current Conduction Review Heat transfer from a hotter object to a cooler object until both objects are the same temperature. 3 types of heat transfer • Radiation – electromagnetic waves • Conduction – touching • Convection- through a fluid (liquid or gas) • All 3 work together to heat the troposphere but Convection causes most of the heating. Review Heat transfer from a hotter object to a cooler object until both objects are the same temperature. 3 types of heat transfer review, review 2 Music Review • Radiation – electromagnetic waves • Conduction – touching • Convection- through a fluid (liquid or gas) • All 3 work together to heat the troposphere but Convection causes most of the heating. Radiation, Convection and Conduction work together to heat the troposphere.