Lecture 1. Course Introduction
advertisement

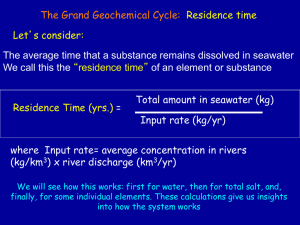
Midterm #1 results posted early next week see BlackBoard Answer Keys for both White and Blue exams will be provided on course website Scantrons will be returned in labs next week Physical and Chemical Structure of the Ocean Why are the oceans blue? How is sound transmitted in the ocean? Why is the ocean “layered” in many locations? How do you keep your beer cool in the tropics? Light Absorption in Water Intensity decreases rapidly with depth Blue and green penetrate deepest, giving the ocean its color Why do objects lose their color with depth? The colors other than blue (and green) are absorbed by the water molecules in the first few meters -only blue (and green) are reflected Sound in Sea Water Sound is transmitted better in water than it is in air Sound velocity in the ocean is about 1500 m/s, or about 4 times its speed in air Sound velocity increases with pressure and temperature SOFAR Sound Channel Sound is focused into the SOFAR channel because it is a low velocity region Sound is transmitted best through this channel -- good for whales and submarines (e.g., “Hunt for Red October”) Heard Island Experiment Global Warming -- faster velocity?? Go to Sounds Ocean Temperature Solar Heating Uneven heating of Earth’s surface Release of heat as infrared radiation Requires flow of heat by oceans and atmosphere Surface circulation Global Heat Budget heat at the Earth's surface (342 W/m2) is supplied by absorption of ‘short-wave’ solar radiation from the sun. heat lost from Earth is through long-wave radiation back to space. The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere is transparent to sunlight (ultraviolet [UV] and visible) Clouds absorb or reflect about half Sunlight heats the Earth’s surface, which then radiates energy as longer wavelength energy (infrared) This energy is trapped by the atmospheric gases (CO2, H2O, CH4) Special Properties of Water RECALL: Melting and boiling points are very high Highest heat capacity of common liquids High heat of fusion and vaporization Sea Surface Temperatures only 0°-30°C world-wide Land: 50°C to 50°C Local Annual Heat Budgets Amount of solar energy captured at one location on the Earth varies with season Local Annual Heat Budgets Where we live Amount of solar energy captured at one location on the Earth varies with season Temperature (vertical profile) Seasonal changes in temperature profile Temperature (vertical profile) Thermocline Cool drinks go here Temperatures with Depth Thermocline -- sharp temperature change Evaporation - Precipitation Over the oceans, evaporation exceeds precipitation The balance is restored by rain over the continents, returning water via rivers Evaporation vs Precipitation Climate Belts Ocean Surface Salinity Salinity Variations Salinity Variations Surface salinity follows evaporationprecipitation pattern Atlantic Ocean is generally more salty than Pacific Ocean, in spite of river input -- why?? Isthmus of Panama Net transfer of fresh water from Atlantic to Pacific Salinity of Rivers and Ocean Water Can’t just concentrate river water to get seawater How do we explain this observation? Rivers Ocean Concept of Residence Time Each element removed from ocean in different ways And at different rates e.g. Cl- vs. SiO2 Residence Time Flux has units of mass per unit time Reservoir has units of mass R/F has units of time Density of Sea Water (Where does Oregon’s seawater plot?) Density of Sea Water (Where does Oregon’s seawater plot?) Oregon’s ocean Bottom Water Density Rules! Where does the Ocean’s Deepest Water Come From? The densest seawater is COLD and SALTY This is formed at high latitudes in the North and South Atlantic: North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW) Could dense seawater form in the tropics? (evaporation!) Dissolved Gases in the Ocean Important Gases in the Ocean Oxygen -- Respiration, Decomposition CO2 -- Photosynthesis, CaCO3 Nitrogen -- Nutrient for growth (NO3) Methane -- a product of decomposition Photosynthesis and Respiration Biology interacts with the Chemistry Dissolved Oxygen Biochemical Recycling Summary: Biochemical Cycles Elements enter oceans through rivers Gases enter oceans thru air-sea boundary Biology alters distribution of elements (“nutrients”) and gases Ocean circulates nutrients to surface, but only in a few places (called “upwelling”) Interaction of physics, chemistry and biology => geological record (sediments)