Chapter 14 - Earth`s Interior
advertisement

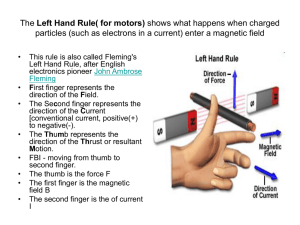
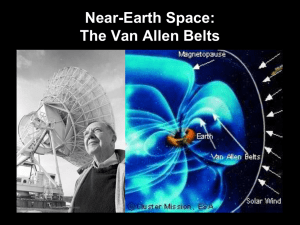
Grotzinger • Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 14: EXPLORING EARTH’S INTERIOR © 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 14 Exploring Earth’s Iinterior About Earth’s Interior • The center of the Earth is about 6,400 km below us … the deepest well is 10 km. • Heat inside the Earth drives the core’s geodynamo and the mantle’s convection. • Earth’s interior is explored by using information from seismic waves and their passage through the body of the Earth. Lecture Outline 1. Exploring the interior with seismic waves 2. Layering and composition of the Earth’s interior 3. Earth’s internal temperature 4. Visualizing Earth’s 3-D structure Lecture Outline 5. Earth’s magnetic field and the geodynamo 1. Exploring the Interior with Seismic Waves ● Basic types of waves ● compressional (P waves) ● shear (S waves) ● Reflection and refraction 1. Exploring the Interior with Seismic Waves ● Paths of seismic waves ● wave bending ● shadow zones (P and S) ● reflection at internal boundaries P- and S-wave paths from an earthquake P-, S-, and surface-wave paths: from focus to seismograph P, S, and surface waves recorded on a seismograph 2. Layering and Composition of the Interior ● Seismology model of Earth’s layers ● crust and lithosphere ● asthenosphere ● mantle with internal phase change at 400 km 2. Layering and Composition of the Interior ● Seismology model of Earth’s layers (continued) ● core-mantle boundary ● core (inner and outer core) Earth’s layering revealed by seismology Earth’s mantle structure beneath an old ocean basin: S-wave velocity to depth of 900 km 3. Earth’s Internal Temperature ● Heat flow through Earth’s interior ● conduction (lithosphere) ● convection (mantle and core) Topography of mid-ocean ridges in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans 3. Earth’s Internal Temperature ● Temperatures in the Earth ● geothermal gradient ● normally 20 to 30ºC / km ● 13001400ºC at base of lithosphere ● 30006000ºC + in core An estimate of the geotherm: temperature increase with depth in the Earth 4. Visualizing Earth’s 3-D Structure ● Seismic tomography ● Earth’s gravity field ● The geoid Mantle structure The geoid: shape of planet Earth 5. Earth’s Magnetic Field and Geodynamo ● Earth’s dipole field ● complexity of the magnetic field ● non-dipole field component ● secular variations in the field ● magnetic reversals Change in the location of the North magnetic pole from 1600 to 2000 5. Earth’s Magnetic Field and Geodynamo 5. Earth’s Magnetic Field and Geodynamo 5. Earth’s Magnetic Field and Geodynamo Earth’s magnetic field lines Earth’s magnetic field reversals: Step 1 Earth’s magnetic field reversals: Step 2 Earth’s magnetic field reversals: Step 3 Earth’s magnetic field reversals: Step 4 5. Earth’s Magnetic Field and Geodynamo ● Paleomagnetism ● records of magnetization ● thermoremanent ● depositional remanent ● magnetic stratigraphy Thermoremanent Depositional remanent Paleomagnetic time scale 5. Earth’s Magnetic Field and Geodynamo ● Magnetic field and the biosphere ● magnetic orientation ● magnetic frame of reference ● field offers protection from Key terms and concepts Compression wave Conduction Convection Core-mantle boundary Depositional remanent magnetism Dipole Geotherm Isostasy Low-velocity zone Lower mantle Mohorovičić discontinuity Paleomagnetism Phase change Seismic tomography Shadow zone Key terms and concepts Shear wave Thermoremanent magnetization Transition zone Upper mantle