Sikand_Satellites - Stevens Institute of Technology
advertisement

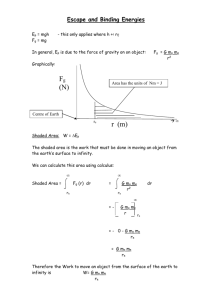
QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Satellite Motion Monika V Sikand Ph.d Student Stevens Institute of Technology Department of Physics. Light and Life Laboratory. Hoboken. OBJECTIVE • • • • Review laws of motion and gravitation Satellite motion Escape velocity Geosynchronous orbit(Telecommunication satellites) Newton’s laws of motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Isaac Newton January 4, 1643 -March31,1727 QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. What is Gravity? Gravity is a pulling force It pulls things down towards the earth Things fall because of gravity Things always fall down Why do people not fall off the earth? QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Newton’s Law of Gravitation Gravity holds everything and every one on the earth In Space, Gravity keeps the planets moving around the sun Gravity on earth and moon QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. So how can we understand orbital motion? Motion of the ball on earth QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Example Earth’s curvature Satellite QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Smaller body revolving around a larger body Natural satellites QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Moon, planets, comet Artificial satellites QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Weather , spy , communication Escape velocity Artificial satellite in a circular orbit around earth first achieving a speed of 7900m/s. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. If speed greater than 7900m/s satellite has a elliptical orbit. If velocity greater than 11km/s then satellite leaves earth’s orbit and has a escape orbit. The escape orbit’s velocity is called escape velocity. Figure 7-22 Satellite orbits Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) Orbit is synchronous with the earths rotation. From the ground the satellite appears fixed. Altitude is about 22,300 miles or 36,000Km. Coverage to 40% of planet per satellite. Conclusion • Newton’s law of gravitation F =Gm1m2/r2 • Satellites are revolving bodies around earth. • Escape velocity is the maximum velocity required to escape the earth’s orbit. • Geostationary orbits are synchronized with earth’s rotation at 36000 km of height.