New Imperialism
advertisement

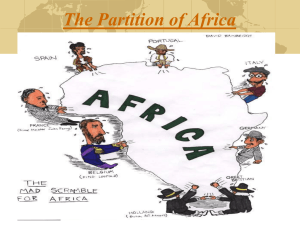
New Imperialism New Imperialism The extension of a nation’s power over other lands. European nations want to expand trade with Asia and Africa for European markets Want direct control Some key events that still impact us today… Competition among European nations leads to the partition of Africa Colonial rule creates a new social class of westernized intellectuals British rule brought order and stability to India, but with its own set of costs. As a colonial power, the United States practiced many of the same imperialist policies as European nations. Europeans wanted control of raw materials and markets. New Imperialism was tied to racism and Social Darwinism – “the fittest will survive” Some believed that Westerners had a moral right to civilize Asia, Africa and Latin America. They must Christianize them. By 1900, most of Southeast Asia was under Western control… Great Britain Singapore Burma France Vietnam becomes a protectorate Cambodia-Annan-TonkinLaos= French Indochina Thailand Only remaining free state in Southeast Asia King Mongkut and King Chulalongkorn – Promote Western learning and remained friendly with European powers Thailand acts as an independent buffer between France and Britain in Southeast Asia and remains independent British control over South America, French control over Indochina, and Spanish control over Mexico are examples of… 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Isolationism Appeasement Nonalignment Imperialism Response Grid 10 Countdown Which of the following was a major reason why European nations colonized other nations? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Need for raw materials Fear of Asian dominance Surplus of manufactured goods Desire to learn about other cultures Response Grid 10 Countdown What was a major factor that allowed imperialist powers to dominate large parts of Asia and Africa in the 19th and 20th centuries? 0% 0% 0% 0% Technological and military superiority 2. Desire of Asians and Africans to convert to Christianity 3. Willingness of imperialists to respect local traditions/customs 4. Spread of nationalism among slave peoples in colonial areas 1. Response Grid 10 Countdown What was an important motive behind the European desire to obtain colonies in Africa in the late 1800s 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 0% 3. 4. ? Africa’s valuable minerals like gold and diamonds Africa’s tea, silk, and other luxury goods Africa’s free labor for the Americas Africa’s advanced industries Response Grid 10 Countdown Which European country in the late 19th century controlled so many colonies around the world that it was said “the sun never set” on its flag? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. France Germany Great Britain Italy Response Grid 10 Countdown Participant Scores 500 Participant 10 500 500 500 500 Participant 19 Participant 6 Participant 23 Participant 2 Goal was to exploit countries natural resources. Rule – allow local rulers to remain in power, yet still answer to the government that had conquered. Westerners argued that they brought civilization to these countries. Indirect Direct Rule – your government runs the new country. Westerners feared indigenous people gaining political power. Native people worked low level jobs for poverty wages. High taxes were placed on peasants. Colonial rule did bring benefits. Modern economic systems began. Improved infrastructure. Expanded exports. Some became Western educated and became professionals. Peasant Revolts Nationalism the reason for revolts. Most revolts were handled with great force. 1930’s begins revolts that bring independence. Africa Africa Europeans did not hesitate to deceive Africans in order to get their land and natural resources. All of Africa under European rule from 1880 – 1890. Slave trading declared illegal in 1890’s by the world. West Africa Slave trade Europeans seek to trade textiles and manufactured goods for natural resources Encouraged by trade – Europeans push for more permanent presence – 1874: Britain annexes the west coastal states as the first British colony of Gold Coast – Britain also establishes protectorate over Nigeria – 1900: France adds parts of West Africa – Germany controls Togo, Caeroon and German Southwest Africa (now Namibia) North Africa Muhammad Ali Suez Canal (NOT ) – Connects Mediterranean to Red Sea – French build canal – links Britain to India… Take great interest in Egypt… Own Suez Canal…Egyptians revolt…Egypt=English protectorate in 1915 – Look to Sudan… Sudan Sudanese resist British rule- 1885 Britain unable to claim Sudan until 1898 Central Africa David Livingstone – Explores the interior of Africa and disappears – Henry Stanley sent to find him “Dr. Livingstone, I presume” King Leopold II Belgian king Real driving force behind the colonization of Central Africa ‘Heart of Darkness’ written about Belgians in the Congo East Africa British and Germany fight over territory In the 19th century, European countries claimed that the conquest of Africa would bring the benefits of Western civilization to that continent. From the perspective of the African peoples, the result was… 0% 0% 0% 0% Loss of political independence 2. Fewer agricultural products for foreign trade 3. New national boundaries based on ethnic and cultural similarities 4. Global appreciation for African cultures and encouragement of their development 1. Response Grid 10 Countdown The belief that it is the right of the strong to take over the weak is known as… 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Social Darwinism Imperialism Racism Creationism Response Grid 10 Countdown 0% 0% 0% 0% The European policy of paternalism reflected the belief that Africans should be.. 1. Separated into ethnic groups 2. Trained to function as leaders 3. Watched over and taken care of 4. Granted more rights and freedoms Response Grid 10 Countdown Which of the following is an example of a positive effect of imperialism? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Wealth Stable economies Lasting stability Roads Response Grid 10 Countdown European colonial actions sometimes resulted in tribal conflict among native Africans. Which colonial practice most frequently resulted in such conflict? 0% 1. 2. 0% 0% 0% 3. 4. Europeans let Africans remain in power Europeans created artificial borders in Africa Europeans converted Africans to Christianity Europeans spread democracy in their colonies Response Grid 10 Countdown Participant Scores 400 Participant 5 400 400 400 400 Participant 9 Participant 7 Participant 20 Participant 23 South Africa Original Dutch settlers--- Boer descendants British take over– Boers leave Boers fight the Zulu people Zulus lead by Shaka, a talented ruler British get involved and defeat Zulu after Shaka’s death British fight Boers, and win – Angered by guerrilla tactics – 1910: British create Union of South Africa To appease voters, only whites can vote By 1914, only Liberia remains free in the entire continent of Africa… – Why Liberia? – Created by freed American slaves – Back to Africa Movement and Marcus Garvey How to rule… Britain relied on existing political elites to govern their territories. Most European nations used direct rule. – French wanted to assimilate the Africans. No more traditions. New African leaders emerge. 20th century sees Western educated Africans lead their people. Organized political parties and movements to end foreign rule. Many admired Western life and wanted to bring it to their nation. African Independence During the 1950s and 60s, most African nations gained their independence. Ghana, formerly the Golden Coast, was the first in 1957. South Africa – African National Congress helped lead the fight. By the 1950s, South African whites, Afrikaners, ruled. Strengthened laws separating whites and blacks. Racial segregation – Apartheid Blacks demonstrated – Nelson Mandela is jailed. (life sentence). Armed resistance is called for . Most new African leaders were Western educated. Most wanted Western Democratic model used for Africa. Some wanted Pan-Africanism : unity of ALL African nations. 1976 – UN asks for end to Apartheid, boycott trade. 1985: Mandela offered freedom, he refuses Bishop Desmond Tutu works to free Mandela. 1990 – FREEDOM 1994 – becomes their first black president. After Independence Many nations rely on a single crop – drought. Corruption and bribery. 1957-1982 : over 70 leaders are overthrown ruled, by military. Some democracies emerge. Poverty is widespread. AIDS has hit these nations the hardest. Women do not have total equality to men. Many still live in rural areas. One factor that motivated imperialism… 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 0% 3. 4. Development of closer political ties with European nations Closing of China to all foreign trade Support of international peacekeeping operations Acquisition of new markets and sources of raw materials Response Grid 10 Countdown In the past, European nations have practiced imperialism. One reason for this is… 1. Industrialization in Europe and the need for raw materials 2. Desire to spread communism 3. European belief in human rights for all people 4. Request of developing nations for modern machinery and technology Response Grid 10 Countdown How did European colonizers view their mining of natural resources in Africa? 0% 0% 0% 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. It was a necessity for their countries to survive It was a way to preserve traditions in Africa It was a way to protect Africans from the Industrial Revolution It was their right to take what they wanted Response Grid 10 Countdown Imperialism affected almost the entire continent of… 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Africa Europe Australia North America Response Grid 10 Countdown This is the country in which apartheid is practiced. 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Egypt India South Africa England Response Grid 10 Countdown Participant Scores 0 Participant 1 0 0 0 0 Participant 2 Participant 3 Participant 4 Participant 5 INDIA India controls India in 18th century. 1857 – Sepoy Mutiny – bullets greased with cow fat (sacred to the Hindus). Revolt crushed in a year. Britain 1876: Queen Victoria named Empress of India as a result of the revolt. Greatest cost to Indian people was economic hardships. Large taxes from peasants. Switch from growing food to cotton to benefit Britain. 30 Million die as a result 1800-1900. Leads to Armritsar Massacre British rule degraded even the elite Indian. (Racial tensions) Top jobs still given to British. 1915 – Mohandas Gandhi leads independence movement. Most of these nations eventually fought for their independence and won, some not until the 20th century. Indian Independence Which was NOT a cost of British rule of India? 0% 1. 2. 0% 3. 0% 0% 4. Destroyed local industries Degraded even elite Indian citizens Shipped food from Burma, causing livestock to starve Started producing cotton, which led to food shortages Response Grid 10 Countdown The Sepoy Mutiny in India and the Islamic Revolution are similar in that… 0% 0% 1. 2. 3. 0% 0% 4. Restored power to the hereditary monarchy Attempted to reject traditions Resisted foreign influence Reestablished the power of religious leaders Response Grid 10 Countdown In ________imperialism, countries would set up trading posts but would not entirely control other nations. 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. New New elite Old school Old Response Grid 10 Countdown Which was NOT a motivation for new imperialism? 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Economic motives Expansion of industrialization Desire for political power Sense of racial superiority Response Grid 10 Countdown Both France and England wanted control of Egypot because Egypt had…… 0% 1. 0% 2. 0% 3. 0% 4. Control of the spice trade An industrial-based economy Vital mineral resources A strategic location Response Grid 10 Countdown Participant Scores 0 Participant 1 0 0 0 0 Participant 2 Participant 3 Participant 4 Participant 5