Photosynthesis
advertisement

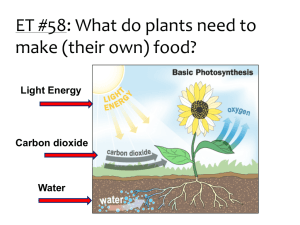
Photosynthesis Conversion of solar energy to chemical energy Photosynthesis – Source of • • • • • • • • Coal Oil Gas Wood Alcohol Grains Fruits Veggies • • • • • • • • Meat Eggs Dairy foods Medicines Flavorings Paper Clothing Plastics Photosynthate -- How Much? • 1.4 x 1014 Kg of CO2 is • converted to carbohydrate yearly (3.1 x 1014 lb) The total weight of humanity (5B x 125lb) = 6.25 x 1011 lb, or 1/1000th the amount • The amount of carbon fixed would yield enough coal to fill 97 railroad cars every second of every hour of every day all year long! Solar Energy Conversion Efficiency • • • • Solar energy --------> Chemical energy 0.1% for poor growing conditions with clouds 3% for intensive cropping 25% for plants grown in controlled laboratory conditions Photosynthesis • Green leaves • CO2 from air • Water from soil • Light from the sun Photosynthetic light: Photosynthesis Products • • • • • Sucrose 6 C Sugar Phosphates 5 C Sugar Phosphates Water Oxygen Photosynthesis Equation nCO2 + nH2O -----------------> (CH2O)n + nO2 Conditions = green plant and light 6CO2 + 12H2O ----> C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2 Photosynthesis Supplies O2 • C. B. Van Neil’s work in 1930 showed that water is the source of oxygen given off in photosynthesis Photosynthesis: Where in the cell? Chloroplast Where ‘dark’ reactions take place Where ‘light’ reactions take place Photosynthetic Rate Factors: • • • • Light Quality • Temperature Light Intensity • Water Light Duration • Plant development Carbon Dioxide and sourceConcentration sink relationships Photosynthesis - Light Quality • • • Pigments = chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids Action Spectrum Photosynthesis rate: net photosynthesis, total photosynthesis Photosynthesis and Light Intensity • • • • • • Sun plants Shade plants Moderate light plants Foot candles Lux PPF (umol•m-2•s-1 ) Photosynthesis -- Light Saturation • Photosynthesis is limited by CO2 concentration and by light intensity Photosynthesis and Photoperiod • The longer leaves receive light, the longer they photosynthesize, and the faster plants grow Photosynthesis and Carbon Dioxide • • • • CO2 in air = 0.03% < CO2 in air to 0.10% doubles photosynthesis rate Greenhouses are often CO2 enhanced Crops may benefit from wind machines Photosynthesis and Temperature • • When light is not limiting, photosynthesis doubles for each 10 °C temperature increase > Photosynthesis and < respiration at very high temps = low plant sugar storage Photosynthesis and Water • When plants lose water faster than they can replace it, water deficits cause stomates to close, leaves to wilt, and CO2 and O2 exchange to stop, resulting in > photosynthesis Source/Sink Relationships • • • • • • • Source = Photosynthesis (PS) Sink = Growth and development 1. Growth Sink - Growth creates demand 2. Nitrogen - N applications energize PS 3. CO2 increase - Increases PS 4. High light /short time - Increases PS 5. Senescence - Vegetative to reproductive Photosynthesis Types • • • C3 Plants C4 Plants Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) Plants Photosynthesis in C3 Plants • • • • Cereals, peanuts, soybeans, Most ornamental plants Bind CO2 with an enzyme (RUBISCO) that competes with oxygen Inefficient system Photosynthesis in C4 Plants • • • • C4 Plants grab CO2 by using a special acid This acid releases CO2 alone with enzyme so no competition with oxygen Efficient CO2 users, better water-use efficiency than C3 plants Corn, sugarcane, millet, crab grass, pigweed Photosynthesis and CAM Plants • • • CAM plants also fix CO2 with organic acids, but at night Cactus, pineapple, orchids Highest water use efficiency plants