States_of_Matter_BH
advertisement
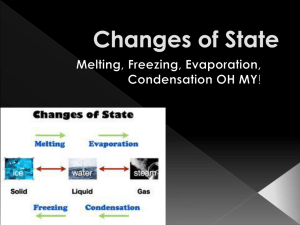
STATES OF MATTER MATTER • Affected by temperature and pressure • A change in temperature and/or pressure can change the state of matter of a substance Kinetic Theory: how particles in matter behave Three assumptions 1. All matter is made of small particles atoms, molecules and ions 2. These particles are in constant motion. The motion has no pattern. 3. These particles are colliding or crashing into each other and into the walls of their container. Thermal Energy • Thermal energy is the total energy of the particles in a material. • Thermal energy includes kinetic energy and potential energy • Solid particles do not appear to be moving but they are! Solid particles move slowly. Absorb or Release Thermal Energy • When particles absorb thermal energy then – Temperature increases or – Temperature remains constant and particles transition to more energetic phase of matter • When particles release thermal energy then – Temperature decreases or – Temperature remains constant and particles transition to less energetic phase of matter Temperature • Measure of the average kinetic energy of the vibrating or moving atoms or molecules of a substance • Absolute zero= no movement • Heat= the total kinetic energy of a substance Pressure • the force per unit area applied on a surface in a perpendicular direction These gas molecules are constantly moving in random directions. When a molecule hits the container wall (green), it exerts a tiny force on the wall. The sum of these tiny forces, divided by the interior surface area of the container, is the pressure. One atmosphere is defined as the pressure caused by the weight of all the overlying air at sea level or 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi). Solid http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/liquids/character.html http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_solid.html • Low Temperature and/or High Pressure • Low Kinetic energy • Definite pattern resulting in definite volume and definite shape • Can be an atom, ion or molecule • Usually in crystalline form, although some are glass Itl.chem.ufl.edu/2045_s00/lectures/fg11_001.GIF Liquid http://www.mcwdn.org/chemist/liquids.html http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/liquids/character.html • Less Pressure, More Kinetic Energy • Definite volume, no definite shape • Melting point= the vibrations of the particles cause the forces holding the solid together to break • These forces are called attractive forces. Itl.chem.ufl.edu/2045_s00/lectures/fg11_001.GIF Gas http://www.mcwdn.org/chemist/gases.html http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/liquids/character.html • Least pressure, most kinetic energy • No definite shape, no definite volume • Evaporation is the boiling point of the liquid • Gravity – prevents escape of gases • Gas would escape to space if not for the Earth’s gravity Itl.chem.ufl.edu/2045_s00/lectures/fg11_001.GIF Plasma • Hot ionized temperatures above 5000°C • Violent collisions cause electrons to be knocked off • Stars, lightning, neon signs, solar wind, auroras, comet tails, welding arcs, fireball made by nuclear weapons http://dewa.com/animated/ Condensation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Condensation • Change in matter to … a denser stage through colder temperatures or more pressure http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Condensation • Gas phase to a liquid phase http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/watercyclecondensation.html Sublimation • Skip a Phase: Solid-->Gas • Carbon dioxide (dry ice), Naphthelene (moth balls) and snow sublime http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/watercyclesublimation.html http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/watercyclesublimation.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/comets/sublimation.html&edu=high Conservation of Matter and Energy • During an ordinary chemical change, there is no detectable increase or decrease in the quantity of matter. LAW • Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change its form. http://dewa.com/animated/ Phase Change From a To a Absorbs or Releases Thermal Energy Condensation gas liquid releases liquid solid releases solid liquid absorbs liquid gas absorbs solid gas absorbs Freezing Melting Evaporation Sublimation Absorb or Release Thermal Energy? http://www.cmmacs.ernet.in/~himesh/Hydrosphere%20Components.gif Recap of Phase Changes • Melting – Solid to • Freezing – Liquid to • Evaporation – Liquid to • Condensation – Gas to • Sublimation – Solid to