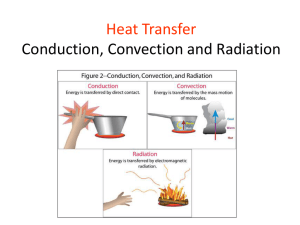
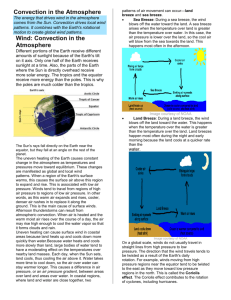
Key Idea 18 Solar Energy
advertisement
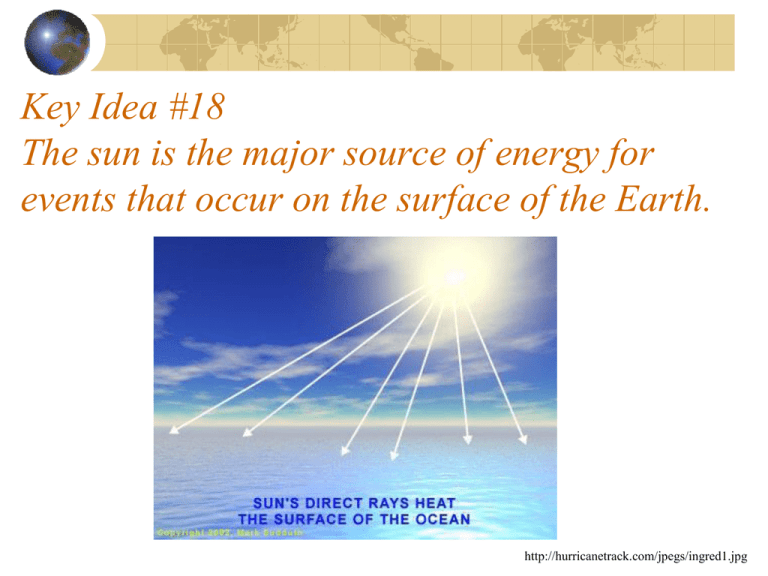
Key Idea #18 The sun is the major source of energy for events that occur on the surface of the Earth. http://hurricanetrack.com/jpegs/ingred1.jpg The Sun and Weather Nuclear reactions that take place in the sun produce large amounts of heat and light. aerospaceguide.net,shatters.net From Solar Energy to Heat http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uO WzNBXk3ss The direct transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves from the sun, is called radiation. Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or molecules. The sun sends energy to the Earth in the form of infrared radiation which is transformed into thermal (heat) energy after it arrives on Earth. The energy that heats Earth’s atmosphere and surface comes from infrared radiation from the sun. http://forces.si.edu/atmosphere/04_00_22.html Only a small percent of light energy from the sun that hits the Earth produces heat energy on Earth. • Most of the sun’s energy is either reflected or absorbed by particles in the atmosphere. http://assets.panda.org/img/original/faq_1_3_fig_1.jpg Earth’s Seasons http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dui QvPLWziQ The heating of the Earth at any location is related to the angle of the sun. (See book pgs 118-119.) The hemisphere tilted toward the sun receives more direct sunlight and experiences spring and summer. The hemisphere tilted away from the sun receives less direct sunlight and experiences fall and winter. http://web.srv.cmes.utah.edu:8080/west/k12/EarthsTiltPic/view Light energy from the sun is changed into heat energy when it is absorbed by land and water on Earth’s surface. The heat energy transfers out of the ground or water and heats the air above by conduction. radiation conduction http://www.shorstmeyer.com/gifs/dayheat.gif Many of Earth’s surfaces reflect light energy away from the Earth. The color of the Earth’s surface affects the amount of heat that the Earth absorbs. Light colored surfaces reflect Dark colored surfaces absorb The large amounts of light energy that are reflected off Earth’s surface can’t be used directly as heat energy. teachingboxes.org Gases in the atmosphere that trap heat are called greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane. The greenhouse effect is the process by which these gases form a blanket around Earth trapping heat in the atmosphere. www2.uvawise.edu The greenhouse effect is very important to life on Earth. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere make the Earth warm enough to support life. Without it, temperatures on Earth would climb during the day and then drop below freezing at night. www2.uvawise.edu According to some scientists increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere may cause global warming by trapping more heat. http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://1.bp.blogspot.com/-cEnNhEynsTs/TYfgtk0RC3I/AAAAAAAAAlc/0u-K4pd-3TE/s1600/Greenhouse-effect.jpg&imgrefurl=http://whereismyka.blogspot.com/2011/03/natures-wake-up-call.html&usg=__Qkja9mpUQAwHKumYyHsFnKu4H0=&h=324&w=550&sz=40&hl=en&start=0&zoom=1&tbnid=NmslNjY57rHK1M:&tbnh=110&tbnw=187&ei=9ymrTc2EFsP1gAfH5JGCCQ&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dgreenhouse%2Beffect%2Band%2Bglobal%2Bwarming%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DN%26biw%3D1003%26bih%3D567%2 6tbm%3Disch0%2C201&um=1&itbs=1&iact=hc&vpx=463&vpy=189&dur=94&hovh=172&hovw=293&tx=155&ty=92&oei=9ymrTc2EFsP1gAfH5JGCCQ&page=1&ndsp=15&ved=1t:429,r:12,s:0&biw=1003&bih=567 FYI Many of the heat –trapping gases, such as carbon dioxide have come from the increased burning of fossil fuels. In the past, Earth’s huge forests have helped control the greenhouse effect by removing some of the carbon dioxide from the air. To slow down the overheating of the planet some scientists believe we need to decrease the use of fossil fuels and protect our forests. theresilientearth.com The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming Conduction, Convection and Radiation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Y3 mfAGVn1c Heat refers to the energy transferred from a hotter object to a cooler one. Heat can travel from one place to another in three ways: Radiation p. 49 Conduction p. 50 Convection p. 50 • Both conduction and convection require matter to transfer heat. 3n1-combinescience.blogspot.com Radiation is the direct transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves. Conduction is the transfer of energy by direct contact (touching). Convection is the transfer of heat energy through liquids and gases by moving particles. mit.whoi.edu esrl.noaa.gov Radiation, conduction, and convection in a lava lamp. Radiation The filament in the light bulb on a lava lamp transfers energy by radiation and heats the glass bottom of the lava lamp. Conduction The heated glass holding the “lava”, causes molecules to speed up and spread out. Convection The warm “lava” rises because it is less dense. The “lava” that is further from the energy source cools causing molecules to move closer together. The cooled “lava” sinks because it is more dense. There is a relationship between the warming of Earth’s atmosphere by the sun and convection within the atmosphere and oceans. http://www.propertiesofmatter.si.edu/images/L5/conv_cell_atmos_labeled.gif serc.carleton.ed Convection currents move warm air through the atmosphere and warm water through the oceans. http://www.propertiesofmatter.si.edu/images/L5/conv_cell_atmos_labeled.gif serc.carleton.ed The upward movement of warm air and the downward movement of cool air form convection currents in the atmosphere. Air will rise if it is warmer than the surrounding air. Warm air will eventually cool at higher elevations and sink. Convection currents in the atmosphere occur because cool air is denser than warm air. Cool, dense air sinks, which forces the warm, less dense air to rise. Convection currents cause most of the heating of the troposphere. http://www.propertiesofmatter.si.edu/images/L5/conv_cell_atmos_labeled.gif Cool air holds less water vapor than warm air because the particles are closer together. At a certain temperature and pressure, water vapor in a cooler air mass will condense into liquid water forming clouds and possibly precipitation. myweb.cwpost.liu.edu Radiation, conduction, and convection work together to heat the troposphere. http://www.kudzuacres.com/wwow/lessons/weather/radiationconduction.gif The warming of the Earth by the sun also produces winds and ocean currents. Convection currents move warm water through the oceans. The warm water moves above the cooler water, and gives off its heat to the surrounding environment. As the water cools, it begins to sink, warm water rises, and the process begins again. Convection results in the continual circulation of ocean water on a global scale. Convection also plays a role in the movement of deep ocean waters and contributes to ocean currents. Like air, warmer water is less dense and will rise above cooler water. Convection currents occur in the ocean because cooler waters sink and warmer waters rise toward the surface. The movement of water at various temperatures helps create ocean currents within the water column. chungpondemanisha.blogspot.com An ocean current is the movement of ocean water and is made up of warm or cool water. An ocean current is caused by the uneven heating and density of the ocean waters. (see p. 115) Wind is the movement of air from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. http://www.weatherquestions.com/wind.jpg FYI: Low Pressure Area (cyclone) Winds are counter clockwise. Warm air rises and spreads out resulting in decreasing air pressure and density. The warm air and the water vapor it holds cools and condenses. The condensed water vapor forms clouds resulting in storms and precipitation. FYI: High Pressure Area (anticyclone) Winds are clockwise. High-pressure centers contain cool, dry air. The high pressure and density is due to the molecules being closer together. Cool air moves downward and warms up. Warm air is forced to rise and the humidity drops. Areas of high and low pressure are caused by differences in the Earth’s temperature. Differences in Earth’s temperature are due to the sun’s uneven heating of the Earth’s surface. Winds develop as a result of differences in air temperature and air pressure. Unequal heating often occurs on land that is next to a large body of water. FYI: Land heats up more quickly than water. The warmer air over the land expands and rises, creating a low pressure area. Cooler air blows inland from the water and moves underneath the warmer air creating a wind known as a sea or lake breeze. FYI: At night land cools more quickly than water, so the air over the land becomes cooler than the air over the water. As the warmer air over the water rises, cooler air moves from the land to take its place. This flow of air from land to a body of water is called a land breeze. Land and Sea Breeze Animation http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es1903/es1903page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization Local Winds blow over short distances. form when no winds are blowing from farther away. are caused by the unequal heating of the Earth’s surface within a small area. Global Winds are the movement of air between the equator and the poles caused by the unequal heating of the Earth’s surface. blow from specific directions over long distances. Since Earth rotates, global winds curve instead of moving in a straight path.(The Coriolis Effect) In the Northern Hemisphere all global winds gradually turn to the right. In the Southern Hemisphere all global winds gradually turn to the left. FYI: If Earth didn’t rotate, global winds would blow in a straight line from the poles to the equator. The Sun and Weather FYI: Beaufort Wind Scale