DPT & Relative Humidity Charts
advertisement

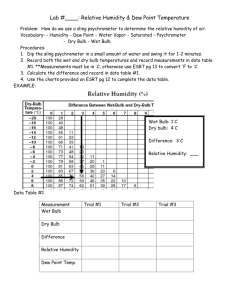
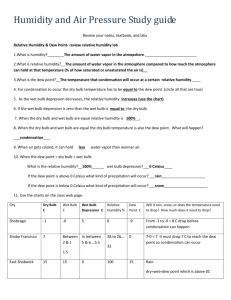
Topic: Moisture in the Atmosphere Water enters the Atmosphere by A) --- Mainly from Ocean 70% Earth’s surface Factors Effecting Evaporation Rate a) Surface Temperature Increases --- b) Surface Area Increases --- Evaporation Puddle A Evaporation Puddle B c) Humidity increases --Air is filled with water, no more evaporation. Evaporation Lake d) Wind Speed Increases -> --- Lake B) --- Evaporation and Transpiration = Evapotranspiration Water is found in all phases in the atmosphere Solid – Clouds, snow 2) Liquid – Clouds, rain 3) Gas - Water vapor 1) How do we measure moisture in the Atmosphere Humidity --- Relative Humidity --- --- Dew Point --- Condensation What happens when the air temperature and dew point are the same? Sublimation / Deposition FROST SNOW Tools used to find Dew Point & Relative Humidity ----- Measuring Relative Humidity Today you need your ESRT out Dew Point & Relative Humidity Charts Best Friend - pg 12 The “Dry Bulb” = Air Temp Don’t let it fool you. It is just a thermometer. 20°C The “Wet Bulb” Has a little wet booty tied to the bottom. Gets cool when water evaporates. Wet Booty 12°C A Dry Day… A lot of moisture will evaporate. The wet bulb will be a lot cooler than the dry bulb. 20°C Difference between wet bulb & dry bulb is 12 °C. 20°C 14°C 12°C 8°C A Humid Day… A little bit of moisture will evaporate. The wet bulb will not be much cooler than the dry bulb. 20°C Difference between wet bulb & dry bulb is 6 °C. 14°C Dry-bulb temperature = air temperature. 20 °C 14 °C Subtract (the difference) between the dry bulb and wet bulb 20°C 14°C 20-14=6 18°C 16°C 18-16=2 Put it all together 20°C 8°C 20-8=12 Relative Humidity = 11% 14°C 10°C 14-10=4 Relative Humidity = 60% The Dew Point Chart works the same way 14°C 10°C 14-10=4 Dew Point = 6°C Try These. Dry Bulb Wet Bulb 26°C 20 °C 14 °C 14 °C 0 °C -3 °C R Humidity DPT % % % °C °C °C Dry Bulb Wet Bulb 21°C 19°C 17 °C 17°C 70°F °C 60 °F °C R Humidity DPT % % % °C °C °C