Age of Exploration
advertisement

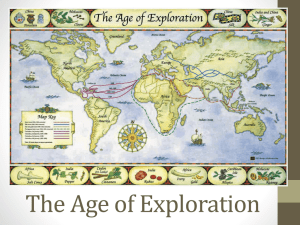
Age of Exploration Scientific Advances from the Renaissance led directly to the advances made in Exploration at this time. Age of Exploration: Technology • Mapmaking improved during this time – Americas not yet known – Believed they could reach Asia by sailing West • Navigation - just as important to Exploring as Mapmaking – Compass - used to give sailors their direction – Astrolabe - used to give their position • New Ships - no longer used oars to travel upwind – New sails made travel faster and easier – Rudders - made steering easier Exploration: Economics • Commercial Revolution - period from 1400’s to 1700’s – Economy underwent massive fundamental changes – Joint Stock Companies - merchant band together to form business • Owners raise money by selling stock in company • Investors who bought stock became part owners • All shared in profit – Coins produced with fixed values (standard system of money) – Monarchs supported exploration as a way to gain riches and resources through discovery Exploration: Economics • Mercantilism - a country’s government should do all it can to increase that country’s wealth – Favorable balance of trade - country brings in more gold and silver than it pays out – Tariffs - taxes on imported goods (discourages buying of foreign goods) – Subsidies - grants of money to help out businesses – Colonies - used to bring in gold, silver and resources to affect a favorable balance of trade Age of Exploration: The Americas • Spain and Portugal are 1st to begin exploration • Portugal heads east around Africa • Spain heads west • Columbus discovers Americas (hispaniola) • Begins the first trade (exploitation??) b/w Europe and the Americas Exploration: Americas QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • Columbian Exchange – Potatoes, tomatoes, beans, and corn, introduced to Europe – Horses introduced to Americas – Europeans also brought diseases (smallpox, malaria, etc.) Exploration: Americas QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • Spain and Portugal often claimed the same lands • Treaty of Tordesillas Treaty to decide who claimed what by using a imaginary line running north and south – Spain claimed west of the line – Portugal claimed east Exploration: Americas QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • Plantations - large agricultural farms that needed much labor • As need for labor increased so did need for slaves • Triangular Trade – Goods and Weapons to Africa – Slaves to Americas (middle passage) – Sold for goods in Americas which were shipped back to Europe Exploration: Colonization Map QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Age of Exploration: China • China actually began exploration before the Europeans (1100’s -1400’s) • Had great ability to become a seafaring nation • China abandons exploration – Ming rulers wanted China to be self-sufficient – Nomadic tribes to the north were threatening China – Didn’t have enough $ to defend China and explore overseas Age of Exploration: China • Portuguese arrive in 1514 • Jesuits arrived with them – Gain influence of Emperor by using their knowledge of astronomy – They helped revise Chinese Calendar – Gradually Jesuits gained great power • Chinese becomes suspicious of Christians – Were worried about their allegiance to the Pope and not to the Emperor Age of Exploration: China • Chinese Culture • Qing Dynasty – Emphasis on Confucianism – Qing were not Chinese (Manchus) – Separate laws for Manchus and Chinese – Chinese had to wear hair in a queue (symbolised Chinese submission to Qing) QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Age of Exploration: China • Portuguese sign trading treaties with China • As more and more countries arrive China is forced to sign treaties under threat of invasion – These are known as the “unequal treaties” QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Age of Exploration: China • Great Britain and other European Powers showed little concern for Chinese culture and people • Taiping Rebellion (1850-1864) – Chinese rebellion against the Qing – Rebellion weakens the government immensely Age of Exploration: Japan • Japan was a Feudal Society in the 1500’s much like Medieval Europe – Ruled by local lords called Daimyo • Japan was unified by 3 warlords (Oda Nobunaga, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, Tokugawa Ieyasu) – Tokugawa Ieyasu sets up a government known as the Tokugawa Shogunate Exploration: Japanese Class Structure QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Age of Exploration: Japan • Portuguese arrive in Mid 1500’s • Brought 2 new items to Japan – Muskets and Christianity – Muskets weakened the Samurai Class • Closing the Society – Shoguns felt Catholics were less loyal than other citizens – Kicked out Europeans and Christians – Japan only would trade w/ the Dutch a few months out of the year – Shoguns focused on domestic affairs and ignored outside world Age of Exploration: Japan • China and Japan were both pressured by Europeans for Trade • United States finally opens trade with Japan in 1854 • Japanese reformers overthrow Tokugawa Shogunate • Set up Meiji Government – Meiji want to modernize Japan to be on equal footing with Europeans and USA