Slide 1 - sheridanhistory

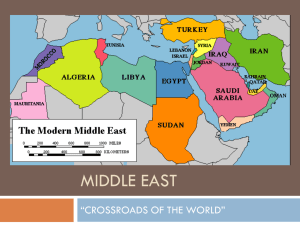
Geography of the
Arabian Peninsula
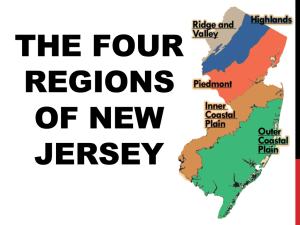
The Four Geographic Regions of the
Arabian Peninsula
• The Desert
• Oases
• Coastal Plain
• Mountains
The Desert
The Desert
• The desert climate is extreme.
• Rainfall is less than 10 inches per year.
The Desert
• Summer temperatures can exceed 120 degrees in the shade.
• Winter temperatures can drop below freezing.
The Desert
• Extremes prevent the development of a solid cover of vegetation.
• Winds create dunes reaching 500 feet high.
The Desert
• Arabian deserts contain wells of salty water, low shrubs, and clumps of tough grass.
• This provides good grazing for camels, sheep, goats, and jackrabbits.
The Desert
• Most of the land of the Arabian peninsula is desert.
• This provides a natural barrier from foreign conquest.
An Oasis
An Oasis
• An oasis is a fertile place in the desert where a spring or a well provides a water supply.
An Oasis
• Main source of lifegiving water and green pastures for camel herds and other grazing animals.
• Nomads travel from oasis to oasis seeking pastures for camels to graze.
An Oasis
• Vegetation in oases consisted of date palms, orchard and ground crops such as myrrh and frankincense.
• Spices were used for religious, medicinal, sanitary and cosmetic purposes.
Oases
• Also became trading centers.
• Nomads bought camel meat and milk.
• Also traded were spices, perfumes, precious metals, ivory and silk.
• Another thing that was traded was ideas .
Coastal Plain
Coastal Plain
• A coastal plain is level land extending along a coast.
• It separates a plateau from the sea.
Coastal Plain
• The coastal plain of the Arabian
Peninsula is more humid than the interior due to its proximity to the sea.
A City on the Coastal Plain
• The Arabian Peninsula has a few deep harbors to encourage seafaring but not one river to provide interior transport and communication.
People of the Coastal Plain
• People living on the coastal plain became effective traders.
• Most of the trading cities are located along the coastal plain.
Advantages of the Coastal Plain
• The coastal plain of
Arabia has one major advantage over the other geographical areas: RICH
AGRICULTURE.
• This region contains most of the cultivated land of the peninsula.
Advantages of the Coastal Plain
• Crops included: coffee, grains, and fruits.
• This cultivation, along with trading, allowed people to develop complex civilizations.
Mountains
Mountains
• Mountains stretch along the coast of the
Arabian Peninsula about 50 miles from the sea.
Mountains
• This causes the climate to be different from the interior basin.
• During the rainy season, flash floods are common.
A Mountain Settlement in Yemen
• Annual rainfall is 20-
30 inches.
A Mountain Settlement in Yemen
• Farmers created banks of earth called terraces to irrigate crops.
• They fertilized with manure and ashes from cooking fires.
A Mountain Settlement in Yemen
• This system of farming produced a number of crops such as dates and oranges.
A Mountain Settlement in Yemen
• Mountains tend to seal people off from the desert and beyond.
• People of the mountains can maintain their culture and traditions.
A Mountain Settlement in Yemen
• Today, homes built of mud brick are decorated with bands of color.
• This is a tradition from ancient times.
The end?
Geography of the Arabian Peninsula
• Assignment :
• Draw a picture and label each of the four types of geography of the
Arabian Peninsula:
Desert , Oases ,
Coastal Plain , and
Mountains
• Write one sentence about each and color