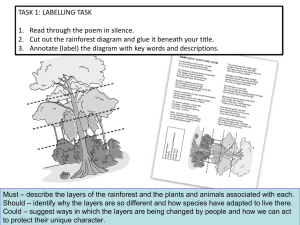
Stratification
advertisement

Vertical layering – usually of plants. Vertical layering – usually of plants. Best seen in a forest Vertical layering – usually of plants. Best seen in a forest Animals can also form vertical layers in the soil, and in lakes/sea o Dragonfish The deep sea dragonfish is a ferocious predator in spite pf its small size. The dragonfish has a long barbel attached to its chin. This barbel is tipped with a lightproducing organ known as a photophore. These fishes are sexually dimorphic (the males and females look different). Dragonfishes live in deep ocean waters at depths of up to 1500 m (5000 feet). Vertical layering – usually of plants. Best seen in a forest Animals can also form vertical layers in the soil, and in lakes/sea In tropical forests, the animals form verticals layers through things like – monkeys staying in the canopy without ever going onto the ground. Vertical layering – usually of plants. Best seen in a forest Animals can also form vertical layers in the soil, and in lakes/sea In tropical forests, the animals form verticals layers through things like – monkeys staying in the canopy without ever going onto the ground. General layers in a NZ forest: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Vertical layering – usually of plants. Best seen in a forest Animals can also form vertical layers in the soil, and in lakes/sea In tropical forests, the animals form verticals layers through things like – monkeys staying in the canopy without ever going onto the ground. General layers in a NZ forest: Canopy Sub-canopy Tree fern layer Shrub layer Forest floor layer Litter layer Fill in the layers of stratification 1. 2. 3. 4. Litter layer Topsoil layer Sub-soil layer Soil parent material Dominant plants in canopy – filter sunlight, cut down the wind, drop the temperature, and increase humidity. There a different micro-climates which form at each level. Dominant plants in canopy – filter sunlight, cut down the wind, drop the temperature, and increase humidity. There a different micro-climates which form at each level. EG. Beech forests – uncomplete canopies. Can be uneven, with sub-canopy filling space Dominant plants in canopy – filter sunlight, cut down the wind, drop the temperature, and increase humidity. There a different micro-climates which form at each level. EG. Beech forests – uncomplete canopies. Can be uneven, with sub-canopy filling space EG. In soil – leaf-litter animals are dark coloured and active. Dominant plants in canopy – filter sunlight, cut down the wind, drop the temperature, and increase humidity. There a different micro-climates which form at each level. EG. Beech forests – uncomplete canopies. Can be uneven, with sub-canopy filling space EG. In soil – leaf-litter animals are dark coloured and active. EG. Topsoil, animals aren’t so dark and are slower-moving, while sub-soil animals are usually large, sluggish (pun!) and pale. Bands of organisms may form in relation to a gradient in a major environmental factor = zonation. Bands of organisms may form in relation to a gradient in a major environmental factor = zonation. As you move down a particular environment, vegetation and animals may change slowly/rapidly. Bands of organisms may form in relation to a gradient in a major environmental factor = zonation. As you move down a particular environment, vegetation and animals may change slowly/rapidly. EG. Rocky shore = bands of organisms form due to exposure to the air (at low tide)