manor
advertisement

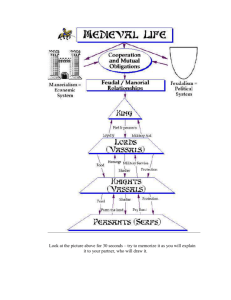
Feudalism in Europe First. . . • What are political, economic, and social systems? – Political refers to government: the way a group is governed, by whom, the laws of the group, etc. – Economic refers to the economy of the group: how laws and events affect trade, employment, the flow of money, taxes, etc. – Social refers to the effects of laws and events on the people’s lives Invaders Attack Western Europe The Vikings invade from the north • From Scandinavia • Seafarers • Fearsome • Remember Leif Ericson? He sailed to the North America around 1000 (500 years before Christopher Columbus). The Magyars attacked from the East (present-day Hungary) The Muslims invade from the South: • Came across the Mediterranean from North Africa • Invaded through present-day Spain and Italy This is Alhambra, built by the Muslim conquerors in Granada, Spain in 889 What were the results of these invasions? Widespread disorder and suffering Constant danger Kings could not defend their lands People no longer looked to a central ruler for security • People turned to local rulers who had their own armies • Feudalism arose in Europe • • • • Feudalism • A political and social system based on rights and obligations – In exchange for military protection and other services, a lord (landowner) granted a fief (land) to a vassal (person receiving the fief) – The vassal would pledge loyalty to the lord What are Serfs? • Most people in medieval times were peasants (people who worked the land) • Most peasants were serfs who worked the land for the lords • Serfs could not: – leave the land they were born on – marry without the lord’s permission – be bought or sold (so they were not slaves) • The serfs’ labor belonged to the lord Manors: The Economic Side of Feudalism • The manor is the lord’s estate • The manor system is the economic arrangement based on the rights and obligations between a lord and his serfs – The lord provides the serf with housing and protection – The serf took care of the lord’s land, animals, and maintained the estate Serfs worked the lord’s land in exchange for a place to live and protection. The Medieval Manor • A manor usually covered a few square miles of land • Peasants rarely traveled more than 25 miles from their manor • Manors were self-sufficient; serfs produced or raised everything they or the lord needed for daily life Manor Life • Peasant life was harsh – They paid taxes to the lord (for grinding grain, marriage, etc.) – They paid a tithe (church tax) equal to onetenth of their income – They lived in tiny houses with their animals – Everyone in the family worked – They had little food, so illness and malnutrition were common – The average life expectancy was 35